Table Of Contents
What is Corporate Governance?
Corporate governance is a set of regulations, policies, and procedures that control the functioning of an organization. It defines the Board of Directors’ role, its composition, the role of Chairman, the role of CEO, risk management strategies, control mechanisms, and action plans.
The primary purpose of corporate Governance is the safeguarding of stakeholders' interests. This includes the Board of Directors, senior management, creditors, suppliers, shareholders, customers, employees, government, banks, and society. It ensures the diversity of the board. It safeguards shareholders' rights—for example, the right to dividend or the right to vote.
Key Takeaways
- Corporate governance is an organization's modus operandi comprising rules, practices, regulations, policies, and procedures. These guidelines control businesses.
- A company with good governance reflects fair business practices. This is made possible by employing robust risk management systems, diversity, independent auditors, satisfied stakeholders, progressive compensation models, transparency, and accountability.
- Poor corporate governance can be destructive. Shareholders and investors will lose faith, consumers will be dissatisfied, and ultimately the brand image will be tarnished.
Corporate Governance Explained
Corporate Governance is the foundation of an organization's functioning and business conduct. Effective Governance includes the following elements:
- A seamless corporate structure— clear roles, responsibilities, policies, practices, procedures, and code of conduct;
- The diversity of the board;
- Strategically designed risk management mechanisms;
- Cordial relations and trust among the different stakeholders;
- Complete disclosure of corporate information, including the sustainability report on the ESG practices (Environmental, Social and Governance);
- Safeguarding and centralizing shareholders' rights— right to dividend and right to vote;
- Containing proxy, influenced voting and other unfair practices;
- Timely review and revision of remuneration; and
- Giving freedom to auditors— to check company's accounts—prepare fair audit reports.
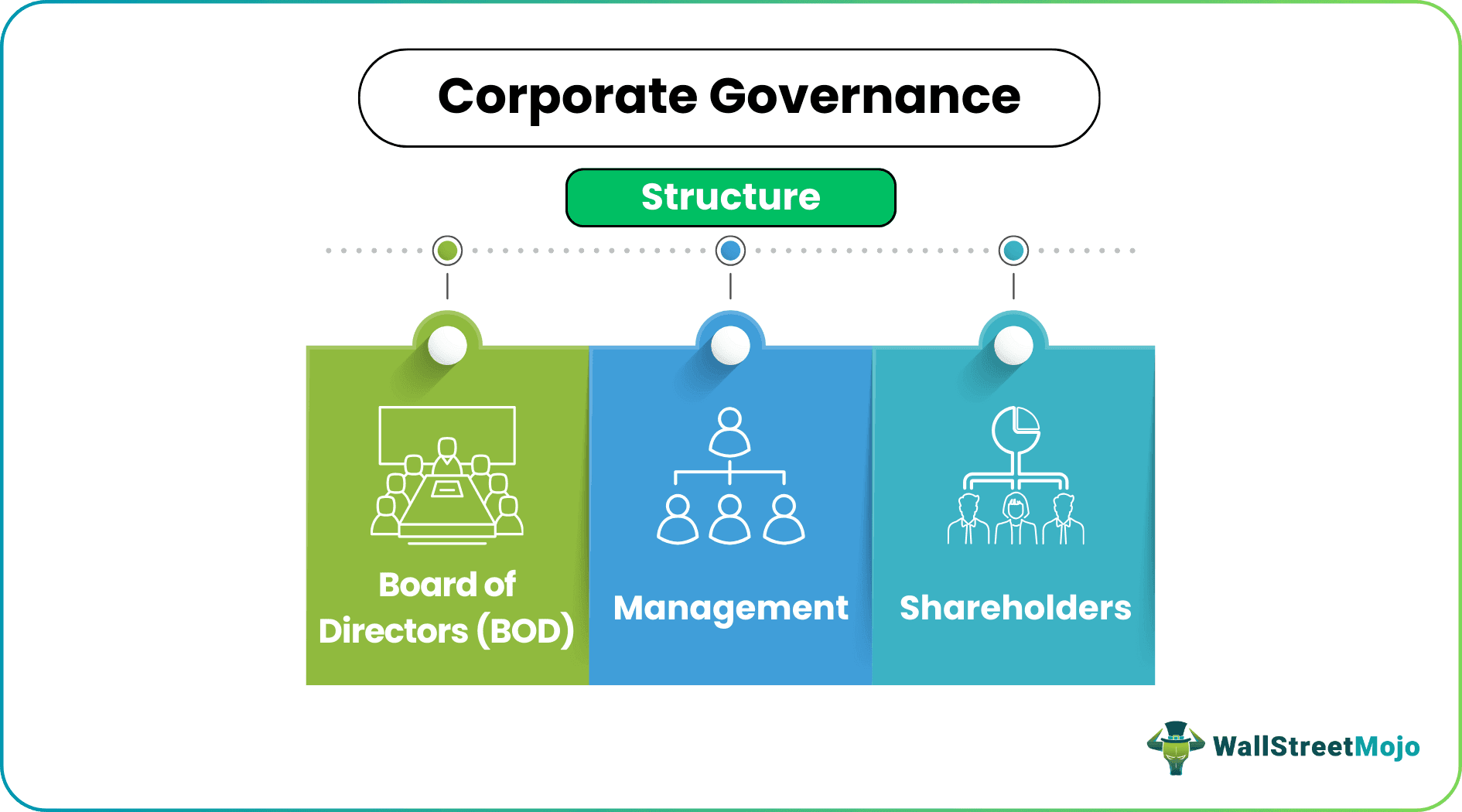
Corporate Governance Structure
The key players in the corporate governance framework are as follows:
- Board of Directors: Board of Directors takes crucial decisions to attain long-term business objectives. They are also referred to as "Those Charged With Governance" (TCWG).
- Management: The management is a subset of the BOD led by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the company. The CEO is responsible for business operations, formulation of strategies, and evaluation of associated risks.
- Shareholders: The stockholders are investors who put their hard-earned money into the company anticipating positive returns. They cannot track corporate affairs on a daily basis, and therefore, rely on the directors. Further, shareholders appoint auditors to dig into the business's financial affairs—provide the audit report.
Legal Framework
The US has a "best practices" approach when it comes to corporate governance. Although there is no particular code of conduct, the state and federal authorities state various rules, regulations, and laws in this regard. The regulations are as follows.
#1 - Federal Securities Law
- The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has put forward the Securities Act 1933 and the Securities Exchange Act 1934. The 1933 Act controls the registration of securities with SEC and national stock markets. The 1934 Act controls the secondary trading of securities. It also established the SEC as the agency primarily responsible for the enforcement of United States federal securities law.
- Sarbanes-Oxley Act was formed in the 2000s to protect and restore the interest of the shareholders.
- Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act changed the public perception of financial institutions. The act improved faith in the financial system.
#2 - State Corporate Laws
- The state corporate laws govern the rights of the directors and shareholders in corporate management.
- The Delaware General Corporation Law (DGCL) applies mainly to the public companies set up in Delaware. Some other states also follow DGCL regulations.
- The American Bar Association puts forward another legislation, i.e., the Model Business Corporation Act, defining the various laws for running a corporation. It outlines everything; from the formation of a company to the voting rights of shareholders.
Example
In 1997, Amazon started with a letter to the Shareholders. The letter read, "the company's fundamental value will be the shareholder value that the company creates in the long run."
Amazon's Corporate Governance aims to achieve:
- Customer-centric approach;
- Increased cash flow;
- Spending wisely;
- Continuous hiring of a talented workforce; and
- Prioritizing long-term considerations over short-term profits.
Satisfied employees across the globe prove Amazon's successful Governance. To reward employees who worked hard during the pandemic (COVID-19), Amazon gave huge performance bonuses.
Principles of Corporate Governance
Following principles guide firms in developing a corporate governance framework:
- Leadership: The board of directors and the CEO should be competent in decision-making.
- Risk Management: There should be a robust risk management mechanism for handling uncertainties.
- Transparency: The management should disclose the complete financial information of the company.
- Responsibility: The board of directors is responsible for running the business on behalf of the shareholders.
- Accountability: The board of directors and the CEO are accountable to the shareholders for their actions and their style of governance. At the same time, the management is answerable to the BOD.
- Fairness: All the stakeholders should be treated equally.
- Effectiveness and Efficiency: The policies and procedures should be clear and uniform. Moreover, it should be well-communicated.
- Independence: The shareholders should be free to vote, and the auditors should be given access to financial data. The auditors should be given the freedom to prepare transparent audit reports.
- Responsiveness: In addition to shareholders, crucial information should also be communicated to vendors, customers, financers, and employees.
Importance
Corporate Governance ensures that stakeholders are not deprived of their rights. In addition, it facilitates compliance. It initiates the formulation of seamless procedures and practices ensuring transparency. It limits corruption and other malpractices.
An efficient framework facilitates better risk mitigation; such balanced firms attract more Investors. Good Governance attracts top talents. Ultimately, a well-run ship reflects into better share prices.
Issues
Poor Governance can destroy a business all the way to its shutdown. It paves the way for accounting scandals, lack of internal control, dishonest managers, and non-disclosure of financial facts.
Without structure, running a business becomes difficult. Poorly run firms even restrict auditors from getting to the bottom of issues. It leads to inaccurate financial reporting. In such firms, top management often plunders enormous amounts from the corporate funds.
Deciding on the compensation for the top-level executives is a crucial part of Governance. Sometimes, vague administration leads to favoritism and discrimination. Moreover, such a corporation loses the confidence of the investors, financiers, auditors, directors, and employees. Such lapses can severely tarnish a firm's brand image.
