Table Of Contents
What Are Working Capital Examples?
Working capital refers to the amount the company requires to finance the day-to-day operation; an example of this includes the working capital of $100,000 with a manufacturer, which is calculated by subtracting current liabilities of $200,000 from the current assets of $300,000.
It is crucial for any business to have a steady flow of funds to meet the daily expenses and ensure smooth running of operations. It helps in meeting shorty term obligations and handle financial issues that may hinder the business process. However, it depends on the nature and size of the business model and overall industrial landscape.
Table of contents
- What Are Working Capital Examples?
- Working capital is the funds a company needs to finance its day-to-day operations and meet its current liabilities and debt obligations due within one year.
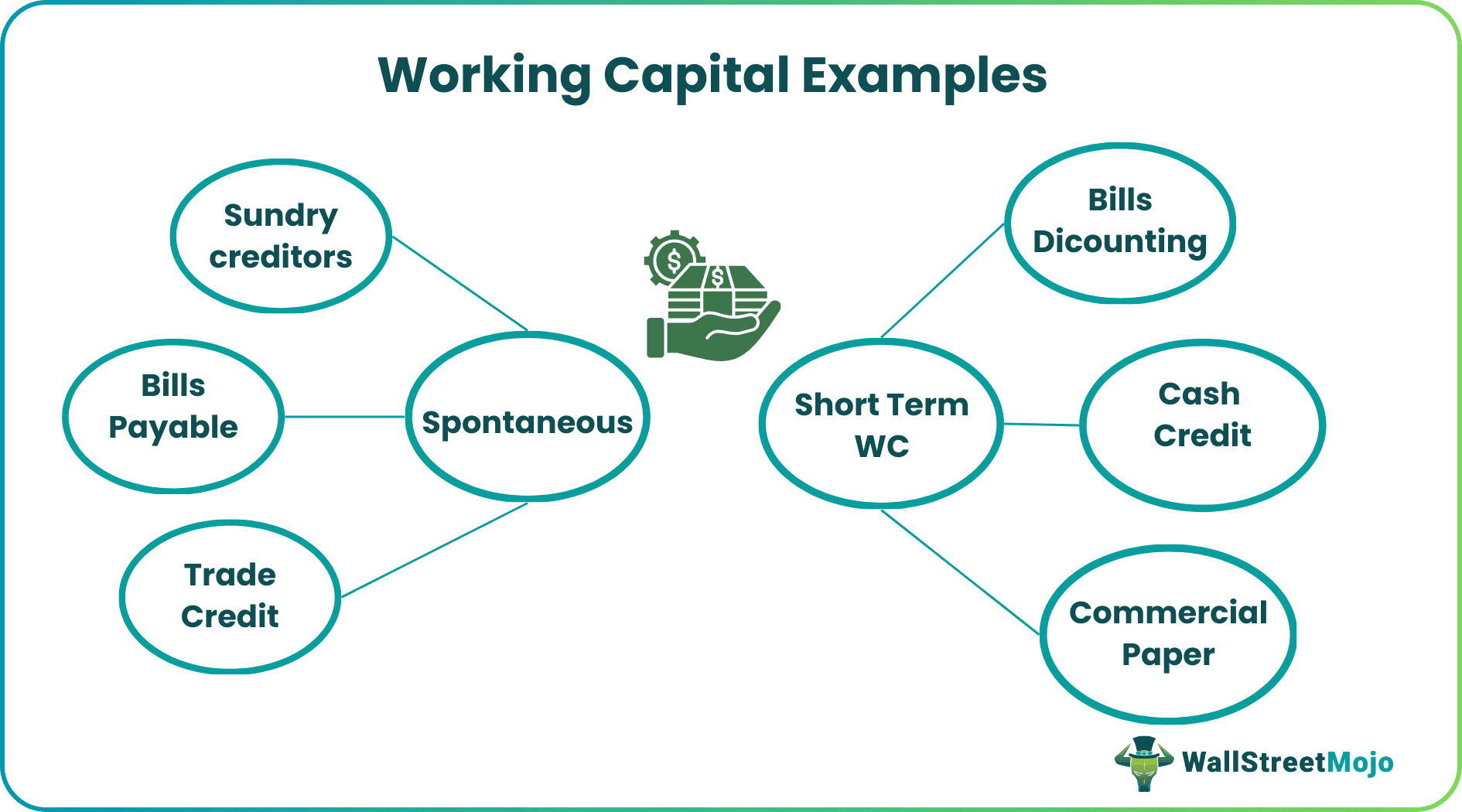
- There are various sources of working capital, including spontaneous funds such as sundry creditors, bills payable, trade credit, notes payable, and short-term working capital like bills discounting, cash credit, bank OD, commercial paper, and inter-corporate loans and advances.
- A strong working capital cycle is essential for a company to operate smoothly, while negative working capital puts the company under tremendous stress due to liquidity issues.
Working Capital Examples Explained
Working Capital refers to the Funds available to the company to meet its day-to-day business operations. It is an indicator of the Short Term Financial Strength of the Company and signifies the capability to meet the Current Liabilities and Debt Obligations due within one year. The following working capital example outlines the most common sources of working capital.
- Spontaneous: It refers to the Funds which are easily available in market
- Sundry Creditors
- Bills Payable
- Trade credit
- Notes Payable
- Short Term WC :
- Bills Discounting
- Cash Credit
- Bank OD
- Commercial Paper
- Inter Corporate Loans and Advances
It is also not advisable to lock a huge amount of Funds in the Working Capital Cycle since there is a cost attached. For example, a high Inventory will be a negative sign for the company since there is a chance of the Inventory becoming obsolete. So on paper, the WC of the Company may look Good in the Short Term; however, it may have a significant impact if the Inventory is not Sold and becomes obsolete.
Hence the company should strategically plan the Cash Flow and the minimum Working Capital required to run the business operations smoothly. There is no high amount locked in the Current Assets, or any liability is understated as this may increase/decrease the WC.
Each example of the Working Capital below states the topic, the relevant reasons, and additional comments as needed.
Calculation of Working Capital Explained in Video
How To Calculate With Examples
Let us understand the concept with the help of some suitable examples, as follows.
Example #1
Suppose ABC Limited has Current Assets of $ 5,00,000 and Current Liabilities of $ 300,000. Fixed Assets are $ 1,00,000. Long Term Debt is $1,00,000, and Short Term Debt included in the Current Liability above is $25,000. Calculate the Working Capital of the Company and analyze the same.
Solution:
Here,
- Gross Working Capital/Current Assets of the Company: $5,00,000
- Permanent Working Capital/Fixed Assets of the Company: $1,00,000
- Current Liabilities: $300,000
- Long Term Debt: $100,000
- Short Term Debt: $25,000
Calculation of Net Working Capital is as follows –

- NWC = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
- = $5,00,000 - $3,00,000
- = $2,00,000
Temporary WC will be -

- Temporary WC = NWC – PWC
- = $2,00,000 - $1,00,000
- = $1,00,000
Analysis:
In the above example of working capital, ABC Limited has a Strong Working Capital to meet its Short Term and Long Term Financial needs. However, the Current Ratio of the Company is slightly below the industry average of 2, which the company needs to improve in the future. Further Temporary WC of ABC Ltd is also positive, which is a good sign.
Example #2
Suppose ABC Limited has Current Assets of $10,00,000 and Current Liabilities of $15,00,000. Next, calculate the WC of the Company.
Solution:
In this case, the Gross Working Capital will be $10,00,000. However, the NWC of the Company would be (-$5,00,000 ) since the Current Liabilities are more than the Current Assets of the Company. ABC Limited is suffering from Liquidity Crisis due to the negative Working Capital of the Company, which will hinder Business Operations in the long term.
Such a high negative WC is a negative sign as far as the Credit Rating Agencies are concerned, forcing them to downgrade the rating by one notch if the situation does not improve.
Example #3
XYZ Limited has Current Assets of $2,00,000 and Current Liabilities of $ $90,000. Accordingly, accounts receivable of$ 75,000 included in current Assets are declared as Bad Debts and shall be written off to the Profit & Loss Account next year.
Solution:
Although the Net Working Capital is positive, i.e., $110,000 on paper, in reality, this would not be the true picture since $75,000 is considered as Bad & Doubtful of Recovery. Therefore, in the true sense, the Net Working Capital will have to be adjusted with the Accounts Receivable portion to work out the Revised Net Working Capital of XYZ Limited. This will impact the Strategic Decision making of the top management.
Example #4
PQR Limited has Current Assets of $2,00,000 and Current Liabilities of $ $90,000. Inventory of$ 1,50,000 included in current Assets has become Obsolete since the Goods have been lying in Inventory for more than six months. The Market Value of the same would be $50,000.
Solution:
In this case, the Net Working Capital of PQR Limited, as per the Balance Sheet view, would be $110,000, which is a positive for the company; however, since the Market Value of Inventories as provided in the example above has been declined to $ 50,000, this should be considered the Actual Recovery price of Inventory.
Hence the Revised Net Working Capital would be ($2,00,000 – $1,50,000 + $50,000 ) – $90,000 = $1,00,000. The management of the Company would have to sell the Inventory as early as possible in order to maintain the Liquidity.
Hence, it forms a major component for analyzing the company's financial position and comparing it with peers. A Strong Working Capital Cycle gives the Company the Cushion to perform the Company's Business operations smoothly. Conversely, a negative working capital puts the company under tremendous Stress since the company is not in the position to pay off its Day to Day obligations due to Liquidity issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Working capital refers to the short-term capital decisions of a company, which are focused on managing current assets and liabilities that can be converted to cash within a year. It is not necessarily another name for short-term capital decisions.
The working capital ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. It measures a company's liquidity, indicating its ability to meet short-term payment obligations.
Working capital can be negative when a company's current liabilities exceed its current assets and revenues. This can happen temporarily, for example, when a company makes a significant purchase, such as buying more inventory or equipment, resulting in a temporary negative working capital. However, it is not limited to purchases alone and can have various other reasons.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Working Capital Examples. Here we discuss its meaning and the various examples of working capital to understand it better. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles –
