Both the terms are often used synonymously. But there are differences as listed below:
Table Of Contents
Portfolio Manager Meaning
A portfolio manager is a financial market expert who strategically designs investment portfolios. These managers understand clients’ investment objectives. They manage a basket of assets, to minimize risk and maximize returns.
Portfolio Managers possess professional knowledge and experience in managing financial assets actively or passively. They are well-equipped to make investment decisions on behalf of their clients.
Key Takeaways
- A portfolio manager is a professional possessing expertise in the financial market. The managers use various investment strategies to create an asset portfolio that matches the investor's financial objectives.
- These Professionals adopt either an active or passive investment method. They cater to both individuals and institutional investors.
- For this profession, managers require a graduate-level qualification in finance, accounting, economics, mathematics, investment, business administration, or statistics.
- The average annual salary drawn by these managers in the US is approximately $98790. The role is therefore considered lucrative as a career option.
What does a Portfolio Manager do?
A portfolio manager is a person who specializes in the field of asset management and assists clients in handling investment portfolios. Such professionals either work individually or as a part of investment banks, mutual fund companies, insurance companies, or equity firms. These managers help investors pool their funds at the right place to get the best returns. They excel in asset allocation, always optimizing market risks. They facilitate wealth management of their affluent clients in collaboration with the investors to achieve financial targets.
We can divide the process of portfolio management into the following steps:
- Understanding the client's investment objective.
- Select the most suitable asset class or a blend of different asset classes.
- Executing strategic asset allocation and assigning the desired weightage to each asset class.
- Performing a tactical asset allocation and adjusting the asset weightage within the portfolio from time to time.
- Managing and minimizing the risk by constantly checking portfolio performance. Managers have to take corrective measures within a tight timeline. These managers use tools like Capital Asset Pricing Model, Treynor ratio, and Sharpe ratio to determine the different risks associated with the portfolio.
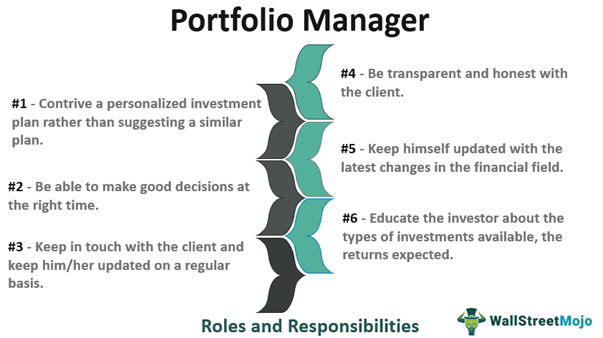
The list of functions, roles, and responsibilities of a portfolio manager are as follows:
- Deciding the best investment plan for individuals based on their preferences, age, risk appetite, income level, etc.
- Educating the investors about the types of investments available. Additionally, managers have to inform the client about expected returns and associated market risks.
- Keeping in touch with the clients and updating them regularly.
- Being unbiased, loyal, and honest with the clients.
- Prompt decision-making. Market knowledge is not of any use once the narrow window is missed.
- Being updated with the market fluctuations.
- Customizing personalized investment plans instead of suggesting the same plan to every client.
- Ensuring the best interest of the client.
A portfolio manager should possess certain qualities like problem-solving, communication, analytical ability, decision-making, and market knowledge of finance. Managers should be transparent and clarify that no matter how much planning is done, unavoidable circumstances in the financial markets can arise. Therefore, the investor has to be made capable of tackling a worst-case scenario. Investors should be prepared for mitigating the losses as well. Therefore, the manager has to plan in such a way that clients retain sufficient funds even after encountering a loss.
Types of Portfolio Manager
A portfolio manager can choose to serve the individual or an institution. The following are the prominent types of portfolio managers:

- Stock Portfolio Manager: These managers are stock market experts and help clients allocate funds in a basket of diversified securities. The selection is based on the client’s risk palate.
- Growth Portfolio Manager: Such experts actively put funds into assets having a high growth rate. However, they work for clients with a broader risk-taking ability and aim to multiply their money rapidly. The growth rate reflects increased market risks as well.
- Income Portfolio Manager: Many clients want to play safe and derive a regular income from their investments in the long run. Such clients avail the services of an income portfolio manager.
All the above-mentioned managers opt for the following investment approaches:
- Active Approach – A manager with an active approach would be aggressive and attempt to beat the market returns.
- Passive Approach – A manager with a passive approach would usually prefer to buy stocks that reflect the market performance, i.e., market index. When such an approach is followed, investors expect returns equivalent to that of the market index.
Portfolio Manager Example
The given numerical example can help us better comprehend the functions of a portfolio manager:
Franklin is a manager; he has experience managing investment portfolios and feels that he can follow a proper strategy rather than just following the market index. He is a manager following an active approach; he is aggressive and chases high-growth potential options.
Solution:
Calculation of portfolio value will be –

Based on client requirements and risk appetite, Franklin can transfer funds from one investment firm to another. In doing so, the total value of the portfolio is maintained as it is. As shown above, Franklin can alter the percentage allocation to shares, ETFs, and Closed-End Funds at any point in time. This way, he can provide better returns or avert risks.
Salary of a Portfolio Manager
Portfolio management is a trending career option among fresh graduates and management students.
In the US, portfolio managers average $98790 annually. For these managers, income ranges from $88250 to $108030.
Goldman Sachs is one of the leading investment banks in the world. They hiked the pay of their entry-level junior bankers by a phenomenal 30%. After the salary bump, the company became one of the preferred locations within investment banking. Consequently, competitors like Credit Suisse and others are lagging. Head-hunters are offered a 6% to 15% salary hike to these managers. The incomes offered to CFA candidates average around $177000.
Advantages
A portfolio manager comes with a host of advantages. These managers pivot investor’s funds in the right direction. They actualize the client’s financial goals. Not everyone is a financial expert; there is always a need for a professional expert. Someone with updated market knowledge and experience is highly recommended. These professionals balance the perfect blend of securities generating the highest income at the same time limiting the market risk.
These managers also track the long-term performance of the portfolio. They ensure that resources are put to the best possible use. Investing without professional help can be disastrous. Further, these managers predict and deal with the capital market uncertainties by devising suitable investment strategies. They improvise and make minute changes throughout the investment period. They also facilitate early withdrawals and liquidation of investments in case the client needs funds urgently.
Financial Advisor vs Portfolio Manager Differences
| Basis | Financial Advisors | Portfolio Managers |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Role | Do not support the long-term financial objectives of the client. Instead, financial advisors give suggestions based on their client’s financial situation. | Take care of the client’s financial and investment-related objectives. |
| 2. Duty | Not legally bound by a trust to serve the client’s best interests. | Lawfully bound by a trust to ensure the client’s best interests. |
| 3. Fee | Earn fees and commission based on the products sold to the client. | Receive a fee based on the percentage of assets. |
| 4. Management | At times, in order to boost sales, they feel compelled to overtrade. | Since they do not receive a commission, they don’t try to oversell non-useful products. |
| 5. Relationship with Clients | Short-term | Long-term |

