Table Of Contents
Asset Protection Definition
Asset protection refers to a set of legal strategies that debtors preemptively implement to protect their wealth from being seized by creditors. It also enables asset owners to avoid taxation and mortgage payment default without violating the debtor-creditor law.
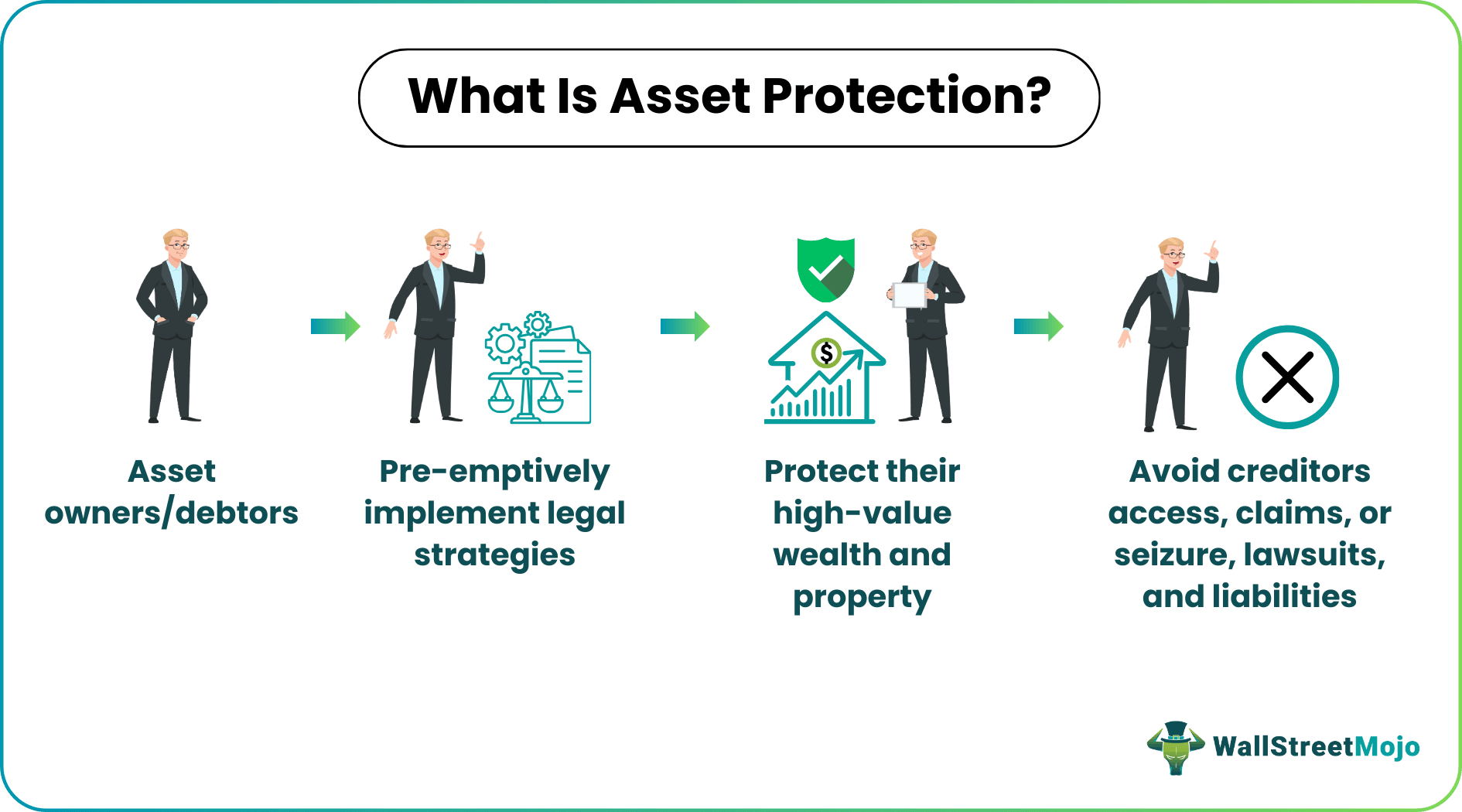
A comprehensive and preplanned protection scheme is necessary in cases involving high-value assets. With this method, individuals and businesses can protect their wealth without engaging in illegal activities like asset concealment, fraudulent fund transfer, bankruptcy fraud, and other liabilities. In short, the practice keeps creditors from accessing valuable assets of the debtor.
Table of contents
- Asset Protection Definition
- Asset protection is a legal strategy that allows the debtor to prevent creditors from accessing or seizing their valuable assets.
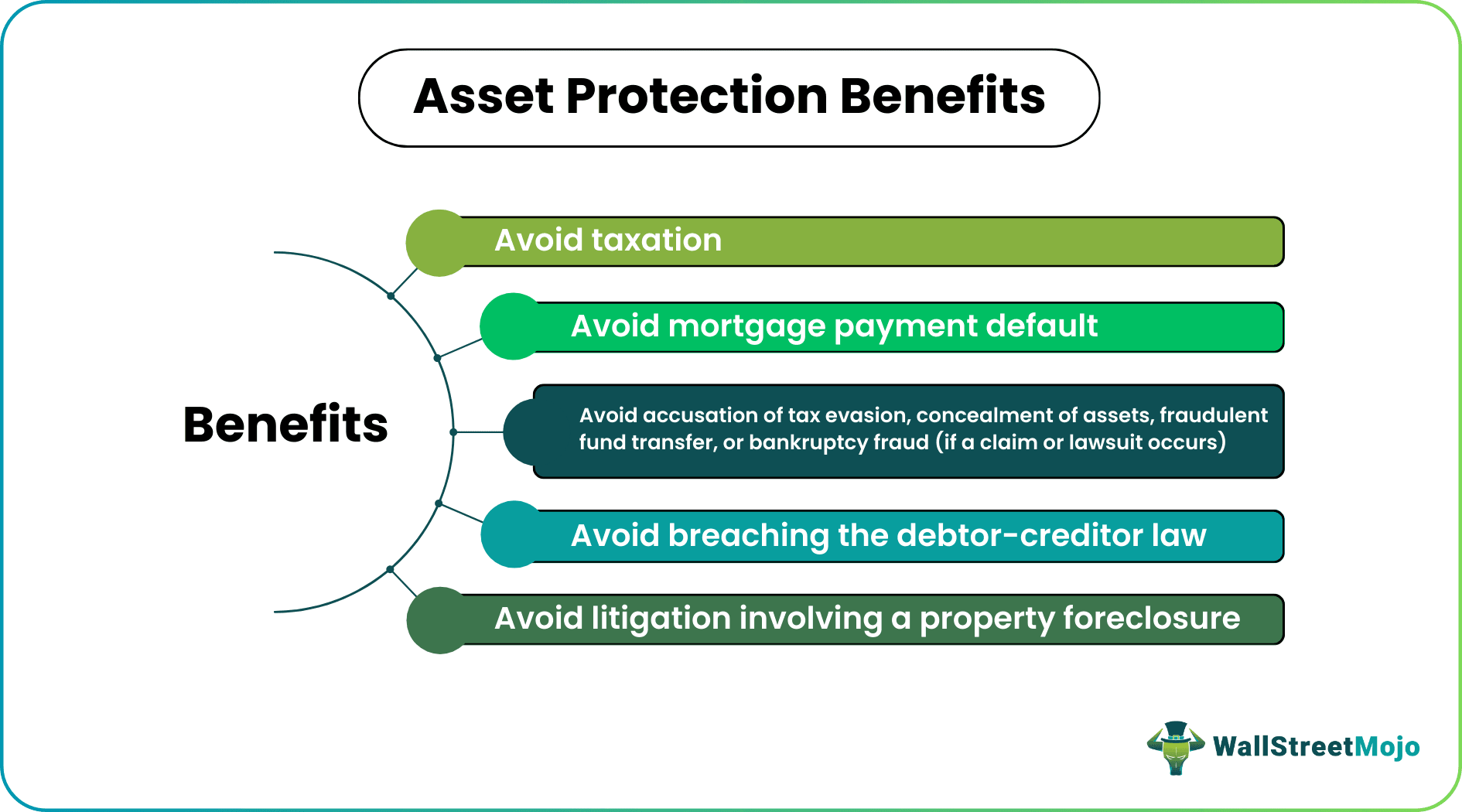
- Asset owners take this preemptive action to avoid paying taxes and other liabilities and being accused of tax evasion, concealment of assets, fraudulent fund transfer, or bankruptcy fraud if a claim or lawsuit occurs.
- It is essential to keep personal and business assets separate and establish short- and long-term financial and estate planning goals.
- Some popular asset protection strategies include limited liability companies, limited family partnerships, asset protection trusts, offshore trusts, tenancy by the entirety, and the transfer of property ownership.
How Does Asset Protection Work?
Asset protection entered the United States financial landscape by the late 1970s. However, the notion gained traction by the 2000s following the success of offshore asset protection trusts in the 1980s. Also, the introduction of regulations favoring the protection of assets by various U.S. states further aided its widespread popularity.
This method provides individual asset owners additional layers of protection for their growing wealth or property legally when they get into debt. Although the concept may seem comparable to bankruptcy, the latter is better suited for fewer assets while the former for significant funds. Business entities use this method for financial privacy and avoid seizures, lawsuits, and losses. If the court finds the creditor's claim for compensation valid, it will result in foreclosure of real estate and other assets.
At the core of each asset protection plan is the idea that creditors or the government can only take one's funds if it officially belongs to them. Under this strategy, funds move such that they do not seem directly tied to the owner. Thus, it becomes harder for the creditor to locate and seize these assets. It is worth remembering that asset owners must plan for property protection before any claim or liability.
In any case, it is vital to differentiate wealth protection from tax evasion, which the law defines as someone trying to evade taxes by not reporting their wealth or property. In the U.S., this offense can result in a five-year jail sentence, a fine of up to $100,000, or both. Unlike tax evasion, it is a legal measure. Furthermore, using third parties, special legal arrangements, or storing assets outside the country may circumvent the law and protect the funds.
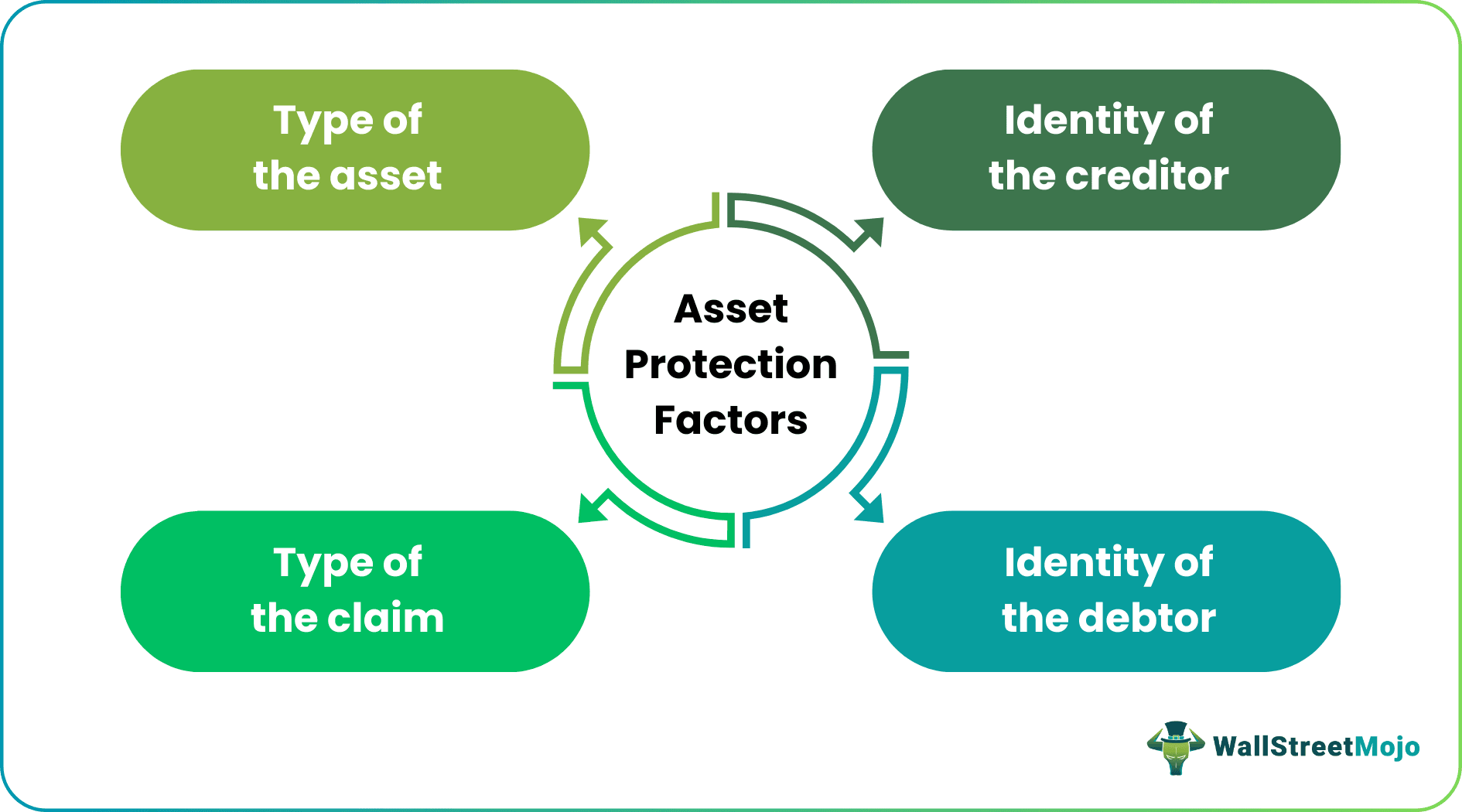
Asset Protection Factors
When it comes to protecting assets, there are four factors to consider:
Asset Protection Strategies
One must first understand the reach of the potential creditor to develop an effective asset or wealth protection strategy without infringing the law. In essence, the asset owner cannot hide any funds, but they can move them around such that it does not appear to be theirs.
It is also essential to understand risk factors while planning to protect assets. Assets like equities, commercial properties, vehicles, and manufacturing equipment pose more liability. On the other hand, assets like savings accounts, stocks, and bonds do not carry the same level of risk.
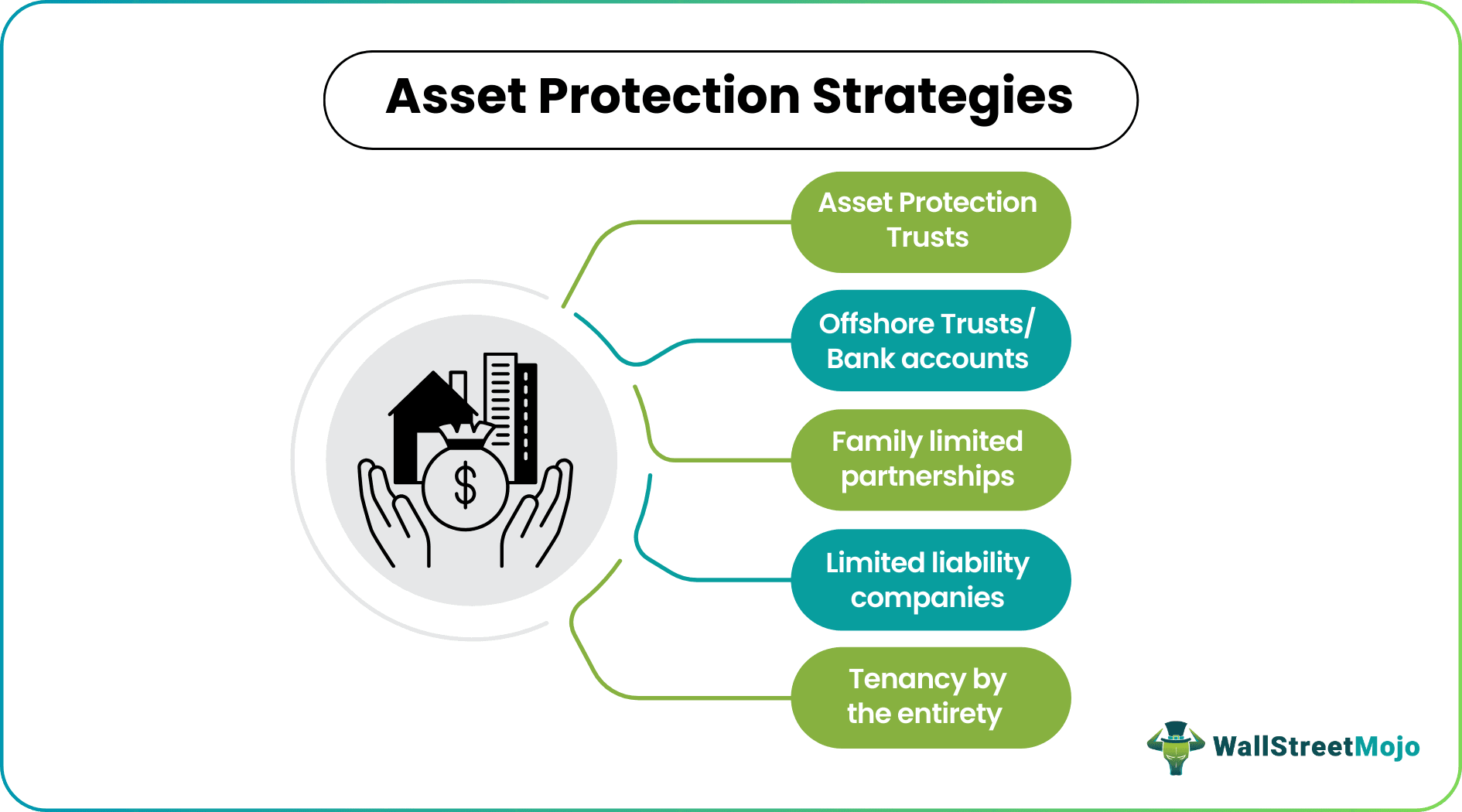
Let us look at different asset protection strategies and understand how they work:
#1 - Limited Liability Companies (LLCs)
LLCs are legally separate from their owners and thereby offer limited liability. It means that one cannot be held accountable for the company’s debt even if they are the sole owner as the firm owns all the assets. So if the debt belongs to the owner, they will not lose funds registered in the company against the creditor’s claim or lawsuit. But if the debt is tied to the company, it may lose the assets.
#2 - Family Limited Partnerships (FLPs)
FLPs provide wealth protection because they are owned by members of a family (partners) rather than a single individual and are labeled as a business. Because the business establishment has multiple owners, creditors cannot collect the assets of an FLP partner.
HOWEVER, many U.S. states consider the above two methods (LLCs and FLPs) unethical and hold business owners liable, allowing creditors to confiscate assets.
#3 - Asset Protection Trusts (APTs)
Wealthy individuals or entities transfer their funds in an APT or trust bank as a means of protection against creditors’ claims. After the transfer of the ownership, owners become beneficiaries, with control over the trust assets but no ability to revoke the trust. Since trust assets do not belong to the owner, creditors cannot claim them. Although the owner will not lose the assets, they cannot use them either. APTs also provide tax benefits to the owner.
#4 - Offshore Trusts /Accounts
This arrangement allows debtors to own and register their property outside their native country. Likewise, they can open savings accounts and make deposits in offshore banks. Both strategies may help the debtor to avoid taxation. Even if assets are in another country, the owner will still be subject to the laws of their home country. Repatriation orders may make them return the property to their native country or face judicial trials.
#5 - Transfer Of Property
Owners may also consider transferring assets to their heirs (family members, relatives, or friends) to protect them from creditors’ claims. This way, the assets will not be directly tied to the owner. However, be warned that this is a high-risk method. One should only transfer assets to those they trust, or they may lose all the funds.
Although the heir becomes the new owner, the actual owner can still use the property. Thus, creditors have a tough time determining who owns the property and seizing it. However, many U.S. states consider the property transfer fraudulent and regulate it.
Tips For Asset Protection
Wealth protection is a way to avoid litigation involving a property foreclosure or a mortgage payment default. Although the above strategies are beneficial, the asset owner or debtor must use them effectively. For instance:
- Making a comprehensive asset protection plan before a claim or liability, or lawsuit occurs.
- Understanding regulatory or judicial oversight post a claim or liability or lawsuit.
- Late planning can result in the court accusing the asset owner of trying to hide assets.
- The debtor may even be charged for tax evasion and arrested in the worst-case scenario.
- It is crucial to take the extra step to ensure that personal assets are separate from business assets. It is because personal assets put into a business entity have more risk of being claimed by creditors.
- Avoid acting as sole owner/proprietor. Instead, putting assets under someone else's name and using a registered business entity.
- Determining short- and long-term financial and estate planning goals.
- Having a commercial insurance policy to avoid legal costs in case of lawsuits.
Asset Protection And Real Estate
Real estate asset protection operates on the same principles as other assets. In short, the owner needs to avoid holding assets under their name because creditors can only seize what the debtor owns. The three essential ways to protect real estate are:
- Having a property under tenancy by the entirety
- Putting the property in someone else's name
- Creating an LLC
The last two options have already been discussed above. So, let us focus on the first method:
The term ‘tenants by entirety’ refers to an arrangement allowing a couple to own the property jointly (as a single entity) rather than an individual. Mutual ownership prohibits creditors of both spouses from force selling the property. The reason is that the couple does not own 50% of the property but both own 100% of it together. Thus, creditors cannot take the asset unless the debt belongs to both property owners. If both renters are in debt, an APT may be a better option for keeping the property in their possession.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Asset or wealth protection strategies safeguard personal and business assets from getting claimed by creditors and the government in case of lawsuits, accountability risks, claims, settlements, etc. Planning can protect the debtor from being accused of tax evasion, concealment of assets, fraudulent fund transfer, or bankruptcy fraud.
Individuals and businesses can shield their assets from creditors' claims using legal measures like limited liability companies, limited family partnerships, asset protection trusts, offshore bank accounts, tenancy by the entirety, and the transfer of property ownership.
Yes, it is a set of legal strategies meant to protect the debtor’s assets from being claimed or seized by the creditor without engaging in illegal activities like fraudulent money transfer, asset concealment, tax evasion, etc.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is Asset Protection & its Definition. Here we discuss asset protection strategies and how it works, along with tips and factors. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –
