Table Of Contents
Buying On Margin Definition
Buying on Margin refers to the process in which an investor who purchases an asset, say stock, home, or any financial instrument, makes a down payment, a small portion of asset value. The asset bought will serve as collateral for an unpaid amount. The balance amount is financed through a bank or brokerage firm loan.
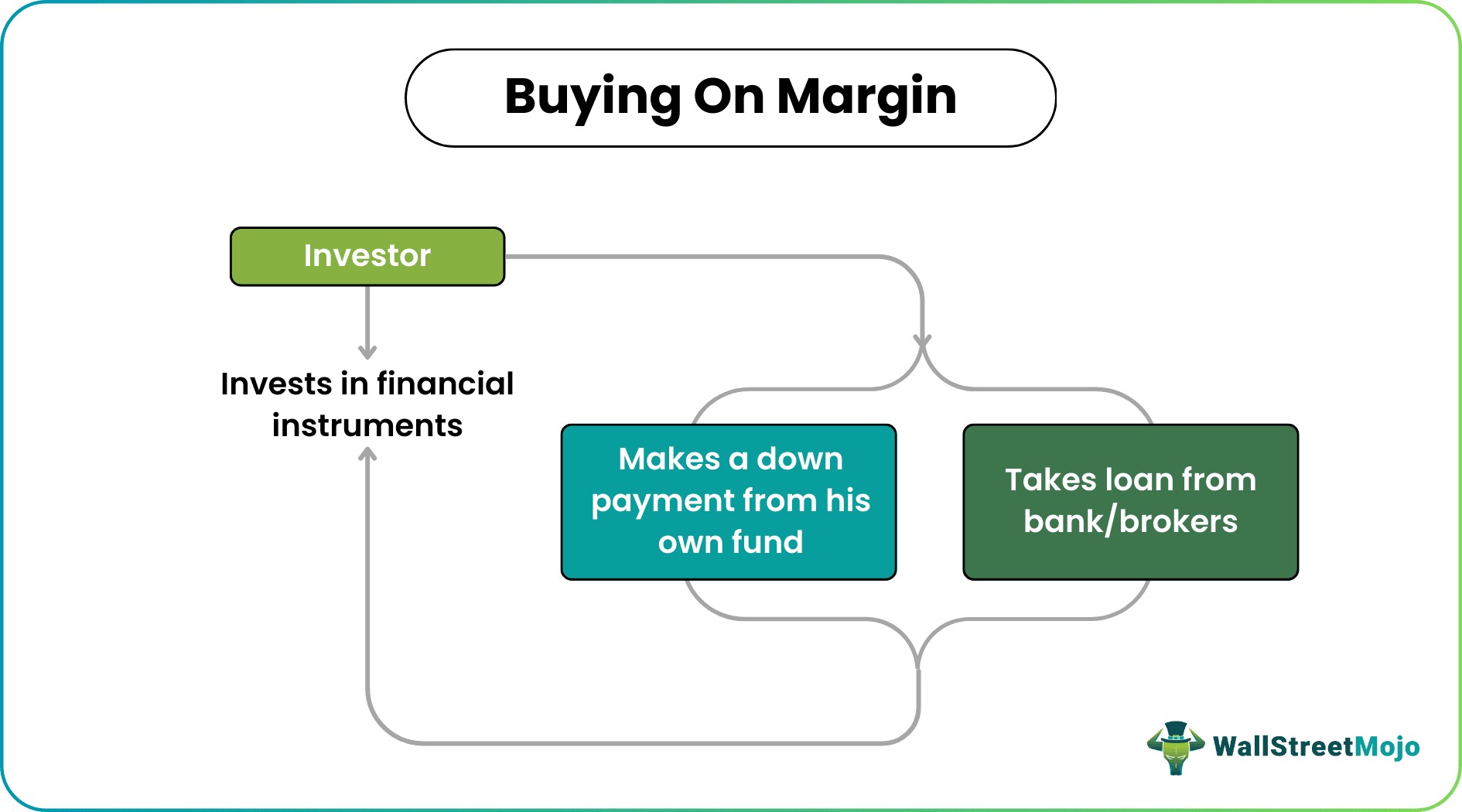
In this process, since a part of the asset financing is done through loan, the investor can afford to buy or invest in securities of higher value. This increases the return and risk because a large part of it is financed through debt. If the investor suffers loss, they lose not only their own money but it also becomes difficult to repay the debt.
Key Takeaways
- Buying on Margin is an investment strategy where an investor purchases an asset, such as a stock, home, or financial instrument, by making a small down payment.
- The purchased asset serves as collateral for the remaining unpaid balance, typically funded through a bank or brokerage firm loan.
- Different types of margins are associated with Buying on Margin, including the initial, maintenance, variation, and clearing margins. These margins ensure that the investor has enough funds in their margin account to cover any losses or fluctuations in the asset's value.
Buying On Margin Explained
Buying on margin is the process of trading or investing in assets of any kind of financial instruments partly through own funds and partly through borrowing. The investor makes some down payment from their own resources and rest is borrowed from a bank or any financial institution through a broker.
Margins are an essential aspect that allows a trader to trade in various financial products, such as futures, options, and stocks. Buying on Margin involves a minimum investment amount deposited in a margin account, allowing a trader/investor to borrow the balance from a broker. The account is adjusted daily to reflect gains and losses.
However, speculation and buying on margin involves a very high level of risk along with high returns. This is because since the investor is able to invest more money than they can afford, the possibility of return is high. On the other hand if the investor suffers a loss, then the loss is also magnified due to a higher value of investment.
Buying on margin significance lies in the fact that it is a very convenient and a useful method of investment, but risky. The burden of debt and interest payment reduces flexibility and increase leverage. There is always the possibility of losing more money than the investment value.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
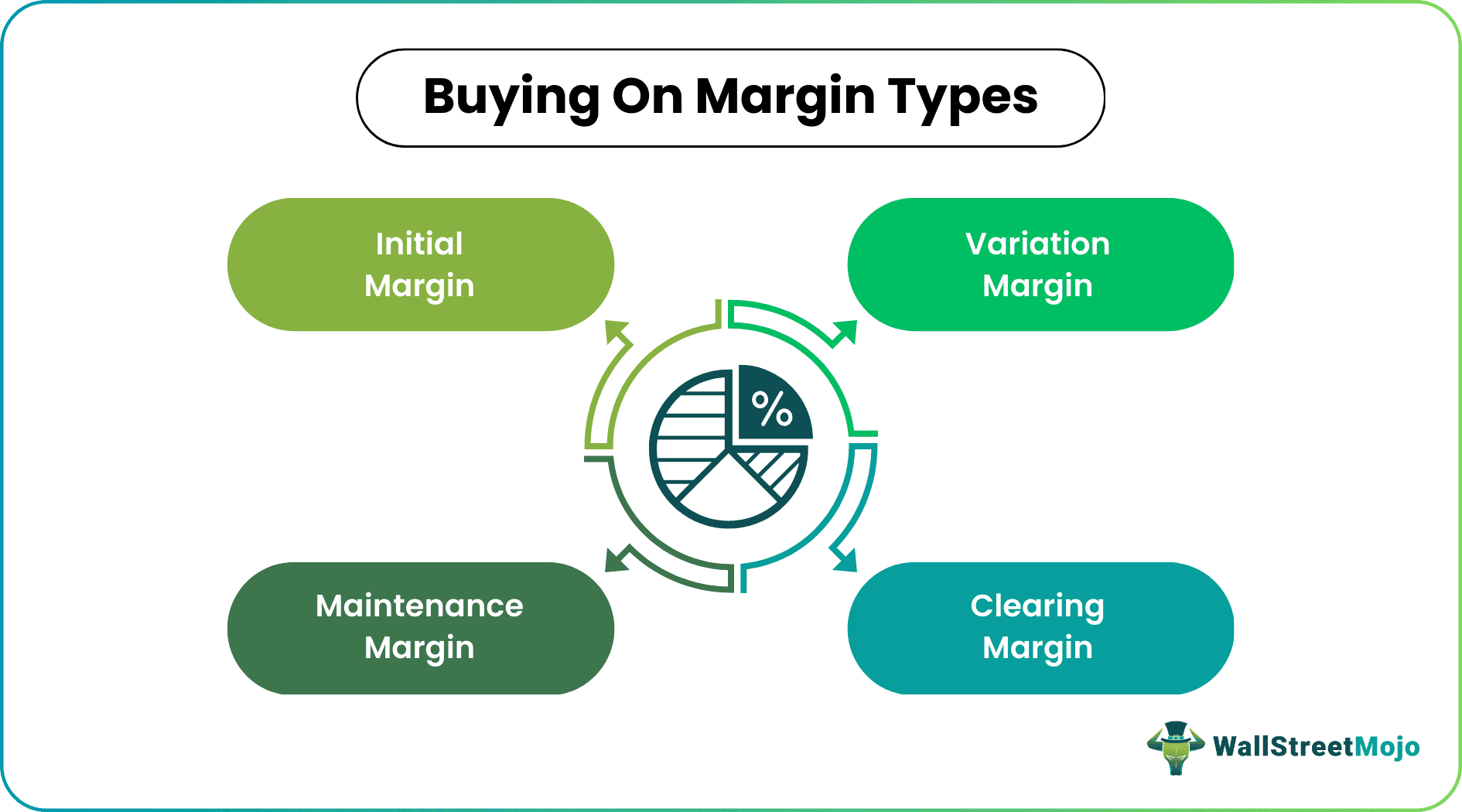
Let’s discuss the following types.
- #1 - Initial Margin - The amount that must be deposited at the time when the contract is entered into is known as the Initial Margin.
- #2 - Maintenance Margin - The investor is entitled to withdraw any balance in the margin account over the Initial Margin. To ensure that sufficient funds are available in a margin, a maintenance margin is set, which is lower than the Initial Margin.
- #3 - Variation Margin - If the investor fails to keep balance in the margin account as a result of which funds fall below the maintenance margin, the investor receives a margin call and is entitled to bring the margin account equal to the initial Margin by the end of the next day. The extra funds deposited are known as variation margin.
- #4 - Clearing Margin - Just as an investor is required to maintain a margin account with the broker, the broker is also required to maintain a margin account with clearing house members, and the clearinghouse member is required to maintain a margin account with the clearinghouse which is known as clearing Margin.
Example
Let us look at some buying on margin example to understand the concept.
- Consider an investor who contacts his broker to buy two December gold futures contracts. Suppose that the current future price is 1,250 per ounce and the contract size is 100 ounces. The Initial Margin is 6000 per contract or 12000 in total.
- Suppose now by the end of the first-day future price has dropped by$9 from 1,250 to 1,241. As a result, an investor has incurred a loss of 1,800 (200*9) because now 200 ounces of gold, which the investor contracted to buy at 1,250, can be sold for only 1,241. Therefore, the balance of the margin account would be reduced by 1,800 to 10,200(12000- 1800).
- Similarly, if the price of December gold rose to 1,259 by the end of the first day, the balance in the margin account would be increased by 1,800 to $13,800(12000+1800).
Thus, the above buying on margin example makes the concept very clear.
Characteristics
Let us try to understand the buying on margin significance through its various characteristics.
- A margin account is adjusted to reflect investor gain and loss at the end of each trading day. This practice is referred to as daily settlement or marking to market.
- To satisfy the speculation and buying on margin requirement, an investor usually deposits securities with the broker, such as treasury bills for about 95- 100% of face value stocks for about 50-70% of their face value.
- Margin requirements may depend on the objectives of the trader. A hedger such as a company that produces the commodity on which the futures contract is written is often subject to lower margin requirements than a speculator due to fewer default risks.
- Day trades and spread transactions often give rise to margin requirements. In a day trade, a trader announces to the broker to close out the position on the same day. In a spread transaction, the trades simultaneously buy a contract position on an asset for one maturity month and sell a contract on the same asset for another maturity month.
- The exchange sets up margin requirements in a derivative contract such as the future. Individual brokers may require a greater margin from their clients than those specified by the exchange.
- Margin levels are determined by the variability of the price of an underlying asset i.e., the higher the variability higher is the margin levels.
Advantages
Let us look at some points which highlight the buying on margin importance.
- Suppose two investors agree to trade on an asset for a specific price in the future. In that case, there are several risks involved, as one of the investors may decide to back out of the deal due to a lack of available financial resources to honor the agreement. So here, margins play an essential role in avoiding defaults on contracts.
- It facilitates daily settlement to avoid adverse movements of an asset, i.e., when there is a decrease in future price so that the margin account of the investor with the long position is reduced and the investor broker has to pay the exchange, which is then passed on to the investor with a short position. Similarly, when the future price increases, the short position pays money to the in-investor broker of the long position.
- The main buying on margin importance lies in the fact that it is a facility of buying an asset on Margin is that it helps to magnify returns. Let’s say an investor buys 100 shares of stock @$ 20 for a total cost of $2,000 using a 50 percent margin, i.e., the initial investment required is $1,000, and the balance amount of $1,000 is borrowed from a brokerage firm. Consider the stock increase to $30, as now the stock is worth $ 3000(100* $30), there is a straightaway gain of 50 percent, i.e., $1000($3000-$2000).
- However, as the investor has bought the shares on Margin, they needs to pay back the amount borrowed, a margin loan of $1000, by selling the stock at the market price of $30.The whole transaction will fetch a net profit of $1000 after excluding the initial investment. By just investing $ 1000, an investor can amplify its gain to 100%.
Disadvantages
- The main disadvantage of buying an asset on a margin is that losses may also magnify. Consider the above example, if the stock instead goes down from $20 per share to $10, now the value of an investment is worth $1000, which is equivalent to a margin loan of $1000, so the entire investment is lost, leaving an investor with zero return.
- An interest charge is also a significant concern. An investor needs to pay the interest on the money borrowed from a brokerage firm, so there is pressure on him to earn more than to cover interest payment as a result of which he might invest in a risky asset that offers a higher return but comes with higher risks too.
Buying On Margin Vs Short Selling
Let us look at some differences between buying on margin and short selling.
- In case of the former, the investor can borrow money from the broker and invest is securities of higher value, whereas in case of the latter, the investor can borrower shares from the broker for investment purpose.
- In the former’s case, the process allows the investor to take bigger trades by paying very less using own funds whereas for the latter the process allows the investor to trade in shares that they do not have in their demat account or cannot afford.
- The former involves the normal process of buying first and selling later whereas in the latter, there is selling first and buying later.
- The former aims to invest in securities that have the potential to rise, whereas the latter aims to invest in shares with the tendency or the risk of price fall.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Buying on Margin allowed investors to purchase stocks with borrowed money, increasing the demand for stocks and increasing stock prices. However, when stock prices started to fall, investors had to sell their stocks to repay their loans, leading to a stock market crash.
Buying on margin allowed investors to speculate on the stock market, creating a speculative bubble that drove stock prices to unsustainable levels. When the bubble burst, investors who had purchased stocks on margin could not repay their loans, causing a wave of selling and a sharp decline in stock prices. This decline in stock prices led to widespread bankruptcies, bank failures, and a general economic downturn that became known as the Great Depression.
Buying on Margin was bad for the economy because it increased speculation and artificially inflated stock prices. When the market eventually corrected itself, investors were forced to sell their stocks to repay their loans, causing a domino effect of falling stock prices, bankruptcies, and a general economic downturn. The widespread use of margin buying also exposed banks to high levels of risk, leading to bank failures and a loss of public confidence in the financial system.

