Table Of Contents
What Is Financial Risk Management?
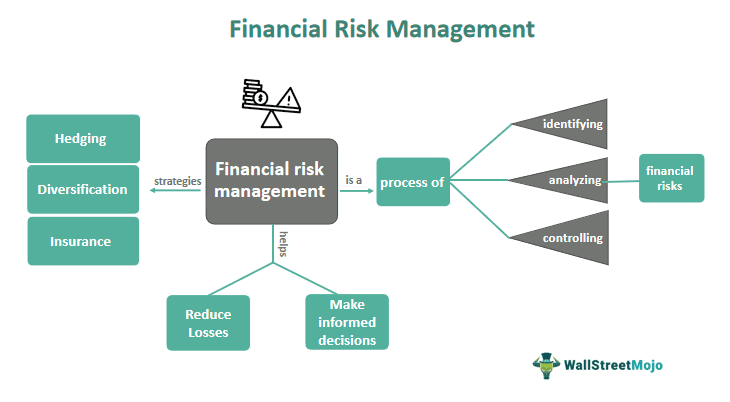
Financial Risk Management involves identifying and analyzing potential risks that could negatively impact an organization's financial performance. Its purpose is to develop and implement strategies to mitigate those risks. Organizations can use various risk management strategies to manage these risks.
It is a vital process for any organization that seeks to protect its financial assets and ensure financial stability. These strategies are designed to help organizations reduce the impact of potential risks and protect their financial well-being. It is a critical function that helps organizations protect their financial assets, make informed decisions, and maintain stability even during economic uncertainty or market turbulence.
Key Takeaways
- Financial risk management identifies, analyzes, and controls potential financial risks affecting an organization's financial performance.
- Effective financial risk management can help organizations reduce losses, make informed decisions, and maintain stable financial performance, even during economic uncertainty or market turbulence.
- Financial risk management strategies can include hedging, diversification, insurance, risk transfer, setting risk limits, scenario analysis,
- and stress testing tailored to the specific risks faced by an organization.
Financial Risk Management Explained
Financial Risk Management refers to identifying, analyzing, and controlling potential financial risks affecting an organization's financial performance. These risks can arise from various sources, including market volatility, credit risk, liquidity risk, interest rate risk, operational risk, etc.
Financial risk management aims to reduce the adverse impact of such risks on the organization's financial health by implementing effective risk mitigation strategies. These strategies may involve using financial instruments such as derivatives, insurance policies, or diversification of investments.
Effective financial risk management enables organizations to make informed decisions, reduce losses, and maintain stable financial performance, even during economic uncertainty or market turbulence. It is a critical function in any organization that seeks to safeguard its financial well-being and sustain long-term growth.
Steps
Organizations can follow these steps to carry out the financial risk management process effectively:
- Risk Identification: The first step involves an extensive assessment of all financial transactions and operations. Companies may consider using tools like accounting software and different applications to uncover hidden and obvious risks faster before they significantly impact the business.
- Risk Analysis: In the next steps, organizations need to analyze the identified risks to comprehend the root causes. Moreover, analyzing the risks is vital to get an idea of their potential impact. Note that organizations can use quantitative and qualitative techniques to figure out if the returns are worth the assessed risk.
- Risk Prioritization: After the analysis of the risks is complete and the company has projected the losses and gains, it can prioritize the risks. The prioritization can be based on the potential impact and the possibility of it materialziing. Based on the prioritization, businesses can allocate their resources and minimize the risks that can cause the most damage.
- Risk Mitigation: This step allows businesses to follow a roadmap. That said, individuals who are responsible for making organizational decisions need to carry out certain actions to minimize or eliminate the risks identified in the first step. The ideal risk mitigation strategy will vary depending on the risk’s possible impact and nature and the organization’s risk profile and resources.
- Risk Tracking And Reporting: Considering that the risks of a business change over time, the strategies implemented to evolve them should change with time as well. Through the monitoring of the risks and by reporting on the progress in minimizing them, businesses can determine whether adjustments are necessary. The cycle of risk tracking and reporting enables organizations to monitor the risks constantly, spot changes concerning the root causes, and report the observations to the key stakeholders.
- Reviewing the Plan And Adjustments: After enacting the risk management plans and recording all results, businesses must analyze their records and make the necessary adjustments. Continuous improvements can allow organizations to stay adaptable and resilient as new risks are addressed and identified.
If individuals want to develop a comprehensive understanding of financial risk management, they can consider choosing the Financial Planning & Analysis Course. The self-paced course dives into the topic and associated concepts to help learners enhance their finance knowledge and boost career development.
Strategies
There are many strategies that organizations can use for financial risk management, depending on the type and level of risk they face. Some common strategies include:
- Hedging: It involves using financial instruments such as futures, options, and forward contracts to offset the risk of adverse price movements in an asset or a liability.
- Diversification: Diversification is a risk management technique that involves investing in various assets or securities to reduce the impact of any one investment on the overall portfolio.
- Insurance: Insurance policies can help organizations manage property damage, liability, and business interruption risks.
- Risk transfer: Risk transfer involves transferring the risk to another party through outsourcing, partnerships, or joint ventures.
- Setting risk limits: Organizations can set risk limits to restrict the exposure to a specific type of risk, such as credit or market risk.
- Scenario analysis: It involves simulating different scenarios and assessing their impact on the organization's financial performance, allowing it to make informed decisions about risk management strategies.
- Stress testing: Stress testing involves simulating extreme scenarios to assess the resilience of an organization's financial position under adverse market conditions.
Overall, effective risk management involves a combination of these and other strategies tailored to the specific risks faced by an organization.
Applications
Let us look at some areas in which the application of risk management methods is common.
#1 - Corporate Finance
Businesses can apply risk management principles to figure out where to invest the funds available to them. Moreover, these principles can help them decide how to safeguard their assets and structure the company’s capital. Comprehensive risk analysis and financial reporting can benefit an organization even if it does not have financial analysts or a chief financial officer. Similar to large corporate financiers and investment firms, even small-sized organizations can focus on building a diversified investment portfolio to minimize external risks, for example, interest rate and currency fluctuations.
In addition, businesses can choose to monitor vital metrics, for example, working capital, as it can help them identify and minimize risks and maintain financial stability.
#2 - Investment Management
The risk management strategies discussed above can help entrepreneurs evaluate the potential risks and returns associated with different investment options, including bonds, stocks, and other financial instruments. They can weigh such options against their long-term plans in relation to how the realization of such returns takes place. If business owners carefully make investment decisions based on this type of assessment, they can make better decisions that are in line with the long-term organizational goals.
#3 - Banking
Risk management, in this case, does not just involve managing accounts. It includes taking measures to reduce risks related to loans, credit, and interest rates. Although organizations may have favorable relationships with banks and depend on their consultation, they can benefit from conducting market research themselves.
Also, they can take the help of independent financial experts to ssess the risks related to important business decisions, for example, applying for a new loan. By carrying out due diligence, organizations can obtain loans that have lower borrowing costs, which, in turn, are aligned with their financial forecasts. This allows them to optimize cash flow while maintaining financial stability and a strong credit profile even during uncertain market conditions.
Examples
Let us have a look at the examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
A hedge fund manager manages a portfolio of stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments for a group of investors. The fund has exposure to the market, credit, and liquidity risks. Therefore, the manager must ensure the fund's risk profile aligns with the investors' risk tolerance and objectives.
The manager implements a range of risk management strategies to manage these risks. For example, they may use diversification techniques, such as investing in various sectors, asset classes, and geographies. It helps to reduce the impact of any individual investment. They may also use financial derivatives, such as options and futures contracts, to hedge against market volatility and manage credit risk.
The manager may also set stop-loss limits to limit potential losses in case of adverse market movements. Also, scenario analysis can identify potential risks and assess the impact of market events on the portfolio.
By implementing effective strategies, the hedge fund manager can mitigate potential risks, enhance returns, and give investors greater confidence in the fund's performance.
Example #2
A manufacturing company based in the United States has recently expanded its operations to Europe. It set up a subsidiary to manufacture and sell its products. However, the company is exposed to currency exchange rate risk. It is so because its revenues are denominated in euros while its costs are denominated in U.S. dollars. Therefore, any euro and dollar exchange rate fluctuation could significantly impact the company's profitability.
The company implements a hedging strategy using forward contracts to manage this risk. Accordingly, it contracts to sell euros at a fixed exchange rate, providing a predictable revenue stream in dollars. This will protect the company from unfavorable exchange rate movements that could otherwise erode its profit margins.
The company can operate more confidently by implementing this financial risk management strategy. As a result, it can focus on its core business activities without being unduly affected by external factors such as currency volatility.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Let us look at the advantages and disadvantages of financial risk management as a concept.
Advantages
- Protection against financial losses: Risk management strategies can help organizations protect against potential financial losses, particularly during economic downturns or market volatility.
- Improved decision-making: It gives organizations a better understanding of their risks and how to mitigate them, leading to more informed decision-making.
- Enhanced investor confidence: Effective risk management can enhance investor confidence in an organization's financial performance and stability.
- Improved regulatory compliance: Implementing risk management strategies can help organizations comply with regulatory requirements and avoid penalties.
Disadvantages
- Cost: Some risk management strategies, such as insurance policies or hedging instruments, can be costly, particularly for small businesses.
- Complexity: Implementing risk management strategies can require specialized knowledge and expertise, which may not be readily available within an organization.
- Over-reliance on risk management: Over-reliance on risk management strategies can lead to complacency and a false sense of security, leading to a failure to identify and mitigate emerging risks.
- Unforeseen events: Risk management strategies may not effectively protect against unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or geopolitical risks, which can significantly impact an organization's financial performance.
Difference Between Financial Risk Management And Enterprise Risk Management
Let us see the difference between them in the following table -
| Financial Risk Management | Enterprise Risk Management |
|---|---|
| Focuses on managing financial risks such as market, credit, liquidity, and operational risks. | Focuses on managing all types of risks an organization faces, including financial, strategic, operational, and compliance risks. |
| Primarily concerned with protecting the organization's financial assets and ensuring financial stability. | Concerned with protecting the organization's overall value, reputation, and sustainability. |
| Typically led by the finance department or a dedicated risk management function. | Typically led by the executive management team or the board of directors. |
| Involves using financial instruments such as hedging derivatives to manage risks. | Involves various risk management techniques, such as risk assessment, mitigation, transfer, and monitoring. |
| Focuses on managing risks that directly impact the organization's financial performance. | Focuses on managing risks impacting the organization's strategic goals and objectives. |
| Limited to financial risks within the organization's control. | Considers both internal and external risks that may impact the organization's performance. |
| Typically has a shorter-term focus on managing risks related to daily operations and financial transactions. | Has a longer-term focus on managing risks related to the organization's strategic objectives and vision. |
