Table of Contents
Deal Structure Meaning
Deal structure refers to a process of ascertaining the method of enterprise value or purchase price payment in a business merger and acquisition deal, I.e., whether in cash, rollover stocks, or both. It determines the consideration timeline and the other terms, conditions, responsibilities, and risk allocation for both parties.
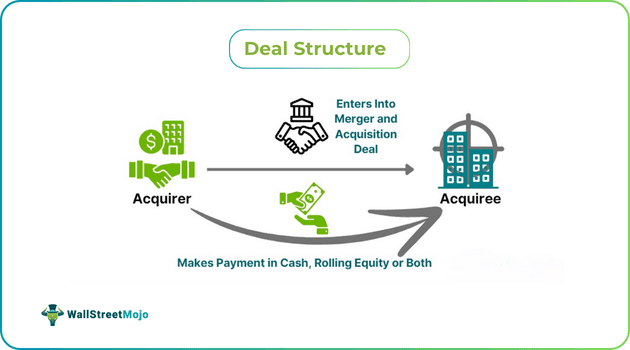
Such an arrangement ensures mutual financial benefit of the buyer and the seller in a business deal. While it primarily aims at maximizing the deal value for the acquirer, it also helps them examine different financing options. Further, it determines the tax considerations of both parties and successfully integrates the target firm into the acquiring firm.
Key Takeaways
- A deal structure is a model that determines the mode of purchase price payment by the acquiring company to the acquiree in a merger and acquisition or other such business deals.
- There can be three primary ways of paying the consideration for a business deal, including cash, rolling stocks, or both of these in specific proportions.
- It emphasizes the creation of a purchase price agreement that favors both the acquirer and the acquiree.
- The five prominent methods of deal structure are equity-based, cash-based, debt-based, hybrid, and earnouts.
Deal Structure in M&A Explained
A deal structure primarily focuses on the method of purchase price agreement formed between the acquirer and the target company in a potential merger and acquisition deal. However, it considers specific other terms and conditions, as discussed below:
- Down payment of the deal;
- Target firm's financing conditions;
- If any purchase price holdback is involved in the earnout agreement;
- Whether it is an asset or stock acquisition;
- Other payment-related terms and conditions.
Since there are various M&A deal structures for the companies to select, as per their needs and goals, both the acquirer and the acquiree can reap the maximum benefit from shaping a purchase price agreement such that it is a win-win for all. It not only maximizes the value these parties derive from such dealing but also mitigates the risk involved due to colossal capital involvement to a certain extent. Moreover, the acquiring and acquiree companies often review their potential tax liabilities and implications before choosing a particular structure for executing a business deal. Indeed, business buyers usually find various financing opportunities to arrange for funds to proceed with such mergers and acquisitions.
However, the acquirers must be careful while opting for a suitable M&A deal structure since it involves a significant capital investment and has a particular opportunity cost. Some of the tips for selecting a favorable model are as follows:
- A business acquisition deal structure must align with the corporate strategies.
- As discussed above, the parties must assess their potential tax consequence from the deal.
- The buyer must internally analyze its financial capacity before selecting a structure.
- Also, the parties should check whether the structure aligns with the cultural integration of the firms.
- The buyer and the seller should follow all the relevant guidelines, regulations, and legal formalities.
- The parties shouldn't hesitate to negotiate to their best.
Methods
There are different M&A deal structure models available for paying the consideration for such a business deal; the prominent ones are as follows:
- Equity-Based: It is one of the most popular deal structures whereby the buyer (acquiring company) reimburses the seller (target firm) of a target business by transferring its stocks equivalent to the deal value.
- Cash-Based: Another convenient and quick option is that the acquirer pays off the total consideration of a business deal in cash. However, it may result in high capital gain tax liability for the acquiree along with more liquidity.
- Debt-Based: In this structure, the acquirer buys a target company through a leveraged fund, I.e., financing the deal from the debt amount against the target company kept as collateral with the lender.
- Earnouts: These are particular types of dealings where the acquirer attracts the shareholders of the target firm with the extra consideration above the valuation analysis payable over the period. Thus, it is a suitable option when the target's shareholders expect more value than what the acquirer determines.
- Hybrid: It is a blend of two or more consideration methods, such as equity-based and cash-based deal structures, customized as per the unique requirements of both parties.
How to Create?
Some of the basic steps to the formation of a business deal structure include:
- Initial discussions and conversations between the acquirer and the acquiree;
- Forming a letter of intent (LOI) stating all the crucial inputs provided by both the parties;
- The LOI includes the purchase price details as well;
- On further negotiation, the LOI transforms into a binding Definitive Agreement, I.e., a Purchase Price Agreement by the legal attorneys of both parties;
- However, no further negotiations should be done on moral grounds since it leads to a breach of trust between the parties.
Examples
Moving ahead, let us find out how a deal structure works in a real business scenario with the help of the following examples:
Example #1
Suppose ABC Ltd. makes a business acquisition deal structure to acquire XYZ Enterprises. The company plans to proceed with a cash-based deal structure at the valuation of $4.7 million since XYZ Enterprises requires urgent funds to pay off its liabilities before dilution. Moreover, ABC Ltd. has sufficient cash reserve to make the payment and wants to close the acquisition deal quickly for its expansion strategy to facilitate a lined-up project. Thus, within 30 days of the deal finalization, ABC Ltd. paid the total consideration in cash to XYZ Enterprises.
Example #2
In 2024, the private equity industry began the year with an impressive $2.59 trillion in cash reserves for investments, distributed among 25 prominent groups. However, they confront obstacles such as a record $2.8 trillion in unsold investments and a sluggish market for exits. Despite these challenges, there's optimism for increased deal activity, particularly with the potential stabilization of US interest rates. Moreover, the PE groups have used complex private equity deal structures like earnouts to actualize such dealings. Also, to address these dynamics, firms are employing financial engineering strategies like structured transactions and corporate carve-outs to navigate the market terrain.
Source - https://www.ft.com/content/079ccde6-3c3d-4791-953b-6e3e8203ef12
Advantages And Disadvantages
A well-designed deal structure makes a business collaboration or buyout a winning bet for both the acquiring company and the target firm. However, it is a strategic decision that brings up multiple challenges for the involved parties. Each form of deal structure has specific pros and cons, as discussed below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Equity-Based Deal Structure | |
| Such an arrangement saves the acquiree from capital gain tax liability. | There can be conflicts between the two companies and their shareholders due to differences in their cultures, processes, policies, and systems. |
| It allows the target firm to crack the deal by accepting stocks in the acquiring company, which may reap high returns in the long run. | Moreover, it is challenging to determine the fair value of the acquiree's shareholding in the company, thus raising disputes between the acquirer and the acquiree. |
| The acquiree may dilute their shareholdings in the acquiring firm for cash, which may hinder the latter's market value. | |
| It often results in a decline in existing shareholders' stock value due to the issuance of fresh shares, making them unhappy. | |
| Cash-Based Deal Structure | |
| Cash-based acquisitions ensure certainty of payment to the seller and speed up the acquisition process. | However, cash transactions involve blocking a substantial sum for a business deal, resulting in a parallel opportunity cost. |
| Such dealings involve less risk pertaining to market fluctuations, uncertainties, regulatory compliances, etc. | It sometimes makes the shareholders unhappy since it deprives them of availing of a more significant ownership stake in the target company. |
| It makes the transaction process seamless since it doesn't involve any equity issuance or external financing. | It may burden the target firm with capital gain taxes on the cash consideration. |
| Moreover, it increases the negotiation power of the acquirer with respect to the purchase price or discount, as well as deal terms and conditions. | |
| Debt-Based Deal Structure | |
| A debt-based acquisition helps the acquiring firm to sustain its cash reserves. | However, it potentially raises the debt cost of the acquirer. |
| It allows the acquirer to claim tax benefits on interest deductions. | Also, it may refrain the acquiring company from taking further loans for new projects in its growth journey. |
| Earnouts | |
| It fills the valuation gap between the acquirer and the target firm.. | Due to the extended payment period, the seller is prone to uncertainty and unfair negotiation from the buyer's end |
| The buyer can avail of a longer payment tenure. | It is a time-consuming process. |
| It serves the interests of both parties. | It hinders the potential growth, progress, and decision-making process of the target company. |
| Hybrid Deal Structure | |
| These models serve as the most appropriate deal structures. | These are complex structures and may require significant resources and time. |
| Such a balanced deal is in favor of both the business buyer and the seller, fulfilling their requirements. | |
| A mixed structure of rolling stock and cash consideration can save time, provide liquidity, and maximize returns for both parties. | |
