Table Of Contents
Financial Distress Meaning
Financial Distress is a situation in which an organization or any individual is not capable enough to honor its financial obligations due to insufficient revenue. It is usually because of high fixed costs, outdated technology, high debt, improper planning and budgeting, and improper management, leading to insolvency or bankruptcy.
After this stage, the company becomes insolvent. There are very few chances for a company to survive after it reaches this stage. The organization has very low liquidity as it cannot repay loan installments, interest, payments to suppliers, and even salaries to its employees. If the organization wants to survive, it needs to lower its costs, restructure its liabilities, and revise its business strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Financial distress means a condition in which an organization or any individual cannot fulfill financial obligations because of inadequate revenue leading to insolvency or bankruptcy. For example, US Recession in 2007-2008.
- Technological changes, improper management, fraud in the company, and inappropriate investment plans are the causes of financial distress. The factors causing a company's financial distress are divided into internal and external categories.
- Non-financial restructuring and financial restructuring are the solutions to the company's financial distress.
Financial Distress Explained
Financial distress is a situation in which the company cannot pay off its fixed costs as salaries to employees, loan installment, payment to raw materials, etc., because of improper planning of working capital, mismanagement at the top level, fraud, change in government policies, etc. A company needs to recognize signs early and take necessary preventive measures not to go into a period of financial distress. Else, it becomes very difficult to find solutions for the same.
The period of financial distress signifies the period that marks the fall of the share market price or the decrease in the value of an asset of a company, leading to adverse financial situations. One of the examples of such instances is the US Recession in 2007-2008.
In this period, the company faces severe problems in cash flow, which impacts and lowers the quality of its products and services. It enables existing customers to buy from their competitors. It declines the revenue, and the situation gets worse. Suppliers will cut short the credit period, and contract terms will get stringent. Ultimately there will be a problem paying salaries to the employees, and the company will do layoffs. The period during which all these situations occur becomes the period of financial distress.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Causes & Effects
For one to understand what is financial distress, it is important to know the causes and effects of the situation.
#1 - Technological Changes
If any company cannot adapt to the technological changes and cannot upgrade itself, it doesn't survive in the market. Its market share will drastically decrease, and ultimately revenue will get lower down along with static fixed costs. Gradually this will lead to financial distress.
For example, Nokia in 2012 could not adopt new technology and had to face such distress.
#2 - Improper Management
Improper management leads to inefficient decision-making and eventually a lower down of revenue.
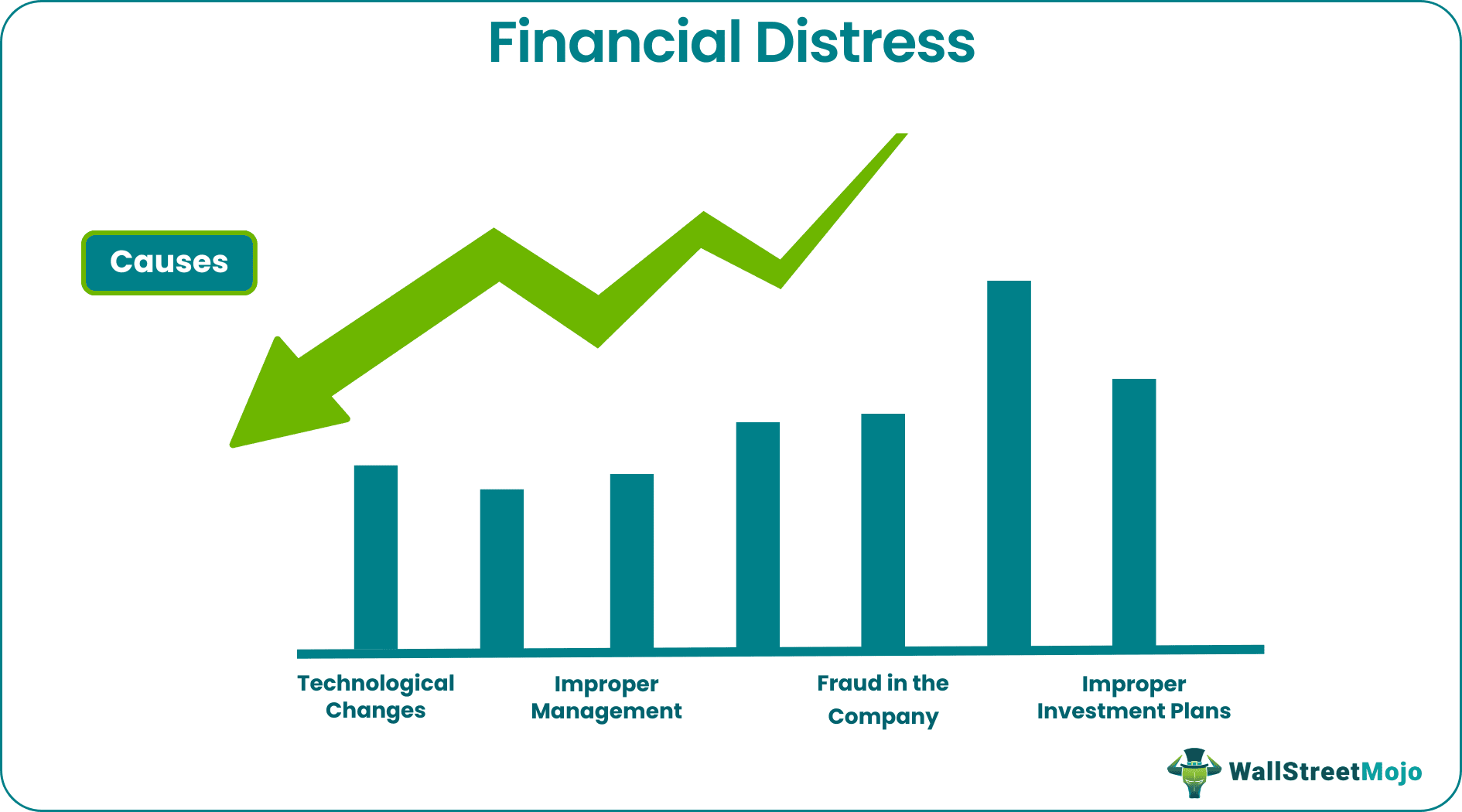
#3 - Fraud in the Company
Any planning of fraud may lead to diverting the organization's objective to maximize shareholder's wealth to the intention of the fraud maker. All the key resources are not used for the organization's benefit, leading to financial distress.
#4 - Improper Investment Plans
It is necessary to maintain proper cash flow and fixed income from investments. If budgeting is not done correctly, either there will be a cash crunch or idle funds. It sometimes leaves the company taking debt over what is required and ultimately leads to distress.
Indicators
Factors that cause such situations fall into two categories – internal and external.
Internal Factors are-
- Improper and ineffective demand forecast
- Poor cash management
- The high rate of employee layovers
- Unsuitable product mix
- Inaccurate estimation of working capital requirement
- Ill-utilization of Assets
External Factors are-
- Weak contracts with suppliers
- Dependency on a single supplier for raw materials
- Exceptionally hike in the price of Raw material
- Change in Government policy in terms of excess import duty, stringent trade practices, etc.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples of financial distress:
Example #1
Fraud in Satyam Computers in 2009 revealed how the company booked fictional expenses and falsified profits figures. It led to the total shutdown of the company.
Example #2
Lehman Brothers was the fourth-largest investment bank in America, but in September 2008, the company filed for bankruptcy. With $639 billion in assets and $619 billion in debt, the instance was the largest in history. It happened as a result of improper decisions that the CFO made.
How to Calculate the Cost of Financial Distress?
When the company is in distress, its assets don’t cost more, and its debts become more expensive. The rate of interest charged by the bank to the company is higher than what is charged to other companies in the same industry (Cost of Debt of AAA Rated company)..
- Calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Debt. Example 10.5%
- Take the cost of Debt of an AAA-rated Company. Example 7%
- If the debt of the company is 100 million
Cost of Financial Distress = Difference of Rates in Step 1 * Total Debt of the company
= (10.5 - 7)% *100 million = 3.5 million
Solutions
Once the company gets into a distressing condition, it isn't easy to revive. High probability tends to cause companies to file for bankruptcy. The management needs to notice the signs and take preventive actions accordingly. However, if any way out if a company comes into a period of financial distress, below are the solutions for the same-
#1 - Non-Financial Restructuring
Suppose on analysis, it is found that the company went into distressed condition because of poor management of inappropriate business plans. In that case, it involves the restructuring board where key personnel of the business are changed. Power is given to the expert, and all business plans are revised. Eventually, the company can steadily come out of the situation without a permanent shutdown.
#2 - Financial Restructuring
If the company is in distress condition because of insufficient cash inflow or incapable of repaying debt, solutions for them are as follows-
#1 - Private Workout
In this solution, the company internally decides and plans to restructure. A few solutions are to:
- Negotiate with borrowers to curtail interest rates or waive charges.
- Have a higher high credit period
- Improvise business strategies
- Implement appropriate marketing and sales strategy to increase sales
- Frame relevant cost-cutting plans
#2 - File Legal Bankruptcy
- Reorganize and Emerge: Once a company files for bankruptcy, the Government, after appropriate investigation, asks debtors to waive off the partial amount payable. Asks the company to follow the necessary steps to reorganize. In all, the power remains with the Government on restructuring.
- Merge with Another Company: In some cases, it is ordered by the Government to merge with another profit-making company in the same or another industry that has enough resources to absorb losses and restructure the company.
- Liquidate: If there is a chance to revive a company, it liquidates.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Several consequences of financial distress are a remarkable and constant downturn in a company's economic behavior, which may result in bankruptcy and make investors and creditors bear the substantial financial loss.
The financial distress costs are the expenditure that a firm during financially distress suffers beyond the business operations cost, like a higher cost of capital. Consequently, distressed companies may face challenges in meeting their financial obligations, leading to a higher chance of default.
The direct costs of financial distress consist of the legal and administrative expenses of the bankruptcy process. The indirect costs of financial distress arise from incentive issues as a firm's economic situation worsens.

