Table Of Contents
What Is A Currency Swap?
A currency swap is an agreement between the two parties involved in the exchanging of notional amounts in one currency with that of another currency. It is useful for hedging the risks associated with interest rates, which can be fixed or floating rates denominated in two currencies.
Currency swap agreements are valid for a specified period only and could range up to a period of ten years depending on the terms and conditions of the contract. As the exchange of payments takes place in the two different types of currencies, the spot rate prevailing at that time is used for calculating the amount of payment.
Table of contents
- A currency swap refers to a financial arrangement between two parties to exchange a sequence of cash flows in distinct currencies over a designated timeframe.
- Currency swaps are widely employed by corporations, financial institutions, and governments to mitigate foreign exchange risk, secure advantageous financing conditions, or obtain access to foreign currencies.
- Within a currency swap, the involved parties agree to swap the principal amount and periodic interest payments in different currencies, typically based on a predetermined exchange rate.
- Currency swaps offer several benefits, including reducing transaction costs, enhancing liquidity management, and providing greater predictability in cash flows for international transactions.
Currency Swap Explained
The currency swap is the agreement between the two parties for exchanging the currencies at the terms and conditions predetermined between each other. The main motive of the currency swaps is to avoid various risks and turbulence in exchange rates and foreign exchange markets. Governments and the Central banks engage in currency swaps with their foreign counterparts in order to ensure that adequate foreign currency is available at the time if there is any foreign currency scarcity.
There are three stages that form part of the currency swap. It includes spot exchange of the principal, Continuing exchange of the payment of the interest during the swap terms, and Re-exchange of the principal amount on the date of maturity.
The principal sum in a currency swap is usually exchanged by the parties in one of the following manners:
- At the start
- During the combination of the start and the end
- At the end
- Neither
Types
The classification can be done on the basis of different types of leg involved in the contract; the most common types are listed below
#1 - Fixed vs. Float
In this type, one leg represents the stream of payments for the fixed interest, while another leg represents the stream of payments for the floating interest.
#2 - Float vs. Float (Basis Swap)
This type is also known as the basis swap, where both legs of the swap represent the payments of floating interest.
#3 - Fixed vs. Fixed
In this type, both the stream of the swap represents the payments of fixed interest.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the currency swap meaning better:
Example 1
Suppose US-based Company A wants to expand its business venture in the United Kingdom and UK-based Company B has similar plans of expanding its business in the United States. As both companies face a shortage of finances, they borrow money from their own countries instead of the nations they want to expand their business to. This is given the lower interest rates. Later, they involve in a currency swap agreement to proceed further and swap a series of payments in one currency with those in another currency.
Example 2
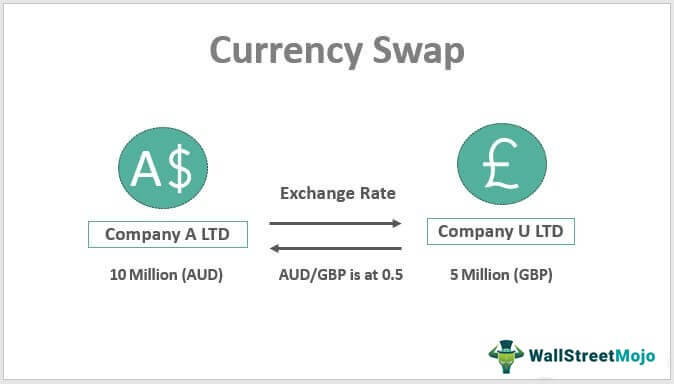
Suppose there is an Australian company named A Ltd., who is thinking of setting up the business in another country, i.e., the UK, and for that, it requires GBP 5 million when the exchange rate AUD/GBP is at 0.5. So that the total required amount in AUD comes to AUD 10 million. At the same time, there is a company U Ltd based out of the UK, that wants to set up a business in Australia, and for that, it requires AUD 10 million. Both companies need loans for the six-monthly repayments. In both countries, there is a high loan cost for foreign companies as compared with the local companies, and at the same time, it is also difficult to take a loan from foreign companies due to the extra procedural requirements.
The cost of a loan in the UK for foreigners is 10%, and for locals, it is 6%, whereas in Australia, the cost of the loan for foreigners is 9% and for locals is 5%. Since both the companies can take the loan in their home countries at a low cost and easily, both decided to execute the currency swap agreement where A Ltd took a loan of AUD 10 million in Australia, and U Ltd took a loan of GBP 5 million in the UK and gave their amount of loan received to each other which enabled both of the firms to start their business in another country.
Now, after every six months,
A Ltd. will pay the interest portion to U Ltd for the loan taken in the UK by U Ltd which is calculated as follows:

U Ltd. will pay the interest portion to A Ltd for the loan taken in Australia by A Ltd, which is calculated as follows:

This payment against the interest will continue till the end of the currency swap agreement when both of the parties give back to the other parties, their original foreign currency amounts are taken.
Advantages & Disadvantages
Currency swap is both beneficial and risky for investors or market managers. Let us take a quick look at both:
Pros
- It helps the portfolio managers in regulating their exposure to the rate of interest prevailing.
- It helps in reducing the different costs and risks which are associated with currency exchanges.
- Based on the existing economic situations, It helps the companies which are having fixed-rate liabilities in capitalizing on the floating-rate swaps and the companies which are having floating-rate liabilities in capitalizing on the fixed-rate swaps.
- Speculators in the market can get benefit whenever there is any favorable change in the rate of interest.
- It helps in reducing uncertainty, which is associated with future cash flows because the currency swap allows the companies to change their debt conditions.
Cons
- Since any of one party or both of the parties can default on the payment of interest or the principal amount, the currency swaps are exposed to the credit risk.
- There is a risk of the intervention of the central government in exchange markets. The same happens in case the government of a particular country acquires a huge amount of foreign debt in order to support their country’s declining currency temporarily, which can lead to a huge downturn in the domestic currency’s value.
Currency Swap Vs FX Swap Vs Interest Rate Swap
A currency swap and Forex swap sound similar and help hedge the risks arising from the change in the currency exchange rates. Hence, they appear to be confusing to investors. Here is a list of differences that one must be aware of before involving in the swap agreement:
- The former refers to an agreement where the parties involved swap a series of payments, including the interest, in one currency with a series of payments in another currency. On the other hand, an FX swap occurs when one party agrees to buy/sell a specific amount of a currency at a specific rate and another party agrees to sell/buy the same amount of a currency at a mutually agreed rate.
- In short, the former is an arrangement where the two parties take up loans and exchange the principal and interest payments. The latter, on the contrary, involves the exchange of a specific amount of one currency with an equivalent amount of another currency.
Currency swap also differs from interest rate swap, which the former often gets confused with. Thus, investors must explore the differences to make sure they are making a well-informed swap deal decision:
- While a currency swap is the swapping of the series of payments that two parties are supposed to make for their loans in each other’s native currency, interest rate swaps involve the exchange of payments with two different interest rates.
- The former is the foreign exchange agreement, the latter is the derivative contract.
- The former involves the exchange of amount in one currency to another currency, the latter involves the exchange of interest payments between the parties involved.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A currency swap differs from a traditional loan in several ways. Firstly, in a currency swap, two parties exchange principal amounts in different currencies and agree to reverse the exchange later. It essentially involves borrowing and lending in different currencies simultaneously. Unlike a traditional loan, currency swaps allow parties to access foreign currency funding without directly borrowing from the market. Additionally, currency swaps often involve fixed interest rates, whereas traditional loans may have variable interest rates.
Currency options provide the right but not the obligation to buy or sell a currency at a predetermined price within a specified period. In contrast, currency swaps involve the exchange of principal and interest payments in different currencies between two parties. While both options and swaps are used for hedging against currency risk, their structure and purpose differ.
Negotiation between the parties involved determines exchange rates in a currency swap. Typically, the parties agree on an exchange rate at the beginning of the swap, known as the swap rate. The swap rate reflects the prevailing market rates and the interest rate differentials between the two currencies.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to what is Currency Swap. We explain the concept with examples, types, vs FX swap, advantages & disadvantages, vs interest rate swap. You can learn more about accounting from the following articles –
