Table Of Contents
Cognitive Dissonance Definition
Cognitive dissonance is mental stress when a person holds two or more conflicting beliefs. Although, in simple terms, newly acquired information conflicts with pre-existing understanding. In that case, people experience mental discomfort, which is cognitive dissonance. In financial terms, behavioral finance measures it.
It happens when the person faces situations that challenge their point of view, which may force them to modify their ideas. It affects the think process and behavior the person. It is a widely studied concept in communication, advertising and psychology which helps the entity to design strategy to encourage a positive behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Cognitive dissonance is the mental discomfort experienced when a person holds conflicting beliefs or when newly acquired information contradicts existing understanding. It is a concept commonly used in behavioral finance to analyze financial decision-making.
- In order to mitigate cognitive dissonance, it is advisable to approach investment decisions with objectivity and analytical thinking rather than being influenced by emotions.
- When faced with cognitive dissonance, individuals often feel compelled to justify their actions, beliefs, and emotions. Understanding this tendency can shed light on behavior in various contexts, including financial decision-making.
Cognitive Dissonance Explained
The cognitive dissonance theory is a psychological term used to explain a person's mental discomfort when encountering situations that go against their behavior and values. The problems might force them to alter their belief to reduce discomfort. This is the only way to behave rationally or control the risk factor.
Such conditions arise due to various reasons like the decision making is not consistent with the belief, or some new information or incident goes against their belief, or a situation arises in which the person will have to decide among two or more alternatives that are equally good.
This concept is thoroughly researched, studied, and used in various fields like marketing, advertising, communication, and psychology.
Cognitive dissonance is on a varied case-to-case basis. It applies to many situations. In cognitive dissonance, most people are motivated to justify their actions, beliefs, and feelings. Therefore, they use self-perception when dealing with any condition, as seen in the above examples. The best way to avoid cognitive dissonance is to be objective and analytical while making investment decisions rather than emotional ones. However, this study helps entities develop strategies to reduce dissonance and encourage a positive mindset.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types
There are various types of this kind of behavior that depeds on the type of situation that the person faces. Given below are some common types of them.
- Choice dissonance – This happens when the person needs to select one out of many options presented to them and all such options have benefits and limitation. In such cases the person has to give up an equally good option in order to get another.
- Induced compliance – The person is bound to accept a situation that goes against their own values. In some cases, people are forced to promote of spread good words about a product or a service that they believe is not worth it. In such cases it is induced cognitive dissonance psychology.
- Belief action dissonance – This is a situation in which people know that their action is not consistent with what they are doing. They may continue using a product or eat a type of food that they know, will not add any value for them.
- Informational dissonance – Such a case happens when some new information comes in which goes against the beliefs. Sometimes we have one type of information about something and later we come to know more about that situation that is just opposite to the previous information. In such cases, the cognitive dissonance is information related.
- Effort justification dissonance – This kind of situation takes place when the person give a lot of effort on work that is not worth it. It will not add much value to the result compared to the effort that it is taking. Such a case is an effort justification related dissonance.
Causes
Let us look at the various causes of such a cognitive dissonance psychology:
- Contradictory belief – It is the major cause of such a situation where one’s own value does not match with the behavior of the person.
- Selective exposure – People sometimes search for situations that support their existing behavioral traits but they may find situations that contradict them.
- Decision making – A person may feel the effect of cognitive dissonance in case they are not able to make quick decisions. They find it difficult to chose between options which present them equally valuable opportunity.
- Social pressure – The presence of social pressure can make a person change their belief to remain a part of a group.
Thus, the above are some of the causes of this behavioral situation.
Examples
The examples below help us understand how cognitive dissonance affects the financial market and how it impacts the individual.
Example #1
John is looking to buy a stock of XYZ Ltd. because he believes that XYZ Ltd. will perform well in the future. XYZ Ltd. stock is currently trading at $70, and John is considering buying a stock if it falls a few dollars to $65. However, in three days, the stock price hit $68, and John believes the stock price will come to $65 sooner. However, after three days, the stock price suddenly increased, reaching $75 because of buying demand from other investors. At this point, John will probably experience cognitive dissonance model.
Now, the question arises, why will John experience cognitive dissonance? So, we will try to find out the answer to this.
Here, John will feel discomfort because of the sudden increase in the stock price of XYZ Ltd., which showed that the stock was good to buy at the cost of $68, and the market suggested this compared to the last trading price. Therefore, there are high chances that John will buy some of the stock at the cost of $75 to relieve the discomfort he feels. Of course, John may think that buying a stock at a higher price is still good because other investors are also buying at the same price, but this rationalizes buying John as irrational.
The above example shows that investors should stick with their decision and not determine the trade by emotion.
Example #2
One of the investors thinks that the current market is too high and may fall soon. Since the market is too high, the investor is worried about it and planning to sell some equity holdings. The investment manager asked investors, “Why does he think the market would fall shortly?” He says that the global economy is slowing down, as published in several newspapers, and corrections will happen in the market. Then, the investment manager advises investors that do not get influenced by numerous news articles.
Even after the investment manager advised, investors sold out his 50% equity, and the next day, the market tumbled by 5%. As the market dropped by 5%, the investor felt good and thought he had made the right decision. Still, after a week, news came out that the global economy was improving, and the market started showing a rally. So, now, investment managers suggest investors add back sold equity into the portfolio to get long-term investment plans on track.
So, the above example shows that investors influenced by particular news articles made sold-out decisions without checking facts and figures and made a mistake. It shows that cognitive dissonance model can cause the investor to fail to recognize the information, which helps him make a good investment decision.
Example #3
Keith bought a stock of Opto circuits at a trading price of $125. The next week, a company's stock price fell. Upon analysis, Keith came to know that their aggressive inorganic growth had filled their balance sheet with debt. By this time, the stock was trading at $75, and Keith bought some more stock again. Keith’s understanding was that the company made good quality products. In addition, he read the report that company stock will perform well once the economic condition improves and interest rates come down. Due to this, Keith purchased at every fall in stock price. During this period, Keith was looking for good news about the company. So, he used it to support the company by buying into the stock every fall.
Keith is still hoping that the company’s position will improve, and he will get at least a stock price of $125.
So, the above example explains that the investor who bought the stock despite it was falling heavily and sitting in huge losses. So, an investor looks for positive news and information about the company to support his buying decision and hold on to the investment to sell it at a profit in the future.
Example #4
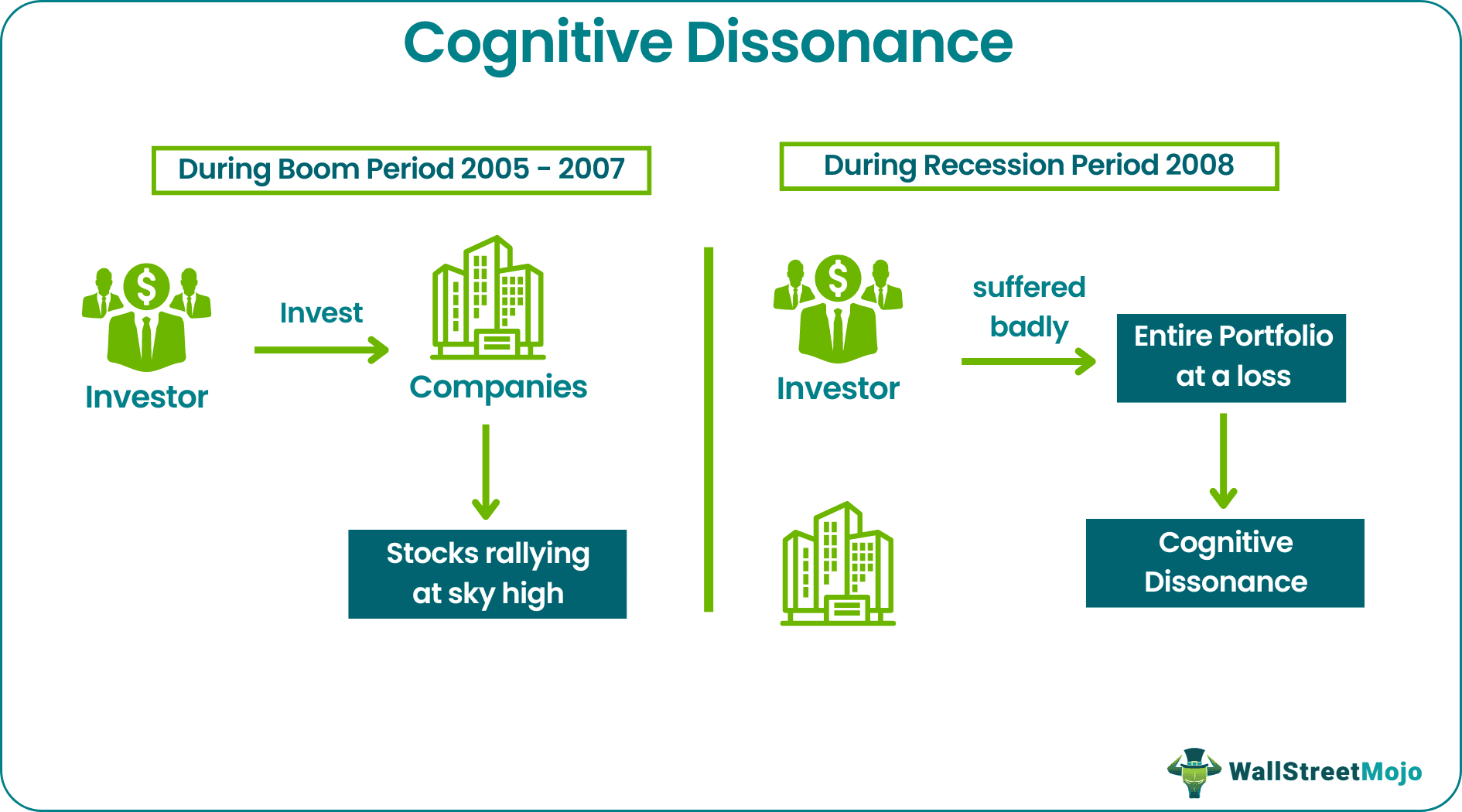
During the stock market rally or boom in 2005-2007, the investors in India were investing in companies of capital goods, infra, and the power sector. Fortunately, at that time, those stocks were rallying sky high. The investor was confident that he had enough skills and expertise to pick stocks because whatever he picked went up almost daily. He also entered into a few hot IPOs. Then, when the global economy was facing recession in 2008, the investor portfolio suffered badly, and he sold off his entire portfolio at a loss.
The above example shows that overconfident investors and traders believe that they are better than everyone else in choosing the best stocks and funds and an even better time to enter and exit the position because they think they are better and wiser than others in choosing an investment.
Effects
Now let us study the effects of cognitive dissonance in marketing:
- Change in belief – People are forced to change their own beliefs or values in order to remain in the group or sometimes that is what looks like the best solution to them.
- Rationalization – People wish to be more rational in the ways in order to reduce stress or risk.
- Self justification – The people may try to justify themselves by controlling the negative sides of their behavior and encouraging the positive sides. This helps the person feel more confident and positive.
- Become more open-minded – People become more open minded because they understand that they cant continue holding to their own beliefs that are contradictory to the current situation.
- Discomfort – Even if for a short time, people experience some kind of discomfort because they need to change their mindset about values that they have been believing for a long time.
Cognitive Dissonance Vs Self Perception
Some basic differences between the two are as follows:
- The former is a situation where the person may hold a belief that contradicts the current condition or their behavior does not match with their belief. But self-perception is understanding one’s own behavior.
- The cognitive dissonance in marketing or any other situation causes mental stress, discomfort, etc., whereas the latter does not do so.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Cognitive dissonance has various applications in marketing. It can be utilized to persuade consumers to change their attitudes or behaviors by creating a sense of discomfort or inconsistency between their current beliefs and desired outcomes. Marketers often employ strategies like offering post-purchase reassurances, emphasizing product benefits, or providing social proof to reduce cognitive dissonance and reinforce positive attitudes towards their products or services.
The opposite of cognitive dissonance is cognitive consonance. Cognitive consonance is a state of harmony or agreement between a person's beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. It occurs when there is consistency and alignment between various cognitive elements, resulting in psychological comfort and satisfaction.
Cognitive dissonance and cognitive distortion are related but distinct psychological phenomena. Cognitive dissonance refers to the discomfort or tension experienced when individuals hold conflicting beliefs or attitudes or when their beliefs and behaviors are inconsistent. On the other hand, cognitive distortion refers to the cognitive biases or irrational thought patterns that individuals may employ to distort or misinterpret information to align with their existing beliefs or preferences.

