Table Of Contents
Financial Intermediary Definition
A financial intermediary refers to a third-party, forming environment for conducting financial transactions between different parties. For example, the banks accepting deposits from customers and lending them to the customers who need money exemplifies the basic financial intermediation process.
The financial intermediation process is not restricted to third-party connecting lenders and borrowers. They significantly manage financial assets and liabilities to prevent financial crises. Furthermore, they are liable to strictly adhere to guidelines or regulatory policies set by authorized agencies like the Federal Reserve Board (FRB) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) if it is in the United States.
Table of contents
- Financial Intermediary Definition
- Financial intermediary refers to the financial entities acting as intermediaries to conduct their clients' financial transactions. It connects entities with surplus funds and deficit funds.
- Intermediaries protect customers' deposits, stimulate money flow in the economy and subsequent economic development.
- They can be banking or non-banking institutes owned by the government or private entities. Furthermore, they are also discerned as primary and secondary intermediaries.
- Examples include commercial banks, NBFCs or non-banking financial companies, mutual fund companies, insurance companies, factoring companies, financial advisors, credit unions, and stock exchanges.
Role of Financial Intermediary
Financial intermediaries function basically by connecting an entity with a surplus fund to a deficit fund. They ease the money flow in the economy and support economic growth. Based on the type of services and products offered by the intermediaries, the complexity in their roles changes. They take the form of channel providing loans, mortgages, investment vehicles, leasing, and insurances, etc.
Some of the significant roles of intermediaries include:
- Link households to the financial market
- They safeguard customers' hard-earned money
- Financial advisory services, provide financial information, and engage in credit rating
- Reducing the cost of business by offering economies of scale to business owners
- It helps corporations optimize the capital structure by obtaining an appropriate mix of equity and debt
- Stimulate economic development
The Hargreaves Lansdown provides access to a range of investment products and services for UK investors.
Types of Financial Intermediary
Various types of entities provide financial intermediary services ranging from banking institutions accepting deposits like Federal Reserve Banks, commercial banks, savings banks, and other depository organizations like credit unions to entities that do not take deposits such as NBFCs. In a nutshell, it is distinguished as bank and nonbank intermediaries. Moreover, it can be government or private entities.
Other types from the insurance sector include property insurance companies, private life insurance organizations, and government insurances. Furthermore, stock exchanges, investment banks, brokers, dealers, and clearinghouses are some examples signifying the heterogeneity in types.
It can also be segregated based on the source of their funds as primary and secondary financial intermediaries. The primary intermediary entities collect their funds from households, business enterprises, or governments and provide loan services to the same groups. In contrast, secondary intermediaries deal with the primary intermediary entities. An example of secondary intermediaries is factoring companies.
The intermediary definition may vary by country and change as time passes. It is also influenced by the prevailing country's legal arrangements and financial customs. Furthermore, the evolution of decentralized finance (DeFi) provides ways to disintermediate financial transactions.
Financial Intermediary Examples
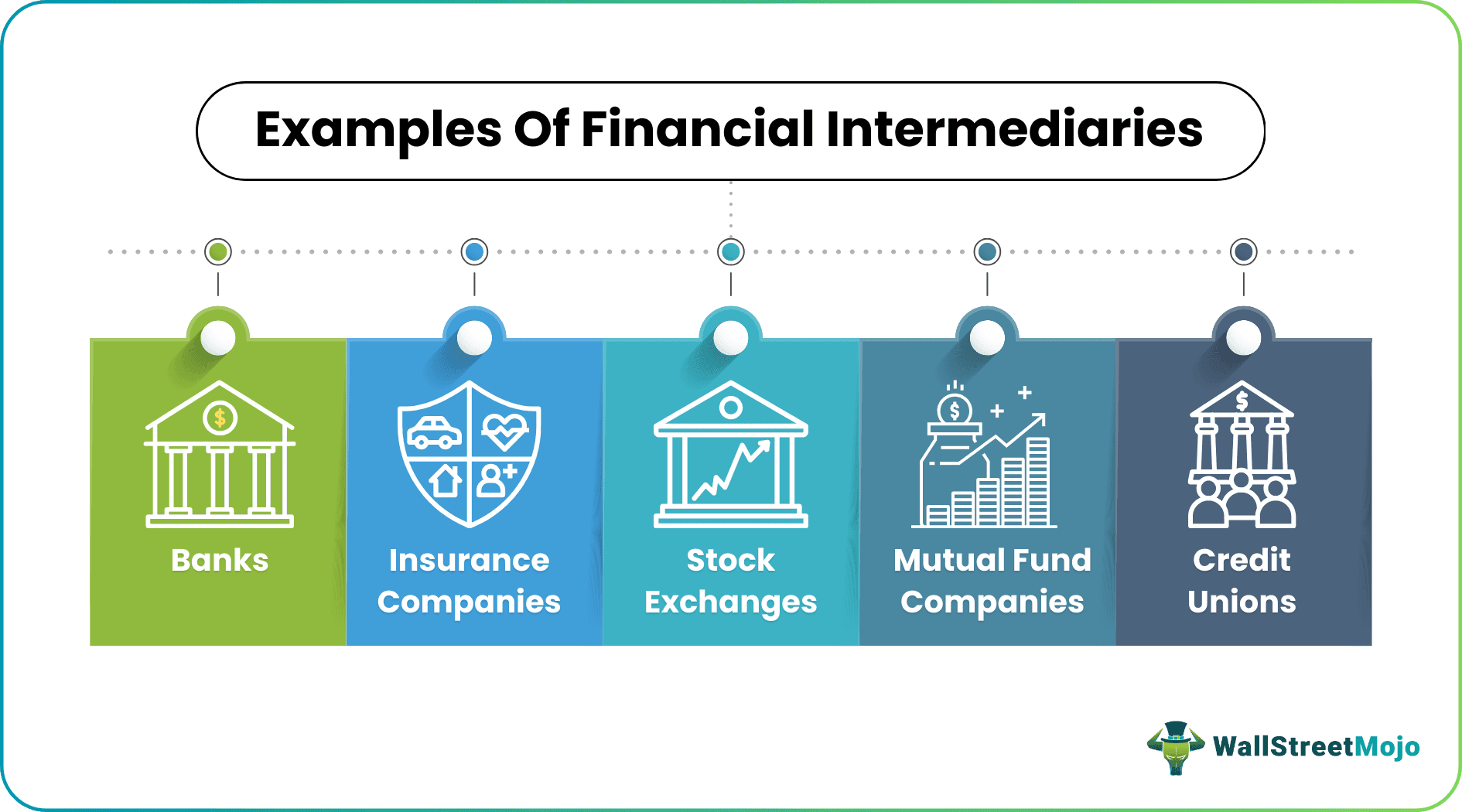
Let's briefly describe some financial intermediary examples like banks, insurance companies, stock exchanges, mutual fund companies, and credit unions.
- Banks: Banks primarily utilize the deposits made by clients to support other eligible clients in need. The interest earned for providing loans serves as income for the banks. Banks also offer several other services like forex services, insurance for deposits, and credit cards.
- Insurance companies: Insurance companies provide various insurance policies like life insurance, home insurance, and liability insurance designed to give financial protection to the customers. They deal with different entities like brokers and agents for completing the transactions. It pools policy holders' premiums and invests them in various investment vehicles like bonds and other money market instruments. Moreover, this way, they make a huge profit and pay claims and other liabilities without incurring massive losses even if the payouts are large. The income from their investments ensures that the insurance company is cushioned against this.
- Stock exchanges: The stock exchange reflects a marketplace where buyers and sellers engage in trading financial instruments like stocks and derivatives. It connects companies that need funding and investors who have excess funds to invest as an intermediary. Even with a small amount of money, one can have an ownership interest in a blue-chip company which may have otherwise been impossible.
- Mutual fund companies: Generally, fund managers in mutual fund companies invest the money collected from retail investors in different financial assets and distribute the return to the retail investors proportional to their investment. Based on the client preferences and investment fund managers focusing on growing the investors' wealth, select appropriate securities and compile them to form the portfolio. Mutual fund companies help clients with investment management.
- Credit unions: Credit unions are usually non-profit entities owned by their members. It functions similar to banks; however, they offer better savings rates and reduced borrowing costs, that is, loans at competitive rates.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Some of the examples are commercial banks, stock exchanges, mutual fund companies, insurance companies, credit unions, non-banking finance companies (NBFCs), pension funds, building societies, financial advisors, investment bankers, escrow companies.
Yes, banks function as intermediaries connecting lenders and borrowers. They primarily collect funds from customers who want to deposit their surplus income and provide them with a return in the form of interest on the deposits. Banks utilize a significant portion of this money collected to lend it out to the people who need money for various purposes like implementing business ideas.
Financial intermediaries create a favorable atmosphere and conduct financial transactions for their customers. They provide a wide array of products and services to cater to the diverse needs of the market participants. Their services stimulate money flow in the economy and subsequent economic development.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Financial Intermediary and its Definition. Here we explain the role of financial intermediary along with its types and examples. You can learn more from the following articles -

