Table Of Contents
What is a Bear Hug?
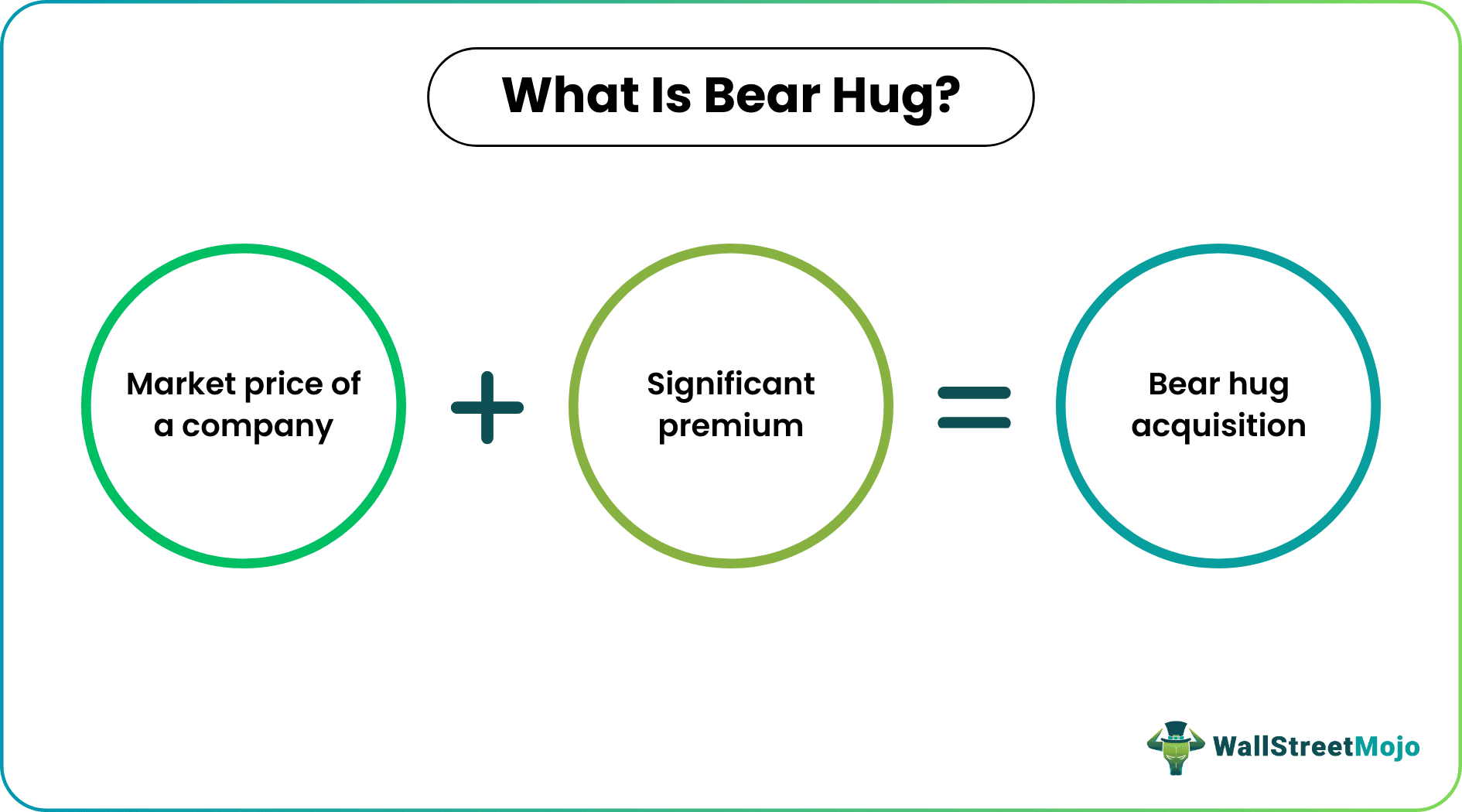
A bear hug is a prevalent acquisition strategy where another company acquires the target company. The acquirer buys all the shares at a much higher premium than what the shares are worth in the market. This kind of strategy is generally favorable to the acquired company, but in the same way, they are generally unsolicited.
Bear hug acquisition is significantly beneficial to the shareholders of the acquired company or the target company because they get a better valuation of their share prices where the target company’s shares are acquired at a much higher rate than what is prevailing in the market.
Table of contents
Bear Hug Explained
Bear hug is a form of acquisition where a company buys the shares of the company it is acquiring at an exorbitant premium. The shareholders of the company experience significant gains during a bear hug acquisition.
For a bear hug to be a successful one, the acquiring company must make an offer where the acquiring company acquires a vast number of shares of the target company at a much higher rate than the market rate. A company may go for this strategy to mitigate a more difficult acquisition or acquisition, which will significantly take longer.
The company, which is acquiring the target company at times, also uses bear hugs to restrict the competition or may go for such acquisition to get hold of goods and services that complement its current product offerings. It is similar to a hostile takeover, but this generally proves more financially beneficial to the shareholders.
Even if there is no management decision to get acquired, it is bound to take bear hug offers seriously because a company is bound to act in the best interest of its shareholders. Sometimes they offer made-for start-ups or struggling business models to believe that the companies and their assets will have a higher value shortly and drive more profits than what is currently driving.
Examples
Let us understand the concept of a bear hug test where a company acquires another company at a significantly higher price than its market value with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
ABC Limited showed interest in buying XYZ Corporations. Since XYZ was under serious mismanagement, it was not doing particularly well in the market. Therefore, ABC decided to acquire XYZ to not only gain a larger market capital but also to block out any further competition. The competition factor played a major role in the decision-making.
Hence, ABC’s management decided to acquire the company at a much higher price than its market value to ensure no other company would enter the race of acquiring it.
Example #2
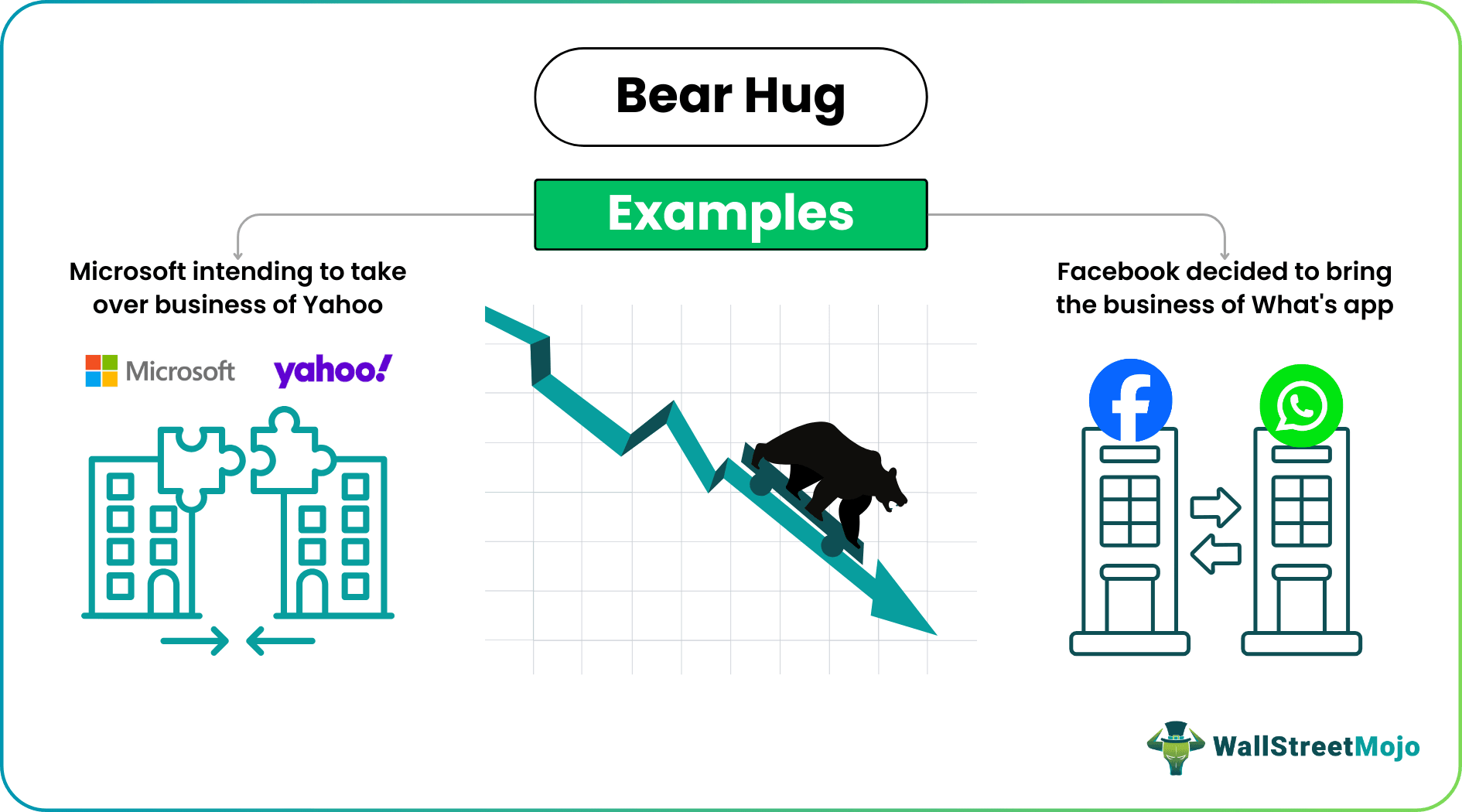
One example of bear hug acquisition was the case of Microsoft intending to take over the business of Yahoo, where Microsoft offered Yahoo to buy its shares at a 63% acquisition premium than what it closed the earlier day. This looked beneficial for the shareholders as then, Yahoo was struggling, and their business was making huge losses.
Failure
As it might have occurred through our discussion so far. A bear hug acquisition does not seem the most lucrative or even sensible decision to make in terms of a company’s financial standpoint. Let us understand why this model of acquisition has failed miserably through the discussion below.
- Bear hugs may prove costly if going ahead; the product offering doesn’t work well in the market.
- At times of desperate acquisition, the target company may acquire at a much higher rate than its worth.
- The target company will always have pressure to exceed its performance to give away its profit as a return on the investment made by the acquiring company.
- At times the entire management or workforce gets replaced by the acquiring company because, after the acquisition, the target company has a full hold over the target company.
- When there is a lawsuit against the management where the board of directors is directly responsible for serving the best interest of the shareholders.
Why are Companies Using Bear Hugs Takeover?
Companies use this takeover strategy due to the following reasons:
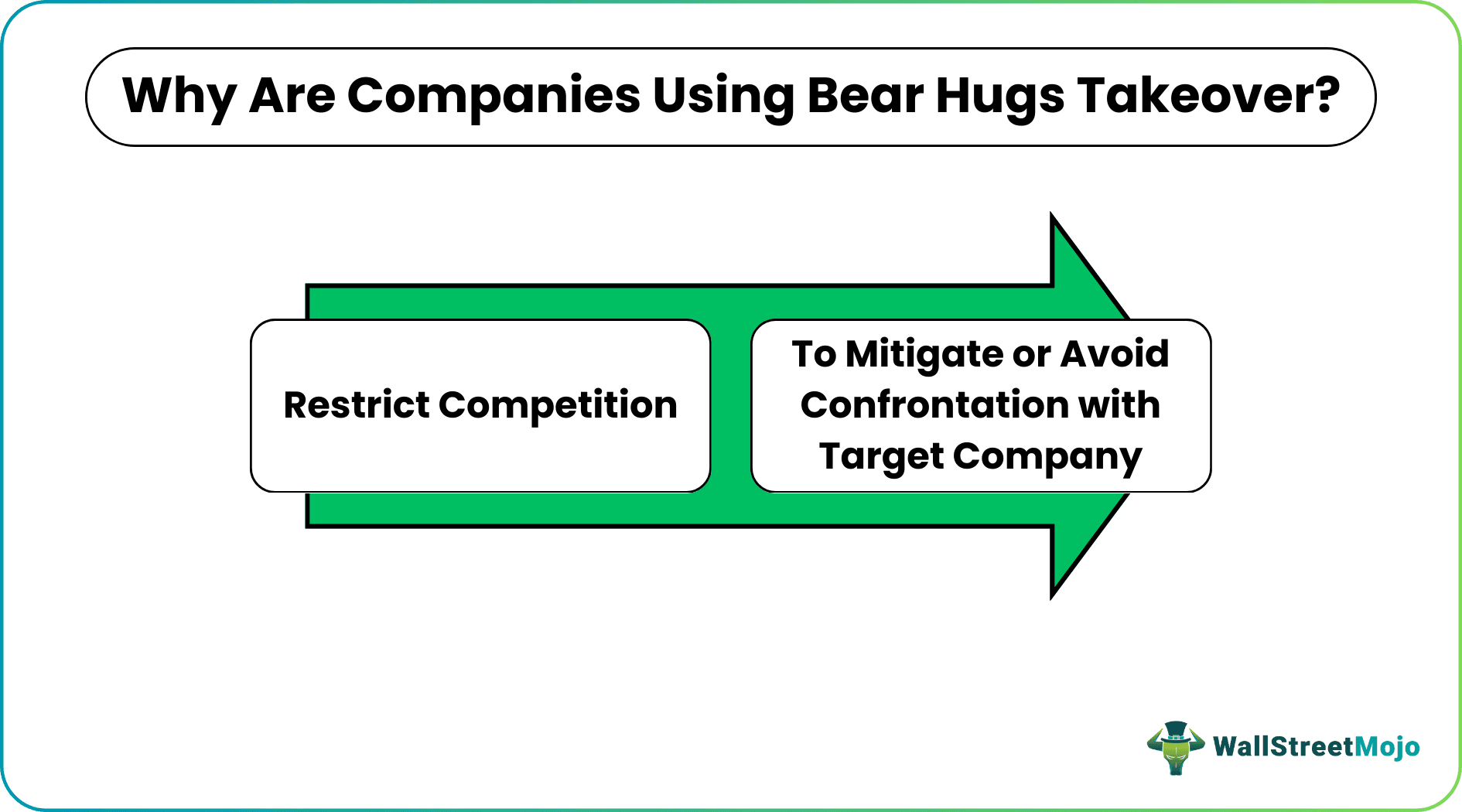
#1 - Restrict Competition
When a company announces its willingness to get acquired, there will be multiple buyers interested in it. Thus they come beneficial in beating the competition where the target company is bound to get acquired because of the price it gets offered, which is much higher than the market rate.
#2 - To Mitigate or Avoid Confrontation with Target Company
Companies may go for this strategy when the target company is skeptical or reluctant to accept the acquisition offer. Thus, the alternative approach to getting the shareholder’s nod is to go for a bear hug where the acquiring company offers a too hard price to refuse.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Let us understand the concept in depth through understanding its advantages and disadvantages in detail.
Advantages
- It works for the best interest of the shareholders, where they get a better price for holding the shares of the company.
- The acquiring company may incentivize the target company to make the takeover successful.
- It helps to limit competition in the market when there is a willingness by the target company to get acquired.
- It helps the company get hold of complementary products and services and extends its market expansion.
Disadvantages
- They can prove costly if the target company fails to perform in later stages after acquiring a higher price.
- There is always pressure on the acquired company to prove its return on investment.
- The present management may lose its control over management decision-making as the acquiring company gets hold of the processes.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is a Bear Hug. Here we explain its examples, failures, why companies use it, advantages, and disadvantages. In addition, you may refer to the following articles to learn more about finance.
