Table Of Contents
What Is Deposit Accounting?
Deposit accounting refers to an insurance and reinsurance company recognizing and measuring an asset or liability for short-term and multi-year contracts. The consideration earned or charged, minus any premiums or fees retained, is used to calculate the said deposit asset or liability.
Insurance companies transfer contracts to lessen the burden of claims filed and manage the amount of risk. In deposit accounting, the contracts requiring no transfer of underwriting risks must be accounted for under the US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) guidelines. It also defines rules for reinsurance contracts that do not compensate or protect the insurer from losses.
Table of contents
- What Is Deposit Accounting?
- Deposit accounting definition implies a method of accounting used to journal the transfer of assets or liabilities with reinsurance contracts.
- The reinsurance contracts with limited or underwriting risks must account for under the US Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) rules.
- Reinsurance contracts help insurance companies to diversify risks and lessen the burden of claims filed. If an insurance company were to experience any significant claims, these risks spread out over multiple insurance companies.
- There are three different forms of deposit accounting, including bank, prospective, and retrospective deposit
Deposit Accounting Explained
Deposit accounting is that of accounting theat is used in the business to measure or identify the assets or liabilities for contracts that are for short term as well as contracts spanning over many years. The businesses earn or charge payments. These payments are used to calculate the liability or deposit value after deducting any premium or fee that the business will keep aside.
However, proper and transparent disclosure of information is required in the financial statements for the users regarding the nature, restrictions, rules or any significant risks and uncertainties or information related to refundability.
It is necessary to note that these deposits are subject to customer deposit accounting treatment related to the particular circumstance or accounting practices followed in the organization. In addition special contractual arrangement or local rules may also affect the accounting procedures of insurance deposit accounting.
Is Policyholders Deposit An Asset Or A Liability?
People purchase insurance policies when they seek protection from losses or liabilities that may occur in situations like:
- Automobile accidents
- Medical emergencies
- Loss of loved ones
- Workplace injuries
- Stolen identity
- Damaged possessions
In exchange for protection from these risks of insurance deposit accounting, they will have to pay premiums to the insurance company. The premium payments will typically be made on an annual or monthly basis by the policyholder.
The insurance company can then save the premium payments and collect them to have enough capital to pay if they receive a claim. The funds must be in cash or other liquid assets for the insurance company to have the ability to convert them to cash quickly.
If the insurance company collects more in premiums than what they must pay in claims, they will be profitable. If the insurer pays more in the claims, it will raise premiums. Traditionally, when the company has a surplus of premium payments, it will be considered the insurers’ assets. And the company's liabilities will be the amount owed to policyholders.
Types
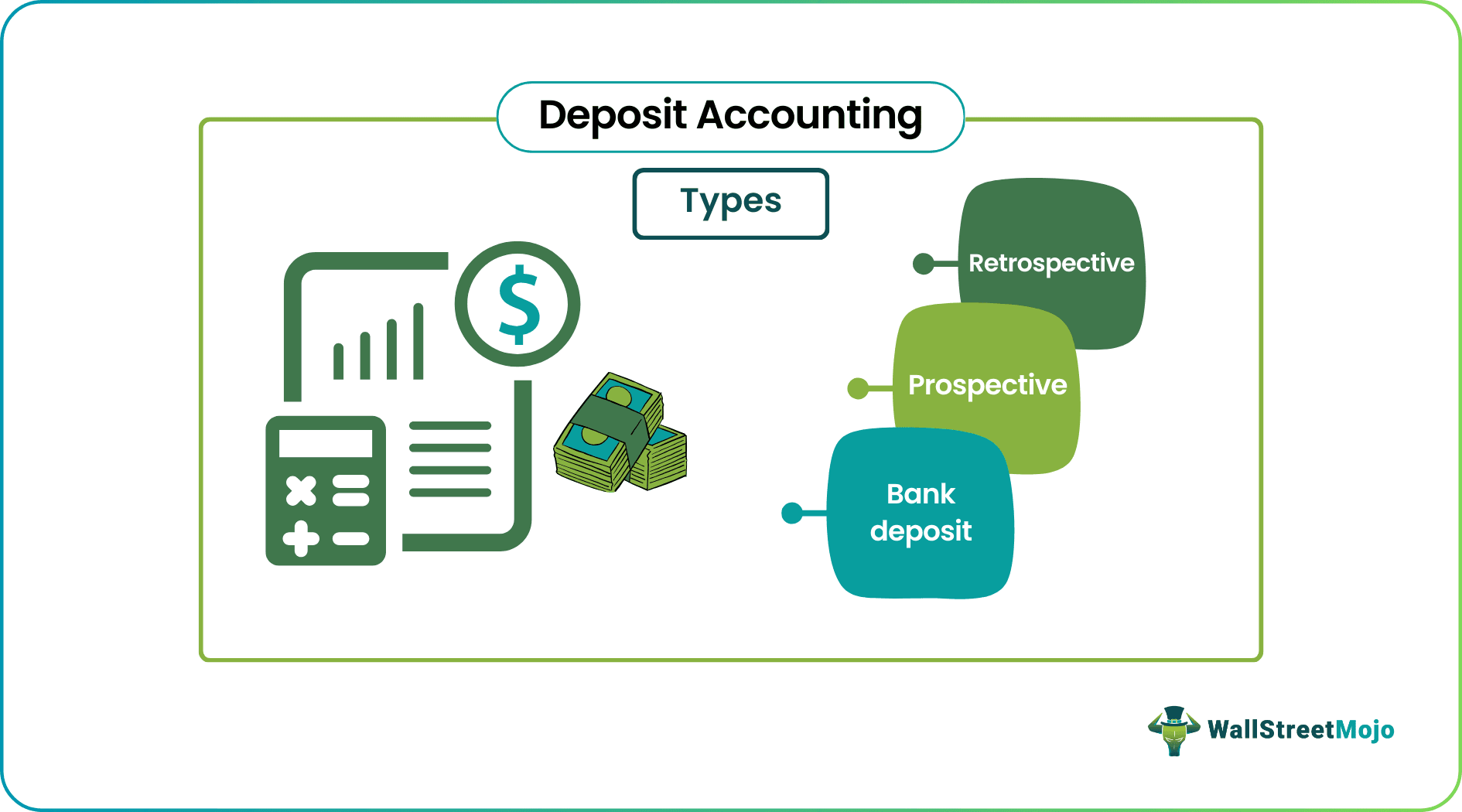
There are different forms of deposit accounting, including:
#1 - Bank Deposit
- The bank deposit form will allow the deposit to grow and earn interest on the initial investment.
- The interest rate in case of customer deposit accounting will typically be a predetermined number but can also be at a variable rate where the current market rate will determine it.
- It is the most straightforward type of deposit accounting.
#2 - Prospective
- In the prospective form, the deposit for refundable deposit accounting will depend on the value of the payment to be made in the future, not the initial investment.
- The interest rate will be dependent on the current market rate. However, it can be calculated at a rate that does not adjust over time or is locked into a specific interest rate.
- The deposit value does change over time as interest is paid.
#3 - Retrospective
- The deposit will be determined by the retrospective method's original, previous, and potential payment.
- The interest rate will be dependent on the money flowing in and out of the contract. It could be beneficial, but it can also produce negative rates when more money is flowing out of the contract rather than into it.
- It is a different concept based on the flow of money in the past and the present.
Accounting Entry
The process of deposit accounting for any contract has to abide by certain rules. Let us try to understand them.
- The accounting process is conducted by taking each individual contract into consideration and not on the basis of the entire portfolio. They are reported in the financial statements as a summary.
- The amount the the business receives from the contract is recorded in the financial statement as a deposit liability. No impoact or revenue or expense is recorded. Thus, there is no effect on income.
- If there is an addition to the receipt or any investment income credits, the deposit liability increases. Similarly, it falls due to payments.
- The deposits represent the current of present value of the payment obligations to be met in future.
Thus, deposit accounting will have the following features:
- There is no transfer of risk.
- The risk transfer is in the form of time. There is not transfer of risk in the form of money. Thus, the factor of uncertainty over here is related to the time of receiving the payment.
Thus the above explanation gives details about the accounting method followed for the deposits or refundable deposit accounting.
Example
For deposit accounting entry, let us take an example of insurance company A looking to enter into a reinsurance contract with insurance company B that does not transfer risk.
According to the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, arrangements that do not transfer risks must be accounted for under the Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) deposit accounting rules. It means that both insurance companies A and B will have to account for the asset or liability with the contract.
The ceding company, in this case, insurance company A, would be transferring liabilities to insurance company B. Insurance company A should note any changes in the timing of payments.
Here are the steps involved in the process to better understand how to do an accounting journal entry:
- Insurance company A must pay $10 million to insurance company B over ten years, with equal payments due at the end of each year.
- It would imply that $1 million in dues will be paid per year.
- Insurance company A agrees to pay $8 million at the beginning of the contract.
- Insurance firm B will refund any portion of the initial deposit that has not yet been repaid after ten years.
- If the timing of these payments changes for some reason, all insurance firms would have to alter their asset and liability balance sheets. For example, if the cash flow changes, the deposit money will also need to be changed.
- If the deposits are increased by insurance company A, the present value of the assets will also increase.
When Is Deposit Accounting Helpful?
The deposit accounting method may be helpful in cases involving insurance and reinsurance contracts, such as:
- No transfer of underwriting risk
- Transfer of timing risk only
- Prospective reinsurance
The amount paid is known as deposit in deposit accounting and can be accounted for as an asset by the ceding party. Deposit accounting will require these contracts to be measured individually instead of as a portfolio. The deposit money will be reported as a deposit liability rather than an asset.
p.s. - Insurance companies will often purchase insurance from other insurers to diversify their risk in a significant claim – a process known as reinsurance.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is Deposit Accounting. We explain its various types and their accounting entry along with an example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –

