Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Do Loop
VBA Do Loop is a set of instructions inside a sub procedure where code runs a specific number of times until the desired criteria reach or any threshold exceeds or safe to say that until obtaining the required data.
While the Loop works on logical results, it keeps running the Loop back and forth while the test condition is TRUE. The moment the test condition returns FALSE, it will exit the Loop. Loops are the heart of any programming language. Our articles demonstrate the importance of loops and ways of coding them. In this article, we are showing you how to use Do Loop.
How to use the VBA Do Loop?
Example #1 - Condition at the end of Loop
We have seen the condition test at the beginning of the Loop. In the earlier code, we have seen the example of inserting serial numbers, and the code was like that.
Code:
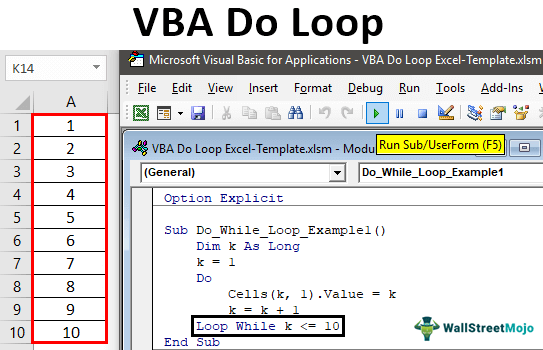
Sub Do_While_Loop_Example1() Dim k As Long k = 1 Do While k <= 10 Cells(k, 1).Value = k k = k + 1 Loop End Sub

You can run this code manually or through shortcut key F5 to see the result.
This code will insert serial numbers from 1 to 10.

But, we can also test the condition at the end of the Loop. So, we need to use the word “while” and the condition test after the word Loop.
The only change here is to apply for the test at the end, as shown below.
Code:
Sub Do_While_Loop_Example1() Dim k As Long k = 1 Do Cells(k, 1).Value = k k = k + 1 Loop While k <= 10 End Sub

Like this, we can also test the condition at the end of the Loop statement.
Note: Code will run, then it tests the condition to go back to loop one more time or not. It means that it will run first and then try the situation later.
Example #2 - Summation Using Do While Loop
Assume you have sales and cost data in your Excel sheet. Below is the set of dummy data we have created for calculation.

Now, we need to get the value of profit in column C. We have already created a code that will do the job for me.
Code:
Sub Do_While_Loop_Example2() Dim k As Long Dim LR As Long k = 2 LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Do While k <= LR Cells(k, 3).Value = Cells(k, 1) + Cells(k, 2) k = k + 1 Loop End Sub

LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
This code will identify the last used row in the first column. In addition, it makes the code dynamic if there is any addition or deletion of the data. Finally, it will adjust my sequence time to run the Loop.
k = 2
We want the calculation done from the second cell onwards. So, k’s initial value is 2.
Do While k <= LRAs we told you, LR will find the last used row in the first column. It means the Loop will run while k is <= to the value of LR. In this case, we have 10 rows, so LR = 10.
Loop will run until the k value reaches 10. Once the amount has passed 10 loops, it will stop.
You can run this code using shortcut key F5 or manually to see the result.

Example #3 - Exit Statement in Do While Loop
We can also exit the loop while the condition is still TRUE only. For example, take the above data here as well.

Assume you do not want to do the full calculation, but you only need to calculate the first 5 rows of profit, and as soon as it reaches the 6th row, you want to come out of the Loop. We can do this by using the IF function in excel. The below code includes the exit statement.
Code:
Sub Do_While_Loop_Example3() Dim k As Long Dim LR As Long k = 2 LR = Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row Do While k <= LR If k > 6 Then Exit Do Cells(k, 3).Value = Cells(k, 1) + Cells(k, 2) k = k + 1 Loop End Sub
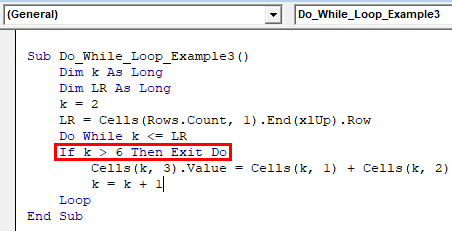
“If k > 6 Then Exit Do”
This line of code will initiate the exit process. Loop will keep running until the value of k reaches 6. The moment it exceeds 6, If condition will execute the code, “Exit Do.”
You can run this code using shortcut key F5 or manually to see the result.

Things to Remember
- The Do Loop works on logical results and keeps running the Loop back and forth while the test condition is TRUE. The moment the test condition returns FALSE, it will exit the Loop.
- We can exit the Loop at any given time by adjusting one more logical test inside the circle using the IF function.
- If we supply the condition or test at the top of the Loop, it will first check the test and progress further only if it is TRUE.
- If we supply the condition or test at the end of the Loop, it will first execute the block of code inside the loop statement. Then, in the future, it will test the condition to decide whether to go back to run the Loop one more time or not.

