Table Of Contents
What Is Tax Deferred Annuity?
A tax-deferred annuity is an employee retirement benefit plan where both an employer and its employee contributes to the saving plan for the purpose of long term investment growth and it offers various benefits like age 50 plus catch up, lifetime catch up, taxes and investment options.
A deferred Tax Annuity plan is a kind of investment plan where income tax on investment income is not charged during the investment term, and any tax liability thereof is postponed until maturity.
Key Takeaways
- A Tax-Deferred Annuity (TDA) is a financial product that allows individuals to save for retirement while deferring the payment of taxes on investment gains and income until withdrawal.
- TDAs are typically offered as retirement savings options through employer-sponsored plans, such as 403(b) plans for employees of non-profit organizations or 457 plans for government employees.
- Contributions to a TDA are made pre-tax, meaning they are deducted from the individual's taxable income for the year, potentially reducing their current tax liability.
- While TDAs offer tax advantages during the accumulation phase, withdrawals from the annuity are generally subject to ordinary income tax, and early withdrawals before age 59½ may incur additional penalties.
Tax Deferred Annuity Explained
A tax deferred annuity mentioned under Section 403(b) of the Internal Revenue Code, is a contract between the investor and an insurance company in which the insurance company receives money from an investor and pays interest on a predetermined rate for a fixed period.
The investor enters into this contract to save money for the future. The investor receives a tax benefit for the contract period in the form of tax-deferred earnings. Income from this contract will be taxed as ordinary income on the withdrawal of money. On the death of the investor, the money will be received by the beneficiary and taxable in the hands of the beneficiary.
Tax Deferred Annuity offers a big advantage as the tax is not to be paid immediately. This is the reason why it is also called a tax-sheltered annuity. This type of annuity is of two types, the first single payment annuity and the second is a series of payment annuity. In a single-payment annuity, a one-time payment is made by the investor, whereas, in a series of payments, annuity payments are made at equal intervals.
- A tax-deferred annuity plan is generally used to manage by Insurance companies.
- Many types of annuities exist in the market with different features and benefits.
- As per the Statutory rules till the age of 59.5, investors cannot withdraw money if the investor does so, then penalty may be imposed for before withdrawal.
- The interest amount accumulates and tax-deferred until the investor receives the money.
- Some companies give an option to their employees to contribute to a tax-deferred annuity plan from their salary for their Long term growth.
Formula
Given below is the formula to calculate deferred tax annuity.
Tax-Deferred Annuity = A* / i
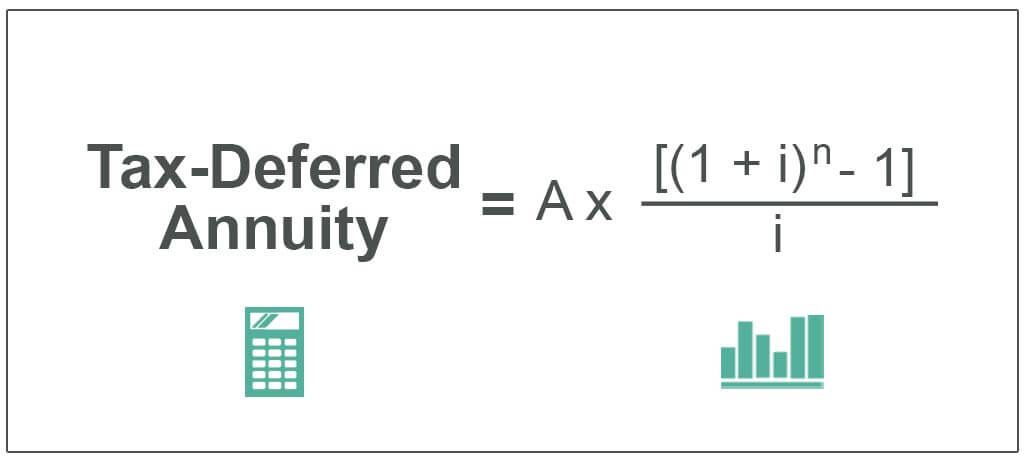
- A = Amount
- i = Interest Rate
- n = Number of Payments
Examples
Given below are the examples that make the deferred annuity definition and its calculation clearer:
Example #1
Mr. Y initiated a deposit from his employer of $ 500 per month starting at the age of 55 until Mr. Y retired, say retirement age is 65. If the interest rate is 3% compounded monthly, what will be the value of the annuity at the end of 10 years?
- Amount (A): $500
- Interest Rate (i): 0.0025
- Number of Payments (n): 120
Here, i = 3% / 12 = 0.0025
n = 12*10 =120
The calculation of annuity value is as follows –

- Deferred Tax Annuity = $500*(1+0.0025)120 - 1 /0.0025
- =$69,870.71
Thus, the annuity at the end of 10 years of Mr. Y will be $ 69870.71/-
Example #2
Mr. Pawan initiated a deposit from his employer of $ 3000 quarterly starting at the age of 50 until Mr. Pawan retired, saying his retirement age is 60 years. If the interest rate is 6% compounded quarterly, what will be the value of the annuity at the end of 10 years?
- Amount (A): $3,000
- Interest Rate (i): 0.015
- Number of Payments (n): 40
Here, i = 6% / 4 = 0.015
n = 4*10 = 40
The calculation of annuity value is as follows –

- Deferred Tax Annuity = $3000*(1+0.015)40- 1 / 0.015
- =$162,804
Thus, the annuity at the end of 10 years of Mr. Pawan will be $162,804/-
Example #3
Mr. Devanand initiated a deposit from an employer of $5000 half-yearly starting at the age of 45 until Mr. Devanand retires, say at the age of 60. Suppose the interest rate is 8% compounded half-yearly. What will be the value of the annuity at the end of 15 years?
- Amount (A): $5,000
- Interest Rate (i): 0.020
- Number of Payments (n): 30
Here, i = 4% / 2 = 0.020
n = 2*15 = 30
The calculation of annuity value is as follows –

- Deferred Tax Annuity = $5000*(1+0.020)30- 1 / 0.020
- =$202,840.40
Thus, the annuity at the end of 15 years of Mr. Devanand will be $ 202840.40/-
Example #4
Mr. Abhinay initiated a deposit from his employer of $ 8000 yearly starting at the age of 55 until Mr. Abhinay retires, saying the retirement age is 60 years. Suppose the interest rate is 8 % compounded yearly. What will be the value of the annuity at the end of 5 years?
- Amount (A): $8,000
- Interest Rate (i): 0.08
- Number of Payments (n): 5
The calculation of annuity value is as follows –

- Deferred Tax Annuity = $8000*(1+0.08)5- 1 / 0.08
- =$46932.81
Thus, the annuity at the end of 5 years of Mr. Abhinay will be $ 46932.81/-
Advantages
This retirement benefit plan has a lot of advantages, which include:
- The investor has to pay tax only once when he withdraws the annuity amount.
- The contribution amount has no limitation. Whatever amount the investor wants to invest, he can invest.
- This annuity provides a lifetime benefit for the investor and his/her spouse.
- This annuity has a death benefit. Suppose the investor dies between the annuity contract; the nominee will receive the amount.
- Most insurance companies provide a guarantee for the loss of principal.
Disadvantages
Despite multiple benefits that the tax deferred annuity plan offers, it also has a few disadvantages, which investors must know of:
- The investor has to bear additional charges like commission, administrative fees, funding expenses, etc.
- The investor can earn a high income by investing money in the stock market instead of investing in an annuity.
- An investor can not withdraw money during the annuity term; if withdrawn, the penalty has to be paid for early withdrawal.
Withdrawal Options
When an investor reaches the age of 59.5, then payment can be received in one of three ways described below:
- Lump-Sum: In this option, the investor will receive a one-time single taxable payment.
- Annuitization: In this option, monthly, quarterly, or yearly payment is received by the investor until death.
- Systematic Withdrawal: In this option, the amount will be paid periodically.
Tax Deferred Annuity Vs IRA
Both tax deferred annuity and Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA) are retirement benefit plans to ensure employees have a financially independent life post-retirement. These options offer huge tax advantages to the one who is entitled to receive the benefits.
Though they share multiple similarities, the two terms differ from each other widely. A few of the differences have been listed below:
- While tax deferred annuity is an asset itself in which employers and employees invest collectively, IRA is the investment plan using which the investors can spend on assets, like stocks, mutual funds, bonds, etc. to secure their future financially.
- The former is an insurance product, the latter is the retirement scheme.

