Table Of Contents
What Are Asset Classes?
Asset classes refer to a group of securities with comparable features and responses to market variations. It aids the investors in deciding the proper investment strategies and receiving maximum profits with minimal risk prospects. The asset classes types include fixed income, cash & cash equivalents, equity, and real estate.
Each asset class is unique regarding the related risk, taxation, ownership, exchangeability, revenue, rules, and market instability. Moreover, the asset classes list is organized according to each asset's nature, response to market volatility, returns, and target.
Key Takeaways
- Asset classes depict a collection of different financial instruments with identical traits and market behavior.
- They are arranged as per the reaction to each asset's market fluctuations, nature, and financial goals.
- There are five crucial asset categories: derivatives, fixed income, real estate, cash & cash equivalents, and equity. Also, the alternative categories include bitcoins and hedge funds.
- Diversification of asset types helps reduce the overall risk and losses and obtaining the expected portfolio returns.
Understanding Asset Classes
Asset classes definition implies an assortment of investment vehicles with similar characteristics and behavior in the marketplace. Besides the types mentioned above, the asset classes list also covers hedge funds, collectibles, and Bitcoin. These are called alternative investments due to being more illiquid and riskier.
Investors must have a complete knowledge of different asset categories. It helps them diversify risks and increase awaited profits. Accordingly, they can choose the apt asset allocation strategy to maximize gains.
Types
Here lie the top five asset classes types:
#1 - Equity
Equity illustrates the capital amount belonging to the shareholders or owner after dues and assets are discharged in case of liquidation. Precisely put, it depicts the proprietorship shares issued by the firm in lieu of the paid-up capital. Unconstrained by the dividend payments, equity is the only funding alternative in the event of credit risk.
Also, it has sub-divisions such as large-cap/mid-cap/small-cap stocks, thematic funds, value funds, sectoral funds, etc.
Here goes the accounting equation:
Equity = Assets – Liabilities
#2 - Cash and Cash Equivalents
It denotes the available money and most liquid (swiftly cash convertible) current assets in an enterprise. Cash and Cash equivalents are short-term investments for operational expenses and have high credit quality. Furthermore, it includes commercial papers, money market instruments, US Treasury bills, etc.
#3 - Fixed Income
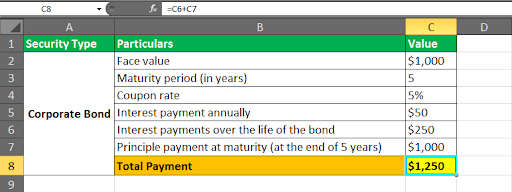
Fixed income offers systematic fixed-rate interest earnings to the investors till the maturity date. Therefore, it is among the earliest and most favored investment types due to being cheaper than equity financing. Examples include corporate debt securities, government (US Treasury bills), corporate bonds, etc. The following asset class example demonstrates how corporate bonds work:
An investor buys a corporate bond worth $1,000 with a maturity period of 5 years. The issuer promises to pay a 5% yearly coupon rate until the bond matures. Now, the payment structure will be as follows:
#4 - Real Estate
Real estate involves tangible assets commonly purchased for either residential/commercial usage or future investment. It entails plots, condos, mansions, retail centers, industrial estates, etc. Furthermore, the asset class provides safety against inflation and guarantees immense financial gains.
#5 - Derivatives
The derivatives are financial contracts between at least two parties whose value relies upon the underlying asset or a group of assets. The financial agreement sets an expiration date when the investors can (obligation for forwards/futures). They are traded to hedge against risks through long or short positions.
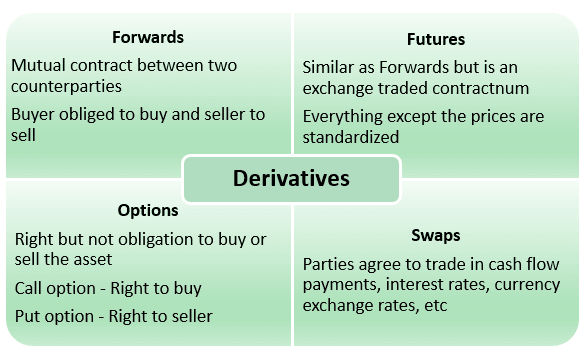
The contract pricing settled at the time of agreement is called the strike price. It has four types, i.e., Forwards, Futures, Options, and Swaps.
Examples
Example #1
Commodities are doing inexplicably well during the sudden inflationary bouts and may be chosen for the retirement portfolio. It is the 3rd best performing asset class in 2021, followed by Bitcoin and West Texas Intermediate (WTI) Oil.
Moreover, the 2021 S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (GSCI) gained 37.1%, surpassing the S&P 500 and other equity indices. They perform well during inflation and are a relevant category during the portfolio’s asset allocation.
However, some experts state that profits from trading commodities are gained at the expense of other traders. Hence, there has been no final opinion on the matter.
Example #2
The alternative asset classes have witnessed a 38% surge in commitments obtained from domestic investors. The increment is due to the clients’ desire to participate in private markets via private equity and personal debt.
Moreover, lower returns on fixed income products and expanded equity valuations are behind such allocation. The robust secondary equity market through 2020-2021 is the significant motivation for the enhanced alternative fund investment.
Diversification Of Asset Classes
Asset categories diversification is essential for development-oriented companies with future expansion plans. No two markets operate likewise at the same time. Therefore, diverseness prevents a corporation’s poor market performance because of a lag in one asset class.
Diversification intends to reduce the general risks and losses and boosts the preferred portfolio returns. Mutual fund specialists make a list of distinct asset classes for investment to avert concentration risk and ensure portfolio diversification.
Investors must examine their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and financial objectives before the allotment of funds. For example, risk-averse investors must select fixed-income securities, while risk-tolerant investors must pick Equity.
Furthermore, the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) is applicable if the rates of common stocks, preferred shares, or debts rise.

