Table of Contents
What Is International Financial Architecture (IFA)?
The international financial architecture (IFA) refers to the framework of rules, practices, policies and institutions governing the international financial system. It serves to encourage global cooperation to ensure global financial and monetary stability, facilitate international investment and trade, achieve goals of sustainable development, aid economic development and fight climate crisis.
It has tried to create a more resilient, balanced and stable architecture of international financials. It has various organizations within its ambit, like the International Monetary Fund (IMF), mechanisms for global cooperation and regulatory bodies. It also creates guidelines for sovereign debt management to ensure smooth capital flow and economic stability.
Key Takeaways
- The International Financial Architecture (IFA) represents the structure of institutions, policies, rules, and practices aimed at promoting global cooperation, combating climate change, ensuring financial stability, and facilitating investment.
- It needs reforms like enhancing governance and coherence, strengthening liquidity, upgrading quota equations, resolving systemic deficiencies,
- promoting responsible borrowing, and advocating for financial development for developing countries special needs.
- Its importance lies in strengthening global financial organizations, resolving sovereign debt challenges, increasing capital flow resilience, contributing to financial development macroeconomic stability, and minimizing financial crisis impact.
How Does International Financial Architecture Work?
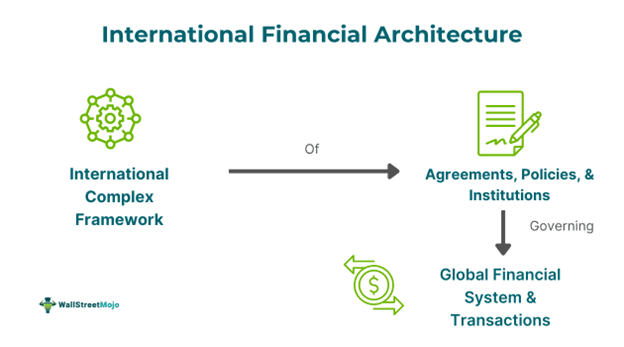
The international financial architecture (IFA) refers to a complex system consisting of agreements, policies, and institutions that decide how financial transactions flow among countries. It depends on a conglomerate of institutions such as interconnected central bank networks, regulatory bodies, the World Bank, and IMF, as well as policy contracts among nations. All these institutions work together to perform the following tasks:
- Reduction of the risk of financial crises
- Maintaining stable exchange rates
- Promoting global economic growth.
- Facilitating capital flow across borders
- Overseeing economic policies
- Offering financial help to needy countries.
Sometimes, it also takes help and invites informal groups of nations like the G7 and G20 that coordinate responses and set norms for international financial problems. It has a framework boasting of enhanced transparency, resilience, and accountability against financial crises, but it has failed to support developing countries adequately.
Its effectiveness has vital implications for the global economic scenario. It has the power to affect debt management, capital flows, and countries' ability to act against financial shocks. If it functions effectively, it can lead to economic growth. However, if it fails, the crisis in developing nations may worsen.
Its full usability largely depends on its inclusivity of governance structures and resource accessibility. Most developing countries struggle to receive help from the IFA due to its stringent financial aid conditions and lack of representation in decision-making processes.
It forms the financial environment by promulgating engagement rules for global finance. Moreover, it influences the manner in which countries act during crises, manage their economies, and conduct global trade. Furthermore, it has to evolve accordingly to address contemporary barriers like economic equality and climate change.
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
History
IFA was established in the aftermath of the 2008/2009 global financial crisis to encourage a more balanced and stable international architecture of the financial system. In the first international financial architecture working group meeting under the G20, IFA aimed to resolve the crisis of developed countries and significantly increased the representation of developing nations in international financial governance.
Moreover, during the presidency of South Korea, the G20 International Financial Architecture Working Group played a critical role in the reform of quota and governance in the 2010 International Monetary Fund (IMF). Similarly, IFA successfully resolved the crisis in the Euro Area while France was the president in 2011.
In recent years, the focus of the G20 international financial architecture has shifted to addressing challenges faced by developing nations due to the combined negative impact of fiscal restrictions in central economies and the pandemic. This is evident from the fact that at the time of the coronavirus outbreak, the IFA eased the debt repayment burden on developing countries through coordinated discussions.
The IFA has taken on the responsibility of optimizing the balance sheets of multilateral development banks, enhancing capital flow analysis, handling capital flow volatility risks, and empowering the global financial safety net. The IFA keeps on adapting and addressing the global financial system's ever-evolving necessity.
Reforms
As per the UNCTAD report, one finds the reforms needed in IFA to create new international financial architecture are as follows:
- Transform its governance to increase its inclusivity and representation.
- Maximize the coherence of the global system by creating a representative apex body.
- It must strengthen liquidity provisions and widen the financial safety net to withstand international financial vulnerabilities.
- Upgrade IMF quota equations to represent the dynamic global architecture to help developing nations handle debt and get finance.
- Resolve systemic deficiencies in its structure to give proper help to developing countries in accessing finance and handling debt.
- Promote responsible borrowing and lending practices to enable financial stability and debt sustainability.
- Advocate reforms allowing finance development to determine and work towards the special needs of the finances of developing countries.
Importance
It has become important in current financial situations:
- It ensures global financial stability by strengthening global financial organizations.
- It resolves sovereign debt challenges, increasing capital flow resiliency.
- IFA increases the representation of young people and developing countries, adding to their resilience.
- It contributes to financial development and macroeconomic stability thereby facilitating high-quality funds flow.
- IFA has successfully minimized the impact of financial crisis upon middle- & low-income nations.
- Multilateral development banks can optimize their balance sheets with their help.
- It decreases risks from volatility as it enhances the tracking and managing of capital flows.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

