Table Of Contents
What is Proportional Tax?
A proportional tax is a single-rated tax, wherein all the incomes, without considering the slabs or other criteria, tax is levied at a flat fixed rate irrespective of the kind of person or kind of income, thus, eliminating the concept of higher and lower earnings. The tax payable is in proportion to the amount subject to taxation.

However, in the case of the progressive tax system, there prevails proper distribution of the tax burden as the individual with more earnings has a more tax burden than those having a low income. Still, in the case of proportional tax rate, all have to bear the same percentage of tax on their taxable value.
Proportional Tax Explained
A proportional tax is a type of taxation system wherein all taxpayers (low, middle, and higher-income groups) are taxed at the same rate. Since the tax is charged from everyone at a flat rate, whether they are earning lower income or higher income, it is also known as the flat tax.
Thus, this system is the mechanism of taxation in which the tax authorities are levying the same rate of tax on all the taxpayers irrespective of the amount of income earned by them.
The people who are in favor of proportional taxes believe that this system helps in stimulating the economy as it encourages the people to work hard and more as there is no penalty of tax for earning more income, which is there in the case of the progressive tax system. Also, it is believed that businesses working in such a tax system are likely to invest more under this system, which will lead to more money circulation in the economy.
How To Calculate?
Some countries follow the flat-rate tax system, and they charge the same rate of tax on the earnings of the persons in the country without giving effect to the number of earnings whether the amount is high or low. So, the income tax system in those countries has a proportional tax system.
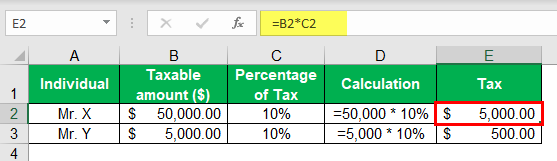
For example, a country follows the proportional tax rate on the earnings of any person to calculate the tax payable by them. The rate of the tax is 10 %. During the year, Mr. X earns an income of $ 50,000 and Ms. Y earns an income of $ 5,000. Calculate the tax payable by Mr. X and Ms. Y on their earnings for the year under consideration.
Solution:
In the above case rate of tax, remains fixed and don't increase with the increase in the income of the person, so it is the case of the proportional tax so, the tax payable by Mr. X and Ms.. Y will be calculated as follows:
Here Mr. X is earning a total of $ 50,000 per annum, and Ms. Y is earning a total of $ 5,000 per annum. Although there is a huge income gap between the two, as the country in which they are residing follows the system of the proportional tax rate, they both will be charged tax at the rate of 10 %.
- Tax liability = Taxable value (Income) * rate of tax
- Mr. X Tax liability = $ 50,000 * 10 % = $ 5,000
- Ms. Y Tax liability = $ 5,000 * 10 % = $ 500
Example
Let us understand the concept of proportional tax system in detail with the help of a detailed example.
In the U. S., on the retail items which are sold in the market, sales tax is being imposed and is paid by the consumer to the retailer, which is usually calculated as the percentage of the retail cost. After collecting the sales tax, the retailer submits the payment collected to the respective state to which it belongs. Sales tax is also one of the examples of the proportional tax rate system because, in the case of the sales tax, the entire person pays the same rate of tax at the flat rate on the particular product, irrespective of the income earned by them during the period.
For example, there are two individuals Mr. A and Mr. B, who went to the same cloth shop to purchase the same items of the same value. Each of the persons purchased cloth worth $ 150 from the cloth shop. The sales tax rate applicable to the cloth is 8 %. So, in this case, both of the individuals will have to pay tax at the rate of 8 % on the value of the cloth purchased by them, which comes to $ 12 ($ 150 * 8 %). Now, the tax amount spent as per the current earnings of both of the individuals will be seen to know the tax paid with respect to the earnings gap between the two individuals doing the same transactions.
The first individual Mr. A earns $ 1,200 per month in total from all the work done by him, and the second individual Mr. B earns $ 12,000 per month in total from all the work done by him. If the ratio of tax paid with respect to the total earning is calculated, for the first person, Mr. A’s percentage of tax paid by him with respect to his income comes to 1 % . In contrast, for the second person, Mr. B’s percentage of tax paid by him with respect to his income comes to 0.10 % only.
It can be seen that the amount of sales tax affects both of the persons differently as even though the same rate of tax prevails for both of the individuals, Mr. B, who is having the lower income, has to pay a higher percentage of tax when compared with Mr. A tax percentage. This flat rate system of charging the same rate of tax to all individuals without considering their earnings is a proportional tax system.
Proportional Tax Vs Progressive Tax
The tax system in the United States of America accounts for three major types- Proportional, progressive, and regressive. While Progressive and regressive form of taxation impacts the high and low-income groups, the proportional tax does not impact any particular group. Let us understand the difference between a proportional tax system and a progressive tax through the comparison below.
Proportional Tax
- A proportional tax rate aims to levy the same tax rates for all individuals irrespective of their income-making capacity.
- The system is curated to ensure equality between the average taxes paid and marginal tax rates.
- Occupational taxes, per capita taxes, and gross receipt taxes are examples of this type of taxation.
- Colorado, Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, and North Carolina follow this type of tax regime.
- It is believed that this helps the economy to grow as individuals are motivated to earn more as there is no extra tax for earning beyond their current levels.
Progressive Tax
- Progressive tax system is based on the taxable portion of the individual’s income. As in, citizens earning more would pay more taxes in comparison to those who earn lesser.
- This system charges the richer citizens more as it is believed that they can afford to pay more. Whereas, a low-income individual might not be able to pay an increased amount of tax, given their daily expenses also might be a challenge if they were made to pay extra.
- The U.S. federal income tax is a progressive tax system.
- Critics often point out that progressive taxes are a form of inequality where high-income earners are penalized more for having the ability to earn more than other sections of the society.
