Table of Contents
What Is SEC Form 5?
SEC Form 5 is the Form filed under the United States Securities and Exchange Commission that talks about annual statements of changes occurring in the beneficial ownership of securities. It is critical information, so it shall be a public record and available for public member inspections.

The details asked in the Form are mandatory. It discloses the holdings and transactions of beneficial owners and directors of companies that have been registered. The SEC can use the information for investigative purposes and taking legal action in cases of involvement of matters about securities law and related other statutes and provisions.
Key Takeaways
- SEC Form 5 is a requirement of annual filing that discloses information on the beneficial ownership of investors.
- Directors and shareholders who have ownership of more than 10% equity shall file them within the expiry of 45 days from the company's fiscal year ending.
- The information disclosed includes unreported and exempt transactions, small acquisitions etc.
- The information is used to understand insider trading, the ownership and for investigative purposes and taking legal actions. The information is available publically and has to be mandatorily disclosed.
SEC Form 5 Explained
SEC Form 5 is the Form to be filed with the SEC before the expiration of 45 days from the company's fiscal year ending and it exclusively talks about the annual statements on existing beneficial ownerships. This is a requirement only in cases where at least one transaction was not reported during the year due to a failure in early reporting or because of an exemption. Form 5 is a statement on holdings of the company equity shares.
Corporate insiders such as holders and directors who own more than 10% of registered equity securities class of a company are required to disclose information on holdings. The disclosure shall be done regularly not just on holdings but on transactions also.
The information disclosure is required under two sections of the securities exchange act of 1934 (section 16(a) and 23(a)). Similarly, the Investment Company Act of 1940, sections 38 and 30(h)also require disclosing such information. Failure of submission can result in criminal or civil actions as a violation of federal securities rules and law. This is because it can be used as litigation in criminal, civil and securities law, including regulatory provisions or statutes. It could also be used as a reference for self-regulatory organizations and governmental authorities.
Requirements
Given below are some of the requirements of the Form.
The requirements as listed by the SEC can be grouped into three categories:
General requirements, Beneficial Ownership Reporting (Pecuniary Interest) and Derivative and Non-Derivative Securities. A summary of them is given as follows.
General requirements
- In accordance with rule 16a-3(f), insiders are required to report any unreported transaction at the end of the fiscal year (earlier if a person ceases to be an insider during the fiscal year) for any security class.
- Report all the transactions that are exempt, including section 16 of the act that is pursuant to another rule under section 16(a). Similarly, reporting of exempt transactions shall be done except in sections 16b-3(c), 16b-3(d), 16b-3(e), 16b-3(f), and 16b-6(b) (to be reported on form 4).
- Report all small acquisitions or their series within 6 months during the fiscal year of issue within a $10,000 market value.
- Report of all transactions to be disclosed on forms 3 and 4 but weren't.
- The form filing shall include reports of the issuer in the last two fiscal years.
- The transactions shall be reported on separate lines using specific codes.
- Irrespective of whether the disposition and acquisition of a class of securities are equal, they shall be reported.
Beneficial ownership Reporting's (pecuniary interest)
- Apart from the 10% criteria, the ownership status shall be given to those with voting or investment control. A person is a beneficial owner even if they have gained profit directly or indirectly (pecuniary interest).
- Direct and indirect interests are reported. Direct ones are in the reporting person's name (or bank, nominee, join tenants, etc.). Indirect ones are those acquired through contract.
- Direct and indirect ownership shall be recorded separately along with specifications of indirect ownership type.
- Reporting shall be made only on proportionate interests of the beneficiary when ownership is through partnership, trust etc.
- In case of multiple owners of the same equity, they shall file forms individually or jointly.
Derivative and Non-Derivative Securities.
- Report non-derivative securities acquisitions, holdings and dispositions as in table I.
- Reporting of dispositions, acquisitions, and holdings of derivative securities (e.g., Puts, calls, options, warrants, convertible securities) shall be done in Table II.
- Purchase or sale prices shall be reported by the owner in column 8.
- The reporting of securities that constitute components of a unit are required to be reported separately on appropriate tables.
How To File?
The reporting person shall file Form 5 in electronic format through the Electronic Data Gathering Analysis and Retrieval System (EDGAR) of the SEC. The website contains detailed information on SEC Form 5 instructions for filing. In cases where the forms or any amendments for that matter are filed with the commission, the owner shall file one with the exchange, and. a copy of the exchange needs to be filed with the exchange regarding the section 16 filings.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose Dan is a director in XYZ Ltd that is into cloth manufacturing. He has direct ownership of XYZ's common stock. Initially, he owned only 5% of the shares of the company and was a small shareholder. Later he acquired additional shares and owns around 21% of the stocks issued by the company. Dan, Previously had no requirement of Form filing. Now that Dan has ownership of more than 10%, he is now required to disclose his ownership through Form 5.
Example #2
Given below is an image of the actual form 5 as given by the SEC.
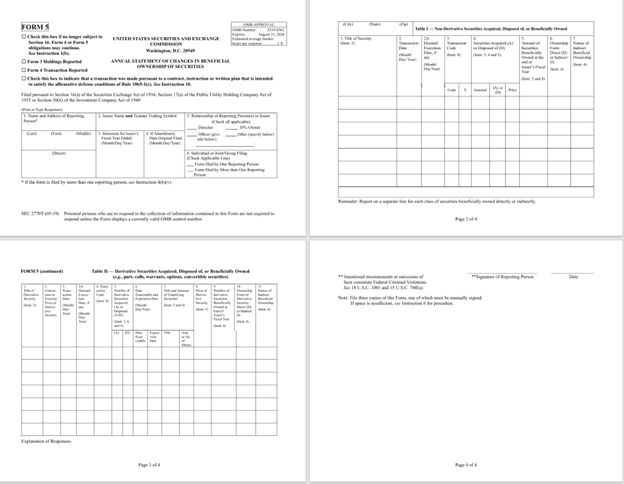
Example #3
A real-life example of Form 5 filing. Elon Musk is the reporting person for Tesla Inc. The filing period or the fiscal period is reported as 2022, and some amendments have been recorded in 2023. The form contains various other details, such as the company's address, the transaction dates and the class of equities on which the transactions were made. The form also discloses whether the ownership is indirect or direct and the nature of the indirect beneficiary, Musk, among other things.
Importance
It is important for the following reasons.
- Sec form 5 discloses information on holdings and related transactions.
- It helps in monitoring insider trading.
- It helps in understanding the investments made within the company.
- The form helps in complying with the requirements of the SEC.
- It aids in easy corporate governance.
