Table Of Contents
IF OR Function in VBA
Logical functions are the heart of any criteria-based calculations. The IF function is the most popular logical function, be it a worksheet function or a VBA function because it serves excellently for our needs. But one more logical function, OR in excel, is the most underrated. It is also important to master when it comes to solving complex calculations. This article will take you through the VBA IF OR function in detail. Read the full article to get the function in detail.
How to Use IF with OR Function in VBA?
We will show you a simple example of using the IF OR function in VBA.
A combination of logical functions is the best pair in Excel. However, combining many logical formulas inside the other logical formula suggests that calculation requires many conditions to test.
Now, look at the syntax of the IF OR function in VBA.
OR OR
It is the same as we saw in the worksheet example. For a better understanding, look at the below example.

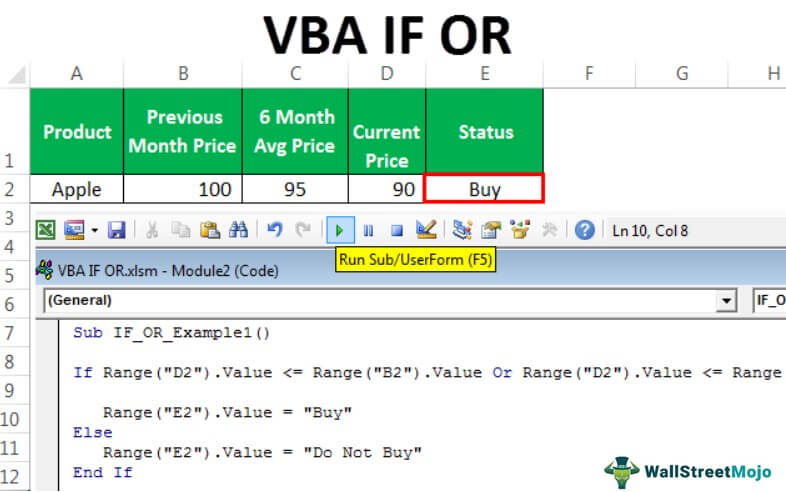
We have the previous month's price, the last 6-month average price, and the current monthly price here.
To decide whether to buy the product, we need to do some tests here, and those tests are.
If the Current Price is less than or equal to any of the other two prices, we should get the result as "Buy" or else should get the result as "Do Not Buy."
Step 1: Open the IF condition inside the Sub procedure.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If End Sub
Step 2: Inside the IF condition, apply the first logical test as Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“B2”).Value
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“B2”).Value End Sub
Step 3: The first logical condition completes. Now, open OR statement.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value OR End Sub
Step 4: Now, apply the second logical condition as Range(“D2”).Value <= Range(“C2”).Value
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value OR Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value End Sub
Step 5: We are done with the logical tests here. After the logical tests, put the word "Then."
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then End Sub
Step 6: In the next line, write what the result should be if the logical test is TRUE. If the condition is TRUE, we need the result as "Buy" in cell E2.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" End Sub
Step 7: If the result is FALSE, we should get the result as "Do Not Buy." So in the next line, put "Else" and write the code in the next line.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" Else Range("E2").Value = "Do Not Buy" End Sub
Step 8: Close the IF statement with "End If."
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() If Range("D2").Value <= Range("B2").Value Or Range("D2").Value <= Range("C2").Value Then Range("E2").Value = "Buy" Else Range("E2").Value = "Do Not Buy" End If End Sub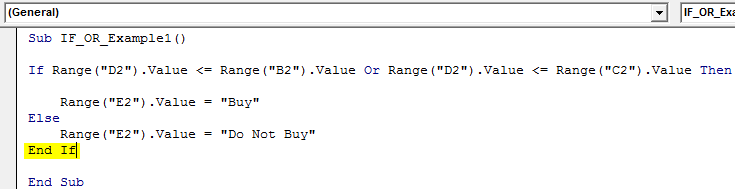
We complete the coding part.
Let us run this code using F5 or manually through the run option and see the result in cell E2.

We got the result as "Buy" because the current monthly price of Apple is less than the price of both "Previous Month" as well as "6 Month Average Price".
IF OR VBA Function with Loops (Advanced)
Once you understand the formula, try to use it with a larger number of cells. In the case of a larger number of cells, we cannot write any line of code, so we need to use VBA loops.
We have added a few more lines for the above data set.

We need to use the For Next Loop here.
Just keep the current code as it is.
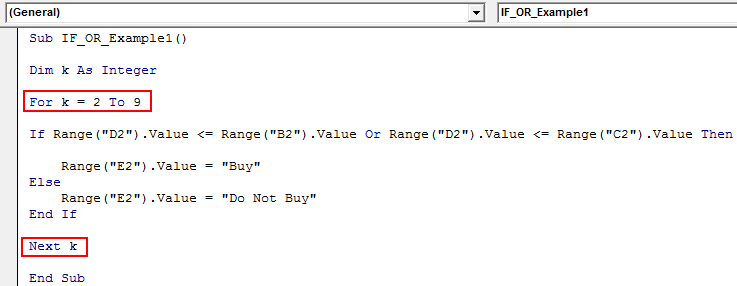
Declare the variable as an Integer.

Now, open For Next Loop from 2 to 9.
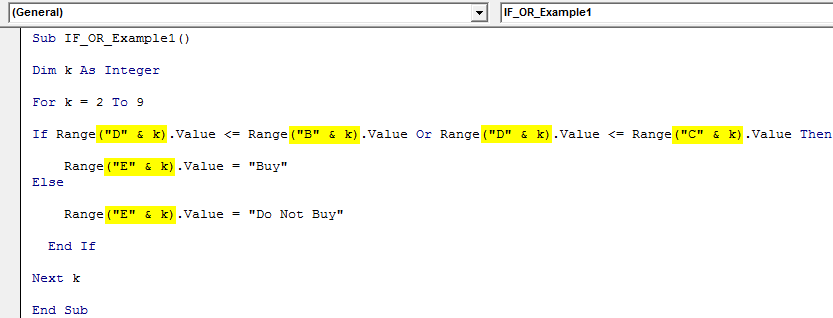
Now, wherever we have cell reference, change the current number, and concatenate the variable "k" with them.
For example, Range (“D2”).Value should be Range (“D” & k).Value
Now, run the code. First, we should get the status in all the cells.

You can copy the code below.
Code:
Sub IF_OR_Example1() Dim k As Integer For k = 2 To 9 If Range("D" & k).Value <= Range("B" & k).Value Or Range("D" & k).Value <= Range("C" & k).Value Then Range("E" & k).Value = "Buy" Else Range("E" & k).Value = "Do Not Buy" End If Next k End Sub


