Table Of Contents
Excel VBA Sleep Function
VBA Sleep function is a Windows function present under Windows DLL files which is used to stop or pause the macro procedure from running for a specified amount of time. After that certain amount, we can resume the program.
There are situations where we need to pause our macro running process to complete other sets of tasks. Other sets of tasks could be part of our coding or other Macro procedures, or they could be input for the current excel macro. How can you pause the program when it is running? We can pause the procedure code for some time specified by the user. After that certain amount, we can resume the program. We can do this in VBA by using the SLEEP function.
What Does VBA Sleep Function Do?
SLEEP, as the name itself, says, "sleep for some time," "rest for some time," "pause for a time," time off for some time," etc. So, for example, the Sleep function allows users to pause our macro code for milliseconds. Using this, we can delay the process of Macro code.
If you think we have a built-in function called SLEEP, then you are wrong because, in VBA, there is no such function. Rather, we have a function called Sleep as a windows function. By entering a special set of codes, we can call this function in VBA. It is a function inside Windows DLL files, so we must declare API nomenclature before the subroutine starts in VBA.
Below is the VBA code.
Code:
#If VBA7 Then Public Declare PtrSafe Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As LongPtr) 'For 64-Bit versions of Excel #Else Public Declare Sub Sleep Lib "kernel32" (ByVal dwMilliseconds As Long) 'For 32-Bit versions of Excel #End If
Please copy the above and paste it into your module before you start writing the macro codes. We should paste it like this in the module.

Example
Before we show you how to write the code, let us explain the Sleep function a little more. It delays the process in milliseconds. So, 1 second is equal to 1,000 milliseconds. So, if you want to pause for 10 seconds, it should be 10,000 milliseconds.
Example #1
Once we paste the API code before the start of the sub procedure, create a Macro name.
Code:
#Sub Sleep_Example1() End Sub

Declare two variables as a string.
Code:
Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String

For the StartTime variable, assign the value of the TIME function. Note: TIME in excel function returns the current time.
Code:
StartTime = Time

Now, we will display this message in the message box VBA.
Code:
StartTime = Time MsgBox StartTime

We will pause the code for 10 seconds using the Sleep function. As we said, it pauses the code in milliseconds to pause for 10 seconds. So, we need to use 10,000 milliseconds.
Code:
Sub Sleep_Example1() Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String StartTime = Time MsgBox StartTime Sleep (10000) End Sub

Now, use the second variable, EndTime, and assign the current time.
Code:
Sub Sleep_Example1() Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String StartTime = Time MsgBox StartTime Sleep (10000) EndTime = Time MsgBox EndTime End Sub

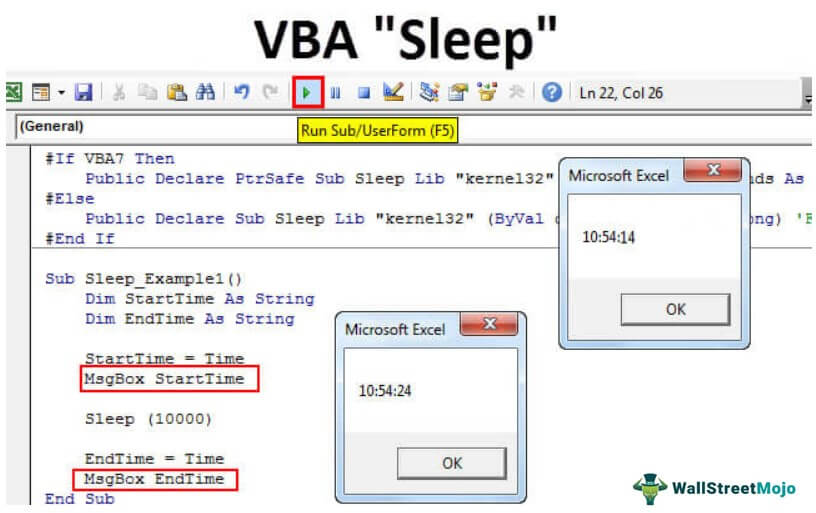
Now, two variables: StartTime and EndTime. It will hold macro beginning and end times. Run this Macro. At first, we will see the Macro starting time: the current time in your system.

Click on "OK." It will sleep for 10 seconds. Next, you can see the buffer symbol.
After 10 seconds, it will resume the code to show the end time. After waiting for 10 seconds, what's the current time now?

Macro started at 10:54:14 and ended at 10:54:24, i.e., the 10-second difference. In those 10 seconds, VBA paused the code running.
Example #2 - Sleep Function in Loops
Sleep is used best with loops in VBA. For example, we want to insert serial numbers from 1 to 10 using the Do while loop in VBA.
After inserting the one number, my code should wait for 3 seconds, so when the loop runs 10 times, it should be 30 seconds.
Code:
Sub Sleep_Example2() Dim k As Integer k = 1 Do While k <= 10 Cells(k, 1).Value = k k = k + 1 Sleep (3000) '1000 milliseconds is 1 second so 3000 is equal to 3 seconds Loop End Sub

Run this code, and you have to wait for a minimum of 30 seconds to complete the process.
To track the exact time, use the below code.
Code:
Sub Sleep_Example2() Dim k As Integer Dim StartTime As String Dim EndTime As String StartTime = Time MsgBox "Your Code Started at " & StartTime k = 1 Do While k <= 10 Cells(k, 1).Value = k k = k + 1 Sleep (3000) '1000 milliseonds is 1 second so 3000 is equal to 3 seconds Loop EndTime = Time MsgBox "Your Code Ended at " & EndTime End Sub

This code will display two message boxes. The first one will show the starting time. In addition, the second one will show the end time.
Note: While running this code, you cannot use Excel. Even the escape key will not work.

