Table Of Contents
What Is An Accounting Cycle?
An accounting cycle refers to culminating the accounting records for further analysis, letting internal stakeholders make well-informed and relevant financial decisions. It summarizes the accounting events in a sequence for a specific accounting period, becoming a quick guide for external stakeholders to decide whether to invest in the firm or associate with it for any upcoming projects.
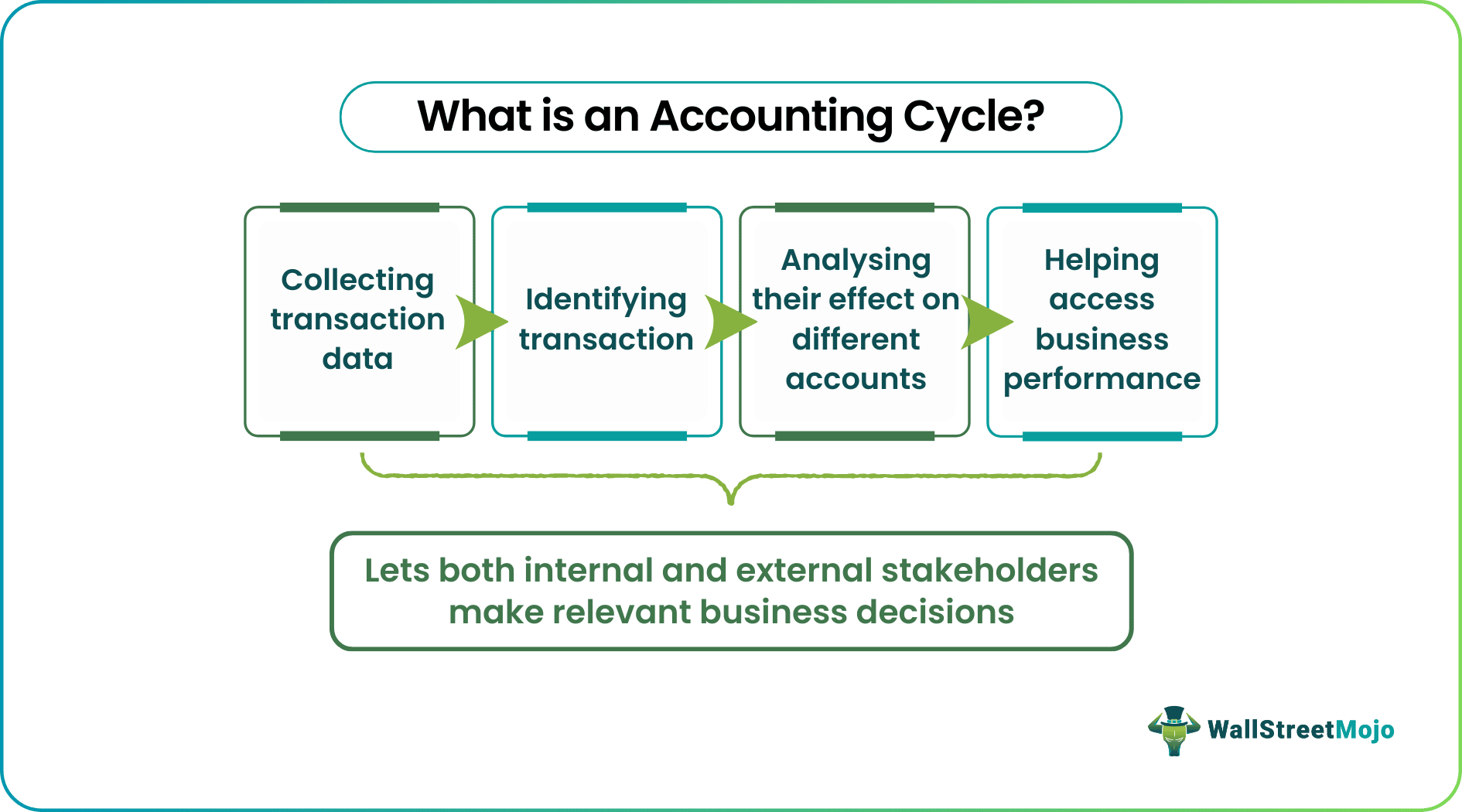
It is easy to understand the accounting cycle definition with the steps involved in the process. The steps include identifying and recording transactions to use them for further collective analysis to be aware of a company's current financial scenario. It is the responsibility of a bookkeeper to maintain and keep a check on the accounting process. Many businesses now use a virtual accounting assistant to make bookkeeping easier and faster.
- An accounting cycle refers to recording transactions for a particular accounting period to help businesses make well-informed and productive decisions.
- The accounting period varies from organization to organization. It can be monthly, quarterly, annual, or any specific time range.
- The accounting cycle steps include everything from identifying and recording transactions to creating journal and ledger entries and trial balances to rectifying accounting errors before closing the books for the period.
- In the United States, businesses need to complete and submit the final statements and reports to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Accounting Cycle Explained
The accounting cycle deals with creating different financial statements that companies go through at the end of each financial year to assess their current market position. These statements let businesses examine their performance and make other decisions accordingly, including launching a recruitment drive or spending on technological advancement and other resources. The process starts with accounting transactions and ends with the closure of the books of accounts.
A bookkeeper or accountant keeps track and records all financial accounting activities for that particular financial year. Companies or businesses repeat the process every financial year to monitor, assess, and understand the real financial scenario. The accounting period for this assessment can be monthly, quarterly, annual, or any specific time range.
In the United States, businesses need to complete the statements and submit final financial reports and documents to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). This way, the companies accomplish the accounting process depending on the respective reporting deadlines. In addition, bookkeepers in companies use accounting software solutions to ensure the utmost accuracy of the process.
Accounting Cycle Steps
Bookkeepers and accountants must follow the accounting cycle steps properly to make the accounting process efficient and accurate.
#1 - Analyze Transactions
The first step of the accounting process is the analysis of the transactions. First, the accountants collect, identify, and classify receipts, invoices, and other financial data. Next, the professionals read the collected data, check each transaction that occurred, and note the reasons that led to those transactions. Finally, they put it under the right label and determine their impact on different accounts based on their analysis.
#2 - Record in journal
The next step is to make journal entries for the transactions. Whether you use a single entry accounting system or a double entry accounting system, applying a debit or credit to every transaction is necessary. Thus, the transactions move to a cash accounting system when money is paid or received. In short, all transactions that occur within an accounting period must find a record in a journal.
#3 - Transfer to ledger
The third step of the accounting process is to post those journal entries into ledger accounts. Thus, the bookkeeper/accountant must put the recorded transaction to the general ledger account. The transactions find a proper breakdown within it, and the accounting events are easily identifiable as a separate account.
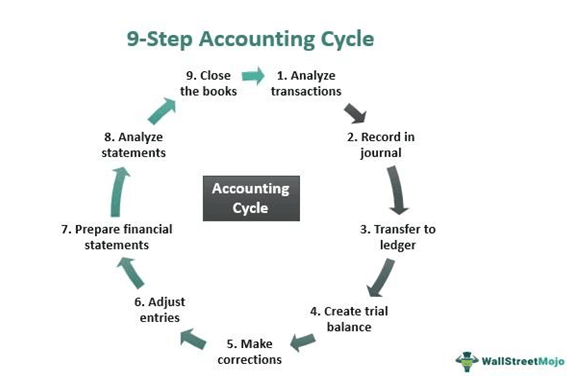
#4 - Create trial balance
With the transfer of all entries to the general ledger, the next step is to create a trial balance to ensure total debits tally with the total credits for the accounting period. This step, however, might indicate some discrepancies, showing an unadjusted trial balance.
#5 - Make corrections
Unadjusted records lead to accounting errors, requiring rectification. Thus, the companies prepare a worksheet to track the errors in the record. As accountants identify the mistakes, they rectify the same in the worksheet to ensure debits are equal to credits.
#6 - Adjust entries
Now it's time to put in the adjusted trial balance entries. It is a crucial step as the discrepancy, if not handled correctly, could mislead internal and external stakeholders while making business decisions. In addition, by adjusting entries, the accountant will ensure the information seekers receive crystal clear accounting details from the trial balance.
#7 - Prepare financial statements
After crosschecking the accounting details and rectifying the errors, the firms prepare the respective financial statements. For professional firms, a thorough accounting compilation checklist is often utilized during this preparation step. These statements are classified as income statements, balance sheets, shareholder's equity statements, and cash flow statements."
#8 - Analyze statements
After creating the respective statements, the accountants analyze the same to figure out some trends indicated through the recorded accounting activities. Then, based on the analysis, they convey their observation to managers and other stakeholders who use the information to assess the businesses' performance and make well-informed and productive decisions.
#9 - Close the books
Making closing entries is the last step of the accounting cycle. It indicates that firms have created all financial statements, and recorded, analyzed, and summarized all business transactions thoroughly. With the closure of the books, however, the bookkeepers and accountants repeat the accounting steps for the next accounting period.
Accounting Cycle - Video Explanation
Example
Let's consider the following accounting cycle example to understand how the process works:
Company X received $500 for its software products on March 15, 2022, and recorded the entry for that particular period. The amount becomes a debit record to the cash account and credit to the Sales Revenue account. If the company's transactions for the day included a cash sale of $500 and $300 with a cash refund of $200, the cash transaction of the business would be a debit of $600.
Other transactions or activities of the company indicated debit balances of $800 as Accounts Receivables and $100 inventory besides $600 cash debit. As a result, the credit balances worth $1,200 don't balance with the debit balances of $1,500 in the trial balance. Thus, the bookkeeper has to find the missing records to tally both the credit and debit sides.
After properly rectifying the entries, the accountants prepare the financial statements and close the books for that particular accounting period.
Accounting Cycle vs Budget Cycle
Most financial players confuse the accounting cycle and budget cycle as both deal with recording transactions. However, these cycles differ with respect to when and for what these transaction details are to be recorded.
An accounting process records a company's financial transactions for an accounting period to provide accurate details to the internal and external stakeholders. On the other hand, the budget cycle includes recording and analyzing the budget-based transaction a company decides to make for a future project.
An accounting cycle records, analyses, and summarizes accounting events for the details to be shared with internal and external stakeholders as they are affected by those activities. On the contrary, a budget cycle is a process where the records are internally used to decide future actions within the company.

