Table Of Contents
What Is A Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM)?
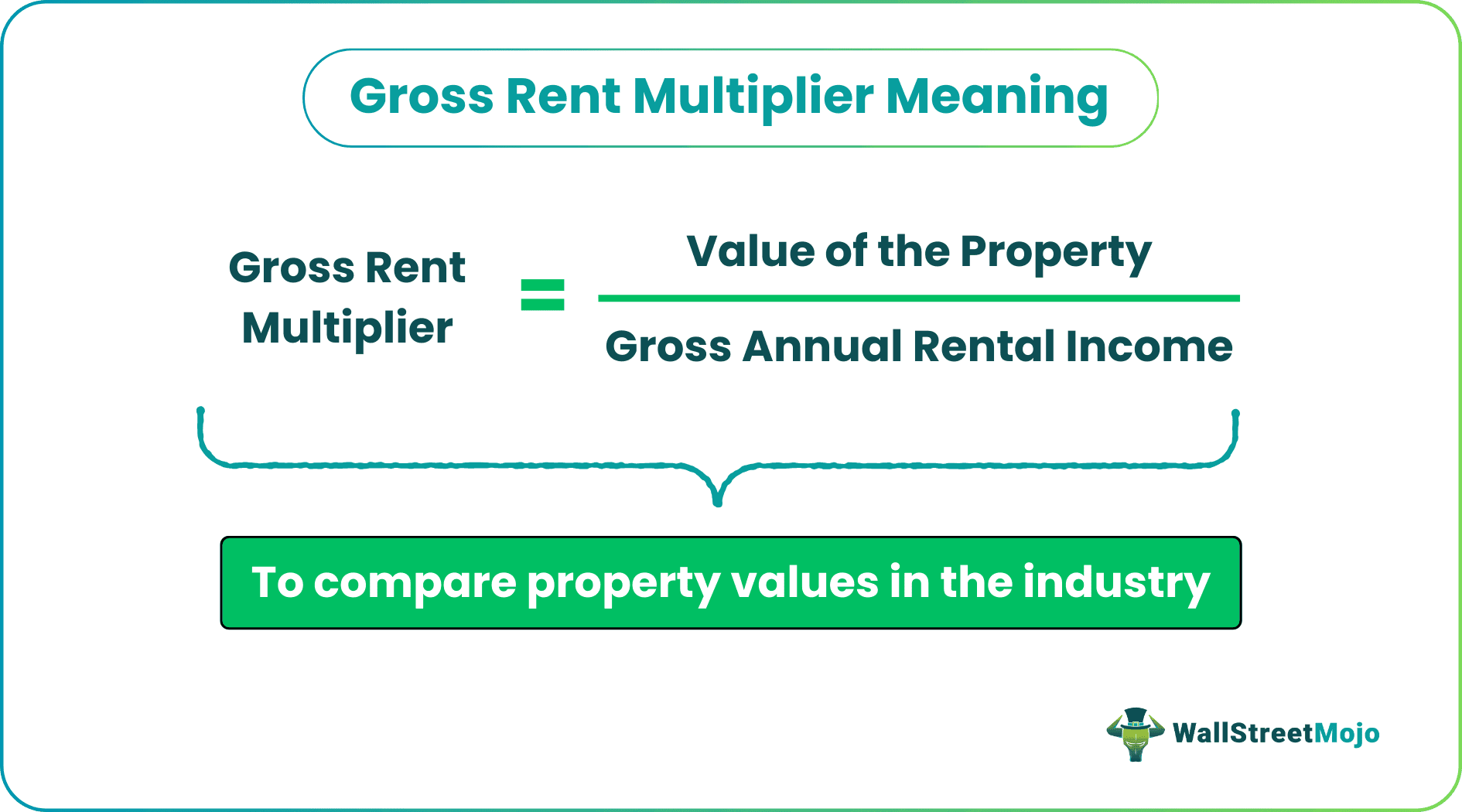
Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM) is a real estate valuation metric calculated by dividing a property's sale price by its gross annual rental income. The purpose of GRM is to provide investors with a quick and simple method to estimate the value of an investment property based on its income.
It is crucial for real estate investors as it quickly gauges a property's value by relating the sale price to annual rental income. GRM serves as a rapid assessment tool, allowing investors to make informed decisions on property affordability and income potential, aiding in efficient comparisons and initial evaluations of the commercial real estate sector.
Table of contents
- What Is a Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM)?
- Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM) is a real estate metric used for quick property valuation, calculated by dividing the property's market value by its gross annual rental income.
- GRM focuses on emphasizing the relationship between property value and gross rental income. In contrast, the cap rate focuses on evaluating the rate of return based on net operating income and considers operating expenses.
- GRM is useful for quick comparisons and initial screening of investment opportunities and is commonly applied in residential real estate for affordability assessments.
Gross Rent Multiplier Explained
Gross rent multiplier is a fundamental tool in real estate valuation, which states the ratio between the price of a property and its gross rental income. It offers a swift and practical means for investors to gauge a property's value based on its rental income potential.
Valuing an investment property is a crucial step for any investor entering the real estate market. Unlike stocks, determining the worth of real estate involves various factors, with income generation often deemed more significant than appreciation. Thus, the GRM is a valuable metric in this context, widely employed by professional real estate investors and industry experts.
The GRM ratio provides a quick and rough estimate of a property's value, offering insights into its income potential relative to its cost. In addition, for real estate investors, prioritizing income over appreciation aligns with the income-centric nature of rental properties, emphasizing the importance of consistent cash flow.
The GRM is comparable to the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio used in the stock market to evaluate companies. Thus, it serves as a counterpart for real estate. In other words, investors utilize GRM to make initial assessments of whether a property's asking price represents a sound investment. Here, a lower GRM suggests a potentially better deal. It indicates that the property's price is lower relative to its income-generating capacity.
While GRM provides a quick snapshot, investors often combine it with other valuation methods, such as the capitalization rate (cap rate) and discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, for a comprehensive understanding. In other words, this multi-method approach allows investors to account for various aspects of a property's financial performance and market conditions.
Formula
The steps to calculate the gross rent multiplier are as follows:
The gross rental multiplier is a straightforward metric that requires only two inputs for calculation:
- Property Value (Fair Market Value): This is the current market value of the property, typically represented by the ask price at which the property is available for purchase.
- Gross Annual Income: This refers to the estimated total rental income that the property is expected to generate within a year.
One can calculate the gross rent multiplier using the following formula:
GRM= Sale Price/Gross Annual Rental Income
Thus, the resulting ratio provides a quick estimate of the property's value relative to its income, helping investors in their initial assessments of real estate investments.
Examples
Let us look at the gross rental multiplier calculation examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
Suppose Jim has a real estate property that he is renting out.
Property Value= $300,000
Gross Rental Income=$30,000
Now, applying the Gross Rental Multiplier (GRM) formula:
GRM= Property Value\Gross annual rental Income
GRM= 300,000\30,000
= 10
In this example, the GRM is 10. This means that, based on these figures, it would take approximately 10 years of gross rental income to cover the cost of the property. Thus, GRM provides a quick snapshot for investors to assess the relationship between property value and rental income, aiding in comparative evaluations of different investment opportunities.
Example #2
Imagine a residential property listed for sale at $400,000. The property has two rental units, and depending on the local rental market, one can estimate it to generate $40,000 in gross rental income annually.
In this scenario, investors looking at this property might assess its potential by considering how the property value aligns with the expected rental income. Thus, the gross rental multiplier conceptually represents the relationship between the property's value and its income potential, offering a quick and intuitive way for investors to gauge the investment's viability.
Gross Rent Multiplier vs Cap Rate
The differences between the gross rent multiplier and cap rate are as follows:
| Gross Rent Multiplier | Cap rate |
|---|---|
| GRM is primarily a ratio that evaluates the relationship between the property's market value and its gross rental income. | Cap Rate assesses the rate of return on an investment property based on its net operating income (NOI) relative to its market value. |
| GRM is calculated by dividing the property's market value by its gross annual rental income. | Cap Rate is calculated by dividing the property's net operating income by its market value. |
Gross Rent Multiplier vs Gross Income Multiplier (GIM)
The differences between gross rent multiplier and gross income multiplier are-
| Gross Rent Multiplier | Gross income multiplier (GIM) |
|---|---|
| It emphasizes the relationship between the property's value and its rental income. | It offers a broader perspective by considering all forms of gross income, not solely rental income. |
| GRM is commonly used in residential real estate and provides a quick estimate of the number of years it would take for the property's gross rental income to equal its purchase price. | GIM is often applied in commercial real estate, where income streams can be diverse. It aids investors in assessing the property's value relative to its overall income-generating potential. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Commercial Gross Rent Multiplier (CGRM) is a real estate metric used in commercial property valuation, similar to the residential Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM). It provides a quick estimate of the relationship between a commercial property's market value and its gross rental income.
The Monthly Gross Rent Multiplier (MGRM) is a variation of the Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM). It provides a quick estimate of the relationship between a property's market value and its gross monthly rental income.
The Monthly Gross Rent Multiplier formula is as follows
MGRM= Property Value/ Gross Monthly Rental Income
In this formula, property value is the market value of the property, and gross monthly rental income is the rental income per month.
The Gross Rent Multiplier (GRM) finds use in real estate for several purposes- it finds common application in quick comparisons of different properties, offering a simplified indicator of affordability and investment potential, particularly in residential real estate. GRM, calculated by dividing property value by gross annual rental income, provides a rapid initial screening tool for investors.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is Gross Rent Multiplier. We explain its formula, comparison with cap rate and gross income multiplier, and examples. You may also find some useful articles here -
