Table Of Contents
What Is Market Risk?
Market risk is the risk that an investor faces due to the decrease in the market value of a financial product arising out of the factors that affect the whole market and is not limited to a particular economic commodity. Often called systematic risk, the market risk arises because of uncertainties in the economy, political environment, natural or human-made disasters, or recession.
It is an integral part of any portfolio. It arises from the additional return an investor expects to generate from an investment. If the investor can hedge it, it can lead to better results and safeguard the losses when the market experiences downward cycles. It can only be hedged; however, it cannot be eliminated by diversification.
Key Takeaways
- Market risk is the risk faced by investors due to a decline in the market value of a financial instrument. It is influenced by factors that affect the entire market rather than specific economic commodities.
- Market risk, also known as systemic risk, arises from economic uncertainty, political factors, natural or artificial calamities, or recessions.
- Diversification alone cannot eliminate it; hedging strategies are typically employed to manage it.
- Interest rate risk, foreign exchange risk, commodity price risk, and equity price risk are types of market risk that investors may encounter.
Market Risk Explained
The concept of market risk refers to the possibility of losses in investments that occur in the financial market. Such risks may arise due to various factors like political risk, changes in financial and economic policies, exchange rate fluctuations or natural disasters.
The market risk models are an integral part of risk management. As it affects the whole market simultaneously, it can be lethal for an investor to ignore market risk while building a portfolio. This risk affect any type of financial instrument like currencies, stocks, commodities, bonds, derivatives, etc.
The market risk management help in measuring the maximum potential loss for a portfolio. There are two significant components here–time frame and confidence level. The time frame is the duration for which the market risk premium has to be calculated while it bases the confidence level on the investor's comfort level. A confidence level determines how much risk an investor or portfolio manager can take. We express it in % terms like 95% or 99%.
It is a statistical concept; hence, its calculations are cumbersome in numbers. The various tools/mechanisms used for calculation are – Value at risk expected shortfall, variance-covariance, historical simulation, and Monte Carlo simulation.
Since market risk impacts the whole investor community irrespective of their credibility or the asset class they operate on, it is closely watched by regulators worldwide. In the last 25 years, we have witnessed four major regulations and many more minor enhancements. Basel Committee is the main regulatory body that comes up with these rules or advisories. The member nations are free to adapt or add more scrutiny to these regulations to make their banking systems much more robust.
Types
There are four significant types of market risk.
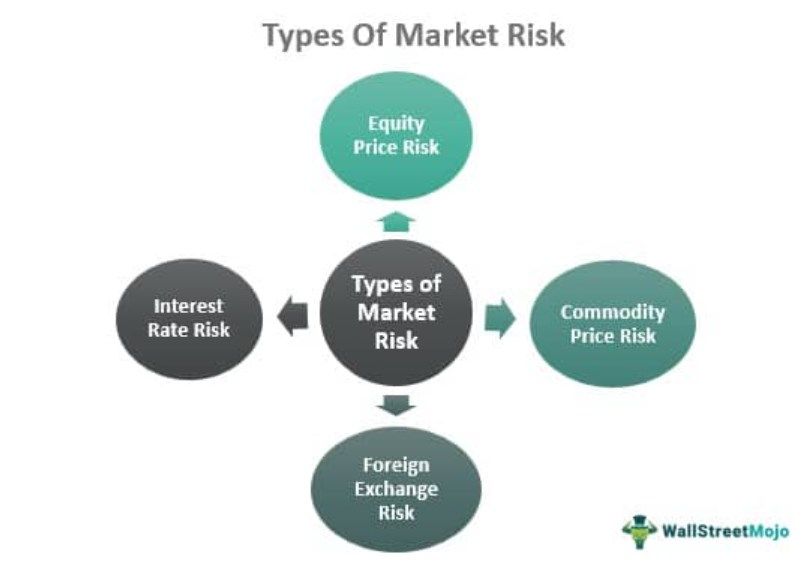
#1 - Interest Rate Risk
Interest rate risk arises when the value of security might fall because of the increase and decrease in the prevailing and long-term interest rates. It is a broader term and comprises multiple components like basis risk, yield curve risk, options risk, and repricing risk.
#2 - Foreign Exchange Risk
Foreign exchange risk arises because of the fluctuations in the exchange rates between domestic and foreign currencies. The most affected by this risk is the MNCs operating across geographies and paying in different currencies.
#3 - Commodity Price Risk
Like foreign exchange risk, commodity price risk arises because of fluctuations in commodities like crude, gold, silver, etc. However, unlike foreign exchange risks, commodity risks affect not only multinational companies but also ordinary people like farmers, small business enterprises, commercial traders, exporters, and governments.
#4 - Equity Price Risk
The last market risk component is the equity price risk, which refers to the change in the stock prices of financial products. As equity is most sensitive to any change in the economy, equity price risk is one of the most significant parts of market risk models.
Example
Let's take an example to understand the concept.
Let’s consider the example of an IT major firm–HP. An investor wants to calculate the market risk premium associated with the stock price, which is currently quoted at $1000. Suppose the investor expects the stock price to be hot at $1100 because of expected growth. The following is the calculation in Excel.
Calculation of Risk Premium will be -

Market Risk Premium = 11%
Advantages
Just like every system has its own advantages and disadvantages, market rik also has them, Some advantages are as follows.
- More often than not, financial products are sold to the investor community through aggressive marketing and presenting only the growth while completely ignoring the risks and downfalls. This is why we see such products being bought more in the economic expansion cycles, while in the recession, investors, especially the retail ones, are trapped. Had the investor known about the concept of The market risk management and its calculations, they could understand the financial products much better and decide if they suited them for such volatilities.
- This concept of risk can be used very efficiently to assess the market's ups and downs at any given time and make profitable and informed investment decisions. In addition, it helps the investor understand which financial product they should or should not invest in.
- It also identifies the correct time of investment to a large extent. However, it is important to have knowledge regarding how to identify the various signal and use the relevant tools for the purpose.
- The market risk premium, as explained in the example above, helps an investor calculate the real return rate. Even though the financial product might enjoy a lucrative return, the investor should gauge the investment in terms of the actual rate it provides. This can be calculated by taking into account the prevailing risk-free interest rate and inflation rate.
Disadvantages
Some disadvantages of the risk are as follows.
- The market risk analyst cannot completely ignore them. An investor must understand what data to analyze and what data it should filter out. It can only be hedged, which comes with a cost and intensive calculations.
- Unlike credit risk, which is very much counterparty specific, it affects all asset classes. It is very prone to recession or cyclic changes in the economy. And since it affects the whole market simultaneously, it is even more challenging to manage as diversification will not help.
- Sometimes investors take the help of professionals who advise them regarding investment options. However, investors must take advice from professionals who put clients' interests before their own. Otherwise, these professionals may not reveal the type and extent of market risk the investor’s fund is subject to and earn profit at the investor's expense.
Market Risk Vs Credit Risk
The two types of risks mentioned above are different in several ways. Let us try to understand the differences between them.
- The former is the risk of incurring loss due to sudden fall in the value of the investment, whereas the latter is the risk due to failure of borrowers to pay back the money that they have borrowed.
- The former depends on various factors like economic and political unrest, market fluctuation, natural disaster, etc, whereas the latter depends on the creditworthiness of the borrower.
- The former arises when the price of investments decline wheres the latter arise when the creditworthiness of the borrower decline.
- The market risk analyst can control them by hedging or diversification of the portfolio so that the profit from another compensates for the loss of one investment. But the latter can be controlled by giving loans after careful analysis and background checks of the borrower and assessing their credit rating.
Thus, both results in potential losses in the financial markets. Hence it is better to do proper financial analysis before taking any investment decision.


