Table Of Contents
Inflation Accounting Meaning
Inflation accounting is the method used to report financial statements by factoring in the impact of soaring or plummeting costs of various goods, which are adjusted according to price indexes to present a clear picture of the firm’s financial position, usually in times of inflationary environments.
Usually, when a company operates in an inflationary or deflationary environment, historical information may no longer be relevant. Hence, inflation-adjusted values would go on to accurately reflect the current values.
Key Takeaways
- Inflation accounting refers to the method used to rectify issues arising from historical cost accounting during high inflation and hyperinflation and adjust the financial statements according to price indexes.
- Inflation accounting comprises two methods: Current Purchasing Power and Current Cost Accounting.
- Currency/money fluctuates regularly. Therefore, an accounting method like inflation accounting provides financial statements to show accurate and fair value accordingly.
- The inflation accounting method is a technique that may complicate the calculations due to many conversions and calculations.
Inflation Accounting Methods
Generally, there are two types of methods:
You are free to use this image on your website, templates, etc.. Please provide us with an attribution link
Inflation - Explained in Detail
#1 - Current Purchasing Power
Under this method, the monetary and the non-monetary items are separated so that monetary items record only a net gain or loss. At the same time, the non-monetary items are updated into figures with a particular conversion factor that is equivalent to a specific price index.
Conversion Factor under CPP Method = Price at Current Period / Price at the Historical Period
#2 - Current Cost Accounting
Under this method, the assets are valued at fair market value (FMV) rather than their historical cost during the fixed asset purchase.
How Does Inflation Accounting Work?
Example 1
Let us consider an illustration where Mr. John purchased equipment on 1st January 2012 for $50,000. As of that day, the Consumer Price Index stood at 150, whereas it reflects 300 as of 1st January 2019. Due to this, we are now required to reflect the revalued value of the equipment under the CPP method.
The details are summarised as follows: -
| Date | Details | Figures |
| 1-Jan-12 | Purchase of Equipment | $50,000 |
| 1-Jan-12 | Consumer Price Index | 150 |
| 1-Jan-19 | Consumer Price Index | 300 |
Applying the conversion factor formula,
Conversion factor under CPP method = Price at Current Period / Price at the Historical Period
(300/150=2)

Hence, the revaluation of the equipment under the CPP method stands at $25,000 ($50,000/2).
Example 2
From the below-given data, compute the net monetary gain or loss per the CPP method.

Solution:
Monetary gain on holding liabilities:

- Monetary gain on holding liabilities = ₹86,250 – ₹60,000
= ₹26,250.
Where, value as per closing balance sheet = Credits + Public Deposits = ₹60,000
Monetary loss on holding a monetary asset

- Monetary loss on holding monetary asset = ₹70,125 – ₹49,500
= ₹20,625.
The calculation of net monetary gain is as follows:

- Net Monetary gain = ₹26,250 - ₹20,625
= ₹5,625.
Advantages
- Fair View: Since the assets are shown after considering and adjusting for inflation at their current values, the balance sheet represents an unbiased view of the firm's financial position.
- Accurate Depreciation: When the true value of the assets is represented, depreciation is calculated on the face value of the assets and not on their historical cost. Hence, this method facilitates an easy replacement for the business as the accurate and fair value is represented and indexed with inflation.
- Reasonable Assessment: When balance sheets of 2 years are presented and adjusted to inflation accounting, it becomes easy and convenient to make the essential comparison as the values reflect after considering inflation. These values are thereby current and not based on historical cost. To some extent, it also feels like the time value of money.
- True Value Reflection: Since inflation accounting shows the current profit based on current prices, it reflects any business’s correct and updated value. Hence, the financial statements will have the figures updated as per the current prices, factoring in inflation.
- No Overstatements: Under this method, the profit and loss account would not be overstating the business income.
- Keeps a Check on Dividend Payment: Based on historical cost, there is a high possibility that the shareholders may claim higher dividend payments. The inflation accounting method helps keep a check as the dividends and taxes are not calculated on a skewed figure, unlike the cost method.
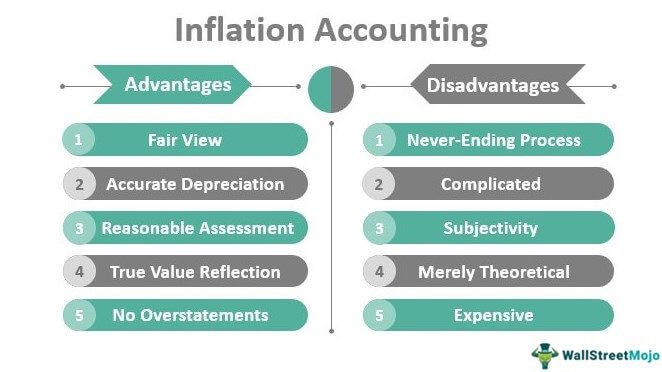
Disadvantages
- Never-Ending Process: The changes in prices continue for infinity as long as there is inflation or deflation in an economy. Hence, the process is never-ending.
- Complicated: There is a possibility that too many calculations make the process all the more complicated. There may be a lot of adjustments that may be difficult for the ordinary person to interpret.
- Subjectivity: Certain discretionary judgments and subjectivity may be involved as adjustments to current values are not as simple as dynamic.
- Deflationary Situation Causes Exaggeration: When there is a deflationary situation, and the prices fall, a company may charge lesser depreciation. As a result, it may cause an overstatement of the business's profits, undoubtedly harmful.
- Merely Theoretical: The concept of inflation accounting is considered more of theoretical appeasement. There may be the possibility of specific window dressing as per the whims and fancies of individuals owing to the subjectivity involved
- Expensive: This method is considered costly, and ordinary businesses may not be able to afford it
Limitations
- Though the method of inflation accounting may be of use to the firm, it is not necessarily so for the income tax authorities, as they refuse it due to low acceptance in the community.
- Change in the price is a continuous process that can’t be averted.
- The system complicates the calculations due to many conversions and calculations.
Final Thoughts
Inflation accounting undoubtedly reflects the actual value of the business but suffers from certain drawbacks, such as non-acceptance by authorities or complications involved in the systems and process. However, the real purpose of a financial statement is to provide an accurate and fair value to the business. Therefore, the income statement must show the company’s actual and precise profit or loss during a specific period, and the balance sheet must reflect the fair and proper financial position.
Since they are represented in monetary value. Currency/money fluctuates regularly, so it becomes necessary that a method such as inflation accounting serves its purpose by enabling the financial statements to reflect accurate and fair value accordingly. This method thus ensures that there will be no significant deviations on the part of the business.


