Table Of Contents
Asset Stripping Definition
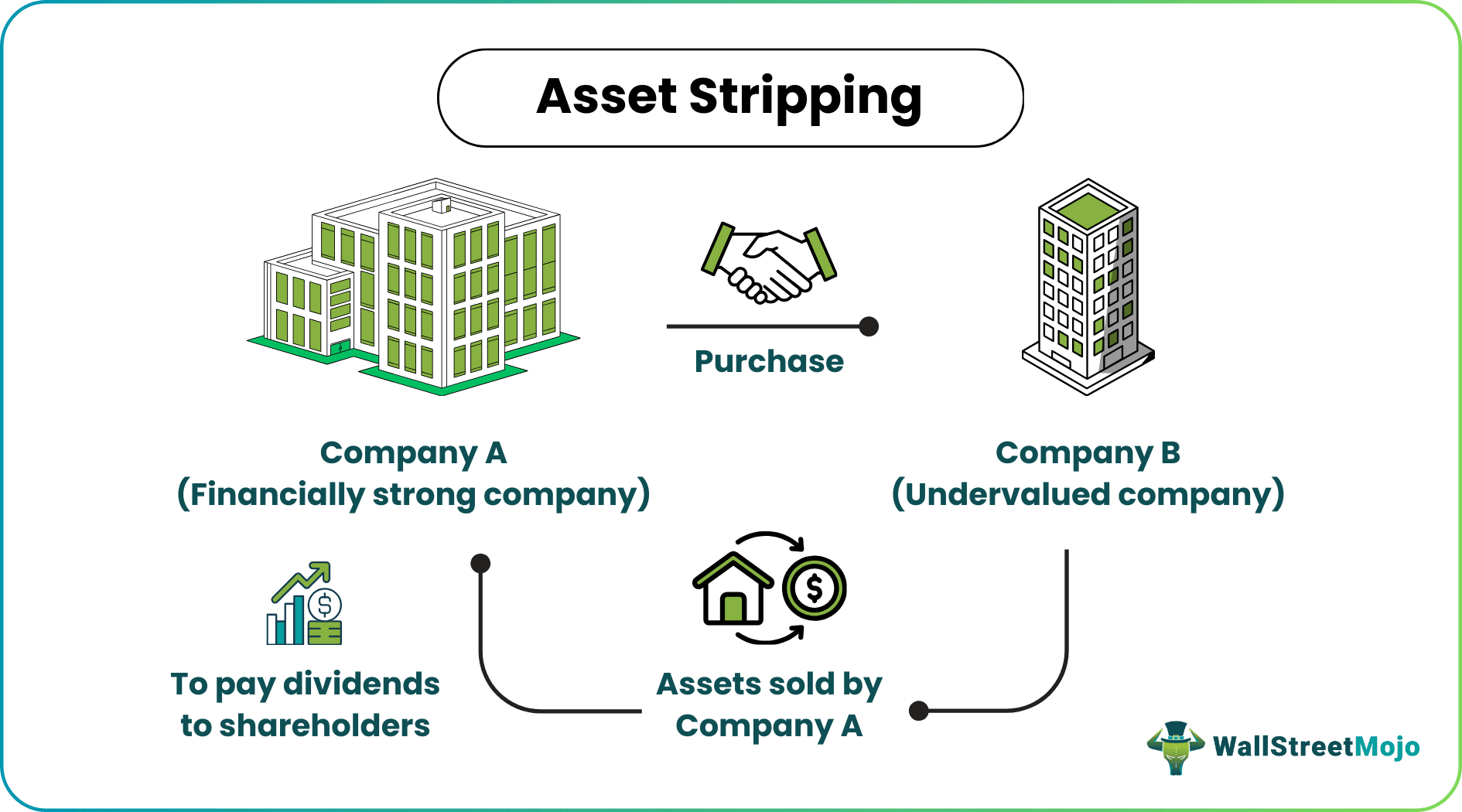
Asset Stripping is the process of selling a company's assets to generate dividends for the shareholders. It mostly happens when the company's value is less than the combined value of assets. So investors generate profit by selling the assets individually and generating dividends for the shareholders.
When asset Stripping is done, mostly the assets with economic value are sold. So if a company loses its economic assets, it makes the company weaker as it loses its assets, so it gets difficult for the company to raise more debts via collateral. The company gets weakened, so the debt charges increase as the company is prone to bankruptcy now.
Table of contents
- Asset Stripping Definition
- Asset stripping sells a company's assets to generate dividends for shareholders when the assets are worth more than the company itself. The investors can sell the assets separately for profit and pay dividends to shareholders.
- Improperly managed companies are at risk of asset stripping, which is why managers must use assets efficiently and work optimally to protect themselves from this threat.
- Private equity firms often engage in asset stripping, which can harm the target even if it's profitable for investors. Governments have regulations to prevent this.
Asset Stripping Explained
Asset Stripping is mostly done on undervalued companies. When an investor sees that a company is undervalued in the market, they try to value the company's Real Assets in the market. Once the value of the assets is determined, it is seen that the value of the individual assets is worth more than the company as a whole. Then the asset stripping companies buy the undervalued company and sell off the assets individually in the market. The cash generated from the sale is distributed as a special dividend to the shareholders.
- Step 1: Private Equity firms engaged in Asset Stripping practices look for undervalued companies with a strong asset base. Companies can be undervalued due to a lack of good management or other reasons.
- Step 2: The Private Equity firm looks for a market where it can sell the assets reasonably. Assets can be sold at a higher value when you get a strategic buyer, a person looking for a particular asset to do the production.
- Step 3: The value of the assets in the market is determined. Then if the value of the assets is more than the company's value as a whole, the process of acquiring the company begins.
- Step 4: Most of the acquisition is made by issuing debt. These are called Leveraged Buyout.
- Step 5: Once the company is bought, the assets are sold to the strategic buyers, and the money generated is used to repay the debt, and the rest is paid to shareholders as a Special Dividend.
History
Carl Ichan, Victor Posner, and Nelson Peltz were investors in the 1970s to 1980s. They started Asset Stripping as a practice to generate profit. Carl Icahn did a hostile takeover of “Trans World Airlines” in 1985 and sold its assets to pay for the debts of the takeover.
Example
Asset Stripping nowadays is primarily being performed by Private equity firms. It is a good way of generating profit for the investors but destroys the target. So, in many countries, government regulations must be followed before applying such strategies.
Let us understand the concept of asset stripping companies with the help of a suitable example.
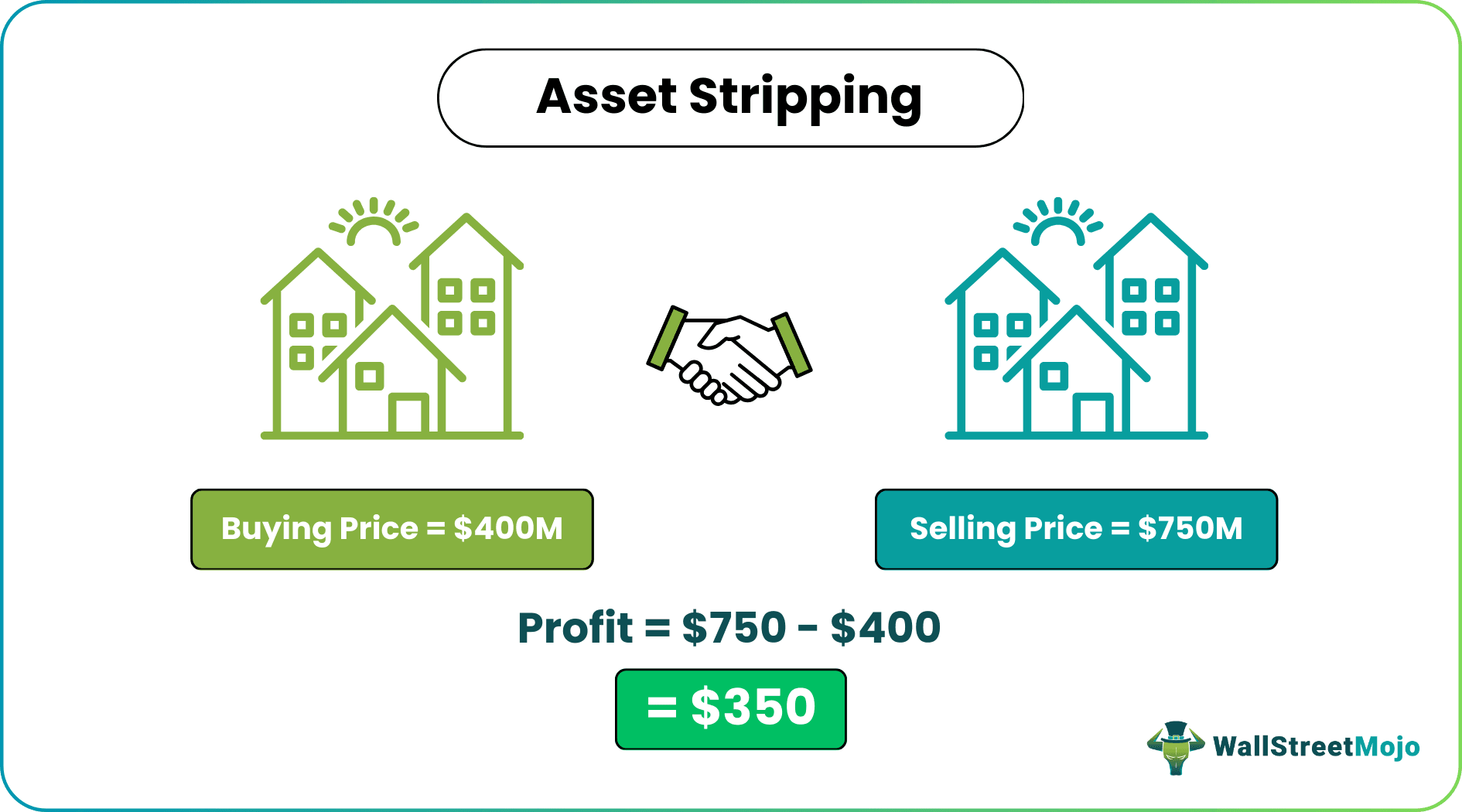
Company A has five different businesses. Due to the current poor economic scenario caused by COVID-19, the company is trading below its Book Value. A private equity firm, which is engaged in Asset Stripping, starts to evaluate the company's businesses. He found that the company's worth now is $400M, but each business separately can be sold at $150M once the COVID-19 fear gets over. So the private equity firm acquired the undervalued company at $400M.
Solution
When the COVID-19 is over and the market recovers, the Private equity firm will sell individual businesses at $150M each.
Total selling price = $150M * 5 (As there are five businesses and each can be sold @$150
= $750M
Profit = Selling Price – Buying Price
- = $750M - $400M
- = $ 350
Percentage of Profit = (Profit / Initial Investment) * 100
- = (350 / 400) * 100
- = 87.5%
So private equity firms make huge profits through Asset Stripping. The main challenge is to find the potential buyer for the assets. Private equity firms are engaged in this kind of business for the long term, so they have contacts worldwide, and it is easier for them to sell assets at a reasonable price.
Opportunities
Most Private Equity firms are engaged in Asset Stripping; they are continually looking for targets. Not all companies in the market are efficiently managed. Some companies are managed inefficiently. That is, the assets are not put to optimal usage. When a particular company is not managing assets properly, they trade below their book value. In severe economic conditions like COVID-19, companies tend to be severely undervalued, which is the perfect asset-stripping opportunity. Undervalued companies will be bought through asset stripping acquisition and sold part-wise for greater profit when the economic condition improves.
Advantages
The concept helps the acquirer generate immediate cash flow and lead to gains from short term investments. How ever, it has both advantages and limitations. Let us look at the advantages first.
- Shareholders who were suffering due to low share prices get their money back in a special dividend.
- Asset stripping is a threat to improperly managed companies. So managers tend to utilize the assets efficiently and manage companies optimally to save themselves from such situations.
- Asset stripping acquisition leads to an immediate inflow of money that can be used to meet financial obligations, invest in profitable ventures, and boost liquidity.
- If the acquirer is able to sell the assets at a profit, then there is substantial gain.
- It can divert the attention of the management from assets that are not so profitable and develop assets and investments that will lead to higher return. Thus, there is a shift of focus to primary operations of the business.
- The acquirer may be able to unlock potential valuable assets that will fetch good profits if extracted and sold.
Criticism
- Asset Stripping breaks a company into several parts, thus creating unemployment. Employees lose their jobs once the parts are sold to different buyers.
- It is a loss for the economy as the company could have turned with proper management and with the change in the economy, but it loses its value and slowly reaches bankruptcy due to asset-stripping.
- Since it focusses more on short term financial gains, and not on long term value, it may lead to adverse results for stakeholders who plan to invest on the business on a long term basis.
- Suppose the management cannot make the correct decision regarding the asset sale and ends up selling off an essential part of the business. In that case, it may lead to a loss of sales, revenue, or market reputation. The company may lose its customer base and competition.
- There may be some legal issues or problems related to rules and regulations because quite often companies indulge in asset stripping in order to delay loan payment, avoid any other short or long term payment obligation stating that business is selling off assets due to fund crunch etc.
- Following this process aggressively may result in fall of good reputation of the business in the market and may create a negative idea about the financial condition in the stakeholders’ minds.
- Thus, it may offer financial help to the acquirer immediately. But is also has its own share of risk and ethical concerns in the business. It may result in financial problems for the acquired company and affect the image of the acquirer and its stakeholders. It is important that the business takes informed decision regarding the same.
Thus, it may offer financial help to the acquirer immediately. But is also has its own share of risk and ethical concerns in the business. It may result in financial problems for the acquired company and affect the image of the acquirer and its stakeholders. It is important that the business takes informed decision regarding the same.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The asset stripping approach is considered fraudulent and can lead to severe punishment from the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA). In this method, corporate raiders acquire a company through hostile means, transfer its assets to their name, and subsequently liquidate the struggling firm.
Asset stripping can weaken a company by reducing its collateral for borrowing and removing value-producing assets, making it less capable of supporting its debt.
Various countries have regulations and laws to prevent abusive or fraudulent asset-stripping practices. These may include restrictions on asset sales, disclosure requirements, and oversight by regulatory bodies to ensure a fair and transparent transaction.
Many private equity firms engage in asset stripping, always searching for potential targets. However, not all companies in the market are managed efficiently, meaning that their assets are not being utilized to their full potential.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Asset Stripping and its definition. We explain it with example, history, opportunities, advantages and criticisms. You may learn more about financing from the following articles –
