The differences between both the concepts are given as follows:
Table of Contents
What Is Labor Rate?
The labor rate is an estimation used to determine employees' monthly compensation; otherwise, it represents the hourly wage costs businesses pay for their staff. More specifically, the labor rate represents workers' total income, including any applicable taxes and perks added to their pay.
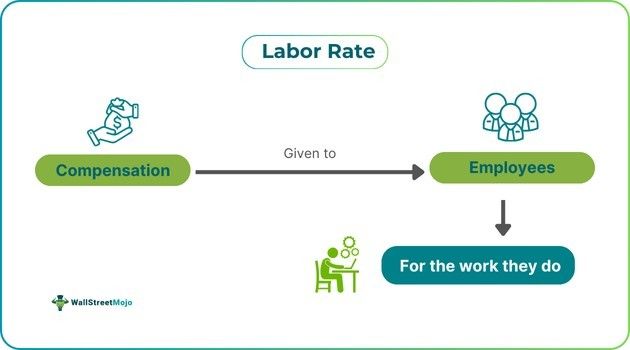
The rate is important for several reasons. It supports cost estimation for projects, workforce planning, and pricing for business services. It helps in the estimation of labor cost comparisons across regions or industries, profitability analysis, and contract negotiations. The primary goal of it is to guarantee that workers receive enough compensation for their qualifications and experience.
Key Takeaways
- The labor rate serves as an estimate to determine employees' monthly compensation and represents the hourly wage costs businesses pay to their staff.
- It aids in understanding labor costs, which can be categorized as fixed or variable expenses.
- Fixed costs are predictable, like commissions and fees for long-term contracts, while variable costs fluctuate based on economic conditions or production demands.
- A standard labor rate refers to an anticipated pay rate per labor hour.
- The direct labor rate is calculated by dividing the compensated amount by the total hours worked.
Labor Rate Explained
The labor rate is a worker's pay and is an important number that accounting and finance departments use. The rate is necessary to calculate the direct and indirect costs that businesses incur when paying hourly compensation to their employees. Direct prices are the hourly rates of employees, including benefits directly related to the company's services or product production. On the other hand, indirect prices relate to the compensation allocated to employees who are indirectly involved in the manufacturing of goods or the rendering of services. Examples include workers in administrative or assistant roles.
The labor rate can be used to understand labor cost, which can be further divided into fixed and variable costs. Fixed expenses, such as commissions and fees for long-term contracts, are regular and predictable. Variable costs are those that change according to the state of the economy or production demands.
A standard labor rate is an estimated cost or rate that reflects the anticipated pay rate per labor hour. It compares actual wage rates with projected wage rates in standard costing and variance analysis to ascertain whether an organization is paying more or less for labor than anticipated. The basic pay, benefits, taxes, and required contributions are all taken into account by the standard rate. It serves as a standard for determining prices for goods and services, creating budgets, and examining deviations. Making informed pricing decisions and estimating labor expenses based on anticipated output levels are both aided by it.
A business's or organization's labor rate is crucial to financial planning, labor cost calculations, and decision-making processes. It is the monetary value ascribed to the time and effort employees devote to their jobs. It includes wages, salaries, and benefits extended to employees.
How To Calculate?
The direct labor rate is estimated by dividing the compensated amount by the total hours.
Direct labor rate= compensated amount/ the total hours
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose Daisy examines labor rates in her capacity as an HR professional to guarantee that workers receive justifiable remuneration. She conducts market research, assesses industry benchmarks, and considers elements like work duties, experience, and abilities to determine competitive labor prices. She could use it to understand the labor rate participation (percentage of people in the working age category who are either already employed or are enthusiastically looking for work). The company could use this labor rate participation to understand the demand in the market. This promotes and maintains employee satisfaction, attracts and retains talented employees, and guarantees that the business's labor and workforce expenses align with industry norms.
Example #2
Suppose Danny is a construction worker who gets a labor rate per hour for the number of hours worked on a project. He had worked for a total of 40 hours, and the compensation he received was $2500. Let us find out what the labor rate per houris.
To find the labor rate of Danny let us use the formula Direct labor rate = Compensated amount / Total hours:
Given:
Compensated amount = $2500
Total hours = 40
Substituting the values into the formula:
Labor rate = $2500 / 40
Calculating the labor rate:
Labor rate = $62.50 per hour
Therefore, the labor rate of Danny is $62.50 per hour.
Labor Rate vs Labor Cost
| Points | Labor Rate | Labor Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Concept | It determines the prices that businesses pay directly and indirectly for the hourly wages of their employees. In other words, the pay that a worker receives for the work done. | The sum that an employer must spend to cover an employee's salary, benefits, and associated payroll taxes is known as the cost of labor.
|
| 2. Formula | Direct labor rate = Compensated amount / Total hours. | Direct labor rate = Compensated amount / Total hours. |
| 3. Purpose | It is used to compensate employees for the hours worked and the work done. | Accounting and finance professionals use labor cost as a key metric to estimate the direct and indirect labor costs that a business incurs. |

