Table Of Contents
What Are Accrued Liabilities?
Accrued liabilities are the liabilities against expenses that are incurred by the company over one accounting period. Still, the payment for the same has not been made by the company in the same accounting and is recorded as the liability in the balance sheet of the company.
They are those expenses that have not yet been paid under accounts payable. In other words, it is an obligation of the company to pay for goods and services they received, but invoices for the same have not yet been received. It exists only in an accrual method of accounting and does not exist under the cash method of accounting.
Table of contents
Accrued Liabilities Explained
Accrued liabilities are expenses incurred by an organization in the previous financial period but whose payment has npt been settled, even after the conclusion of the financial period. These are recorded in the financial statements during one period and reversed in the next period. It will allow the expense incurred to be charged at the accurate price when payment is made in full.
Accrued liabilities are usually periodic and paid in arrears, i.e., after consumption. For instance, a company receives a water bill after the month-end in which the water is consumed. Therefore, it is essential to record the water expense in the period in which the water is consumed by making relevant accounting entries at the end of that particular accounting period. Accrual expenses result in the presentation of accrued expenses under the appropriate account heads in the income statement and accrued liabilities on the balance sheet.
Accrued Liabilities Explained in Video
Types
Let us understand the different terminologies through which accrued liabilities accounting is carried out through the explanation below.
- Accrued interest: Interest on an outstanding loan that has not been billed by the end of the accounting period;
- Accrued payroll: Taxes on employee wages which are due in the next period;
- Accrued services: service received under the current period but are billed in the next period;
- Accrued wages: Employees earn wages for the service in the current period but are paid in the next reporting period.
- Accrued utilities: Utilities used for your business but the bill for the same not received;
There is a tiny but important difference between accrued liabilities and accounts payable. While such liabilities are recorded at the end of each accounting period and involve considerable estimation, accounts payable are normally recorded as the normal course of business based on proper invoices from suppliers.
Examples
Let us understand the concept in depth with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
A business has an annual building rent of 12,000. However, it did not receive an invoice from the owner, and thus the rental expense was not recorded in the accounting books.
Key Assumption
- Period = 12 months
- Annual rent = 12,000
- Accounting period = 1 month
- Accrued expense per period = 12,000 x 1 / 12 = 1,000
Debt/Credit
| Account | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Rent Expense | 1,000 | |
| Accrued Expense | 1,000 | |
| Total | 1,000 | 1,000 |
The accrued liabilities journal entries shown above debit the rent expense account that represents the cost to the business of that particular month for using the premises. The credit entry, which reflects the liability to pay the supplier (owner of the building) for the amount of service consumed during the period, is credited to accrued expenses.
Balance Sheet
As per the Accounting Equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity. For this transaction, the Accounting equation is shown in the following table.

In this case, the income statement incurred a rent expense of 1,000, and balance sheet liabilities (as accrued expenses) have been increased by 1,000. As a result, the expense in the income statement reduces the profit after tax, closing retained earnings, and, therefore, owners’ equity in the business.
Example #2

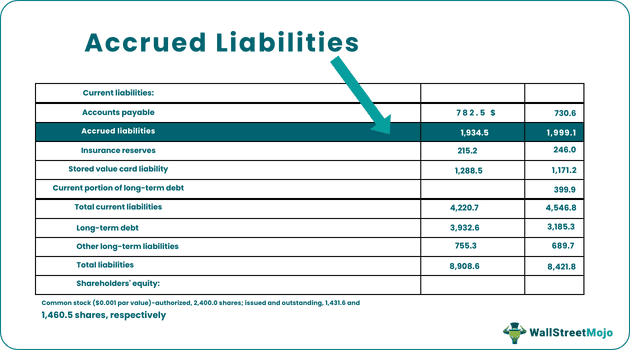
source: Starbucks SEC Filings
The list of accrued liabilities in Starbucks is -
- Accrued Compensation and Related Costs
- Accrued Occupancy Costs
- Accrued Taxes
- Accrued Dividends Payable
- Accrued Capital and other Operating Expenditures
Journal Entry
The expense will be debited to record the accrued expense in the income statement, and a corresponding payable is created on the liability side of the balance sheet. The accounting entry will, therefore, be as follows:

Step 1:- when the expense is incurred
Organizations incur the expense in a particular accounting period and own debt but have not yet been billed. We need to record this expense as an accrued liability in the books of accounts. We need to debit the expense account. This debit entry will increase expenses.
Also, we need to create an accrued liability expense account and credit it with the same amount. It will increase our liability.
Debit expense
Credit expense payable
Step 2:- when payment is made
In the next accounting period, when payment is made, you need to reverse the original entry, passed in the books of accounts. To reverse the transaction, debit the accrued liability account. The debit will decrease liability and credit cash or bank account because you paid the expense in cash. However, it will decrease the assets also.
Debit expense payable
Credit cash
Importance
When a company prepares financial statements using accrual accounting, prepared financial statements are more accurate as it is a complete measure of the transactions and events for each period.
This complete picture helps analysts to better understand a company’s present financial health and predict its future financial position in a better way. This is unlike the cash basis method of accounting, which only records financial transactions and events when cash is exchanged, resulting in understatements and overstatements of income and account balances.
How is it Different from Cash Accounting?
ABC Inc.’s biweekly pay period ends September 30, and salaries to the employees will be paid two days later, on October 2. The total wages owed to employees for the period ending September 30 are $15,000.
Cash Basis Accounting
Since the last bi-weekly payroll of $15,000 was incurred in September but not paid in that month itself, the amount will not be included in September’s income statement. As a result, it will cause the company’s total wages to be understated than what was incurred in September, which in turn causes the company’s profit to appear higher than actual.
Accrual Liabilities Accounting
The entry will be made at September end as follows: — Credit wages payable $14,000 –Debit wages expense $14,000. This entry results in a more complete, accurate presentation of the company’s liabilities and expenses on its financial statements to the cash method of accounting.
Accrued Liabilities Vs Accounts Payable
Accrued liabilities and accounts payables refer to third-party payments that are yet to be paid, despite the accounting period completion. Let us understand the difference between accrued liabilities accounting and technicalities and accounts payable through the discussion below.
Accrued Liabilities
- It determines the payments outstanding for products and services received no invoice has been raised.
- It is recorded as a current liability on the balance sheet.
- An increased accrued liabilities would indicate an increased cash inflow. On the other hand, a decrease would indicate a cash outflow.
- Accrued expenses could be wages, rent, and utilities.
Accounts Payable
- Accounts payable are the invoices raised by suppliers for products or services delivered.
- It is recorded as a current liability on the balance sheet.
- Increased accounts payable indicate cash inflow and a decrease indicates an outflow.
- Accounts payable refer to the invoices from vendors relating to raw materials and other essentials.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what are Accrued Liabilities. Here we explain its examples, journal entry, and importance and compared it with accounts payable. You may also have a look at these articles below to learn more about Accounting basics –

