Table Of Contents
Dollar Cost Averaging Meaning
Dollar cost averaging refers to a strategy whereby individuals or firms prefer breaking down their investment into multiple segments, irrespective of the price of the equity involved, ensuring the market volatility does not affect the entire purchase but only a portion of it. In short, it is an investment tactic through which investors minimize the risks associated with a security.
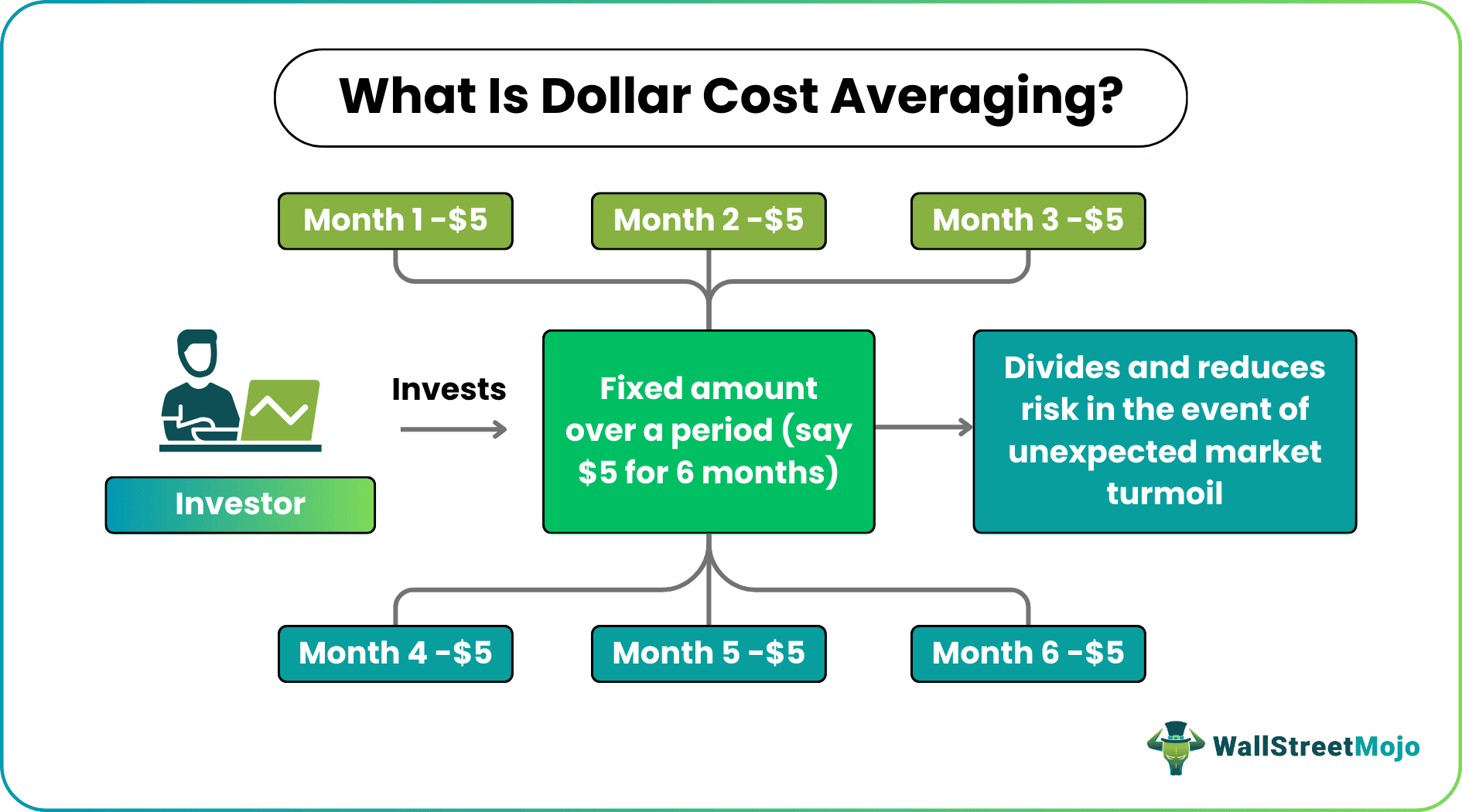
Also referred to as unit cost averaging, this strategy makes investors spend on security at regular intervals and ensure their returns are not affected even if the market downfalls. As a result, it does not only help individuals and firms reduce the volatility risks but also lets them build their position over a period.
Key Takeaways
- Dollar or unit cost averaging is an investment strategy whereby individuals or firms invest a fixed amount over a period to buy a security.
- It helps investors keep off from market fluctuations as they divide their investment in equal proportions for a specific period, reducing the risk associated with it.
- The unit cost averaging strategy helps prevent the repercussions of timing the market, which might go wrong and lead to adverse losses for investors.
- Investing in a 401(k) plan is one of the best examples of such an incremental averaging strategy.
How Does Dollar Cost Averaging Work?
The dollar cost averaging strategy refrains individuals or firms from investing the entire amount at once. Instead, it allows them to invest a fixed amount in a security over a period at regular intervals. Strategizing investment helps investors keep off from the sudden fluctuations in the securities' prices.
Given the possible negative price movements, using the available funds to buy all the stocks at once is quite risky. This incremental averaging investment strategy gives investors a chance to divide their investment in equal proportions over a period. As a result, even if the market suffers turmoil at a specific time, it will only impact the investment during that particular tenure. In short, only a part of the total investment would be affected while keeping the rest of them made at another period safe against any market fluctuation.
Studying dollar cost averaging vs lump sum helps investors understand why the former should be preferred. For example, if a person invests $50 in a security on the first day of every month for two years, it becomes unit cost averaging. Using this strategy helps investors reduce the risks associated with the deal to a limit. How?
If a market is struggling to keep up its position on a global platform for a month or two, it would only affect that portion of the investment. On the contrary, if an individual decides to invest $1,200 for two years at once, it would be affected adversely for two consecutive months, leading to huge losses to investors.
Dollar Cost Averaging in Video
Calculation Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the concept better:
Example #1
The most significant dollar cost averaging example is 401(k), a common workplace retirement plan in the United States. The employees invest in the scheme, not knowing it's one of the phenomena of the unit cost averaging. Individuals invest in a number of mutual funds of a fixed amount irrespective of the current market scenario. The investment made every payday ensures the returns remain safeguarded. Even if the market fluctuates, it will only affect the investment for that particular period. The rest of the returns beyond that tenure remains unaffected.
Example #2
Jack invests $100 monthly, and he decides to use that amount to buy shares of the NASDAQ index every month. In the first month, the stocks trade at $10 per share. Thus, the investor buys a total of 10 shares. However, in the coming months, if the price per share decreases to $5, it would allow Jack to purchase 20 shares in total, which would mean a profitable deal for him. On the other, if the price increases to $20, the same investor would only be able to buy 5 shares.
In such a situation, dividing the purchase worth $100 into different segments seems a great idea. It helps Jack divide the risks while ensuring profit when the market is in favor.
Benefits
This strategy offers multiple benefits over other investment strategies that investors adopt and implement.
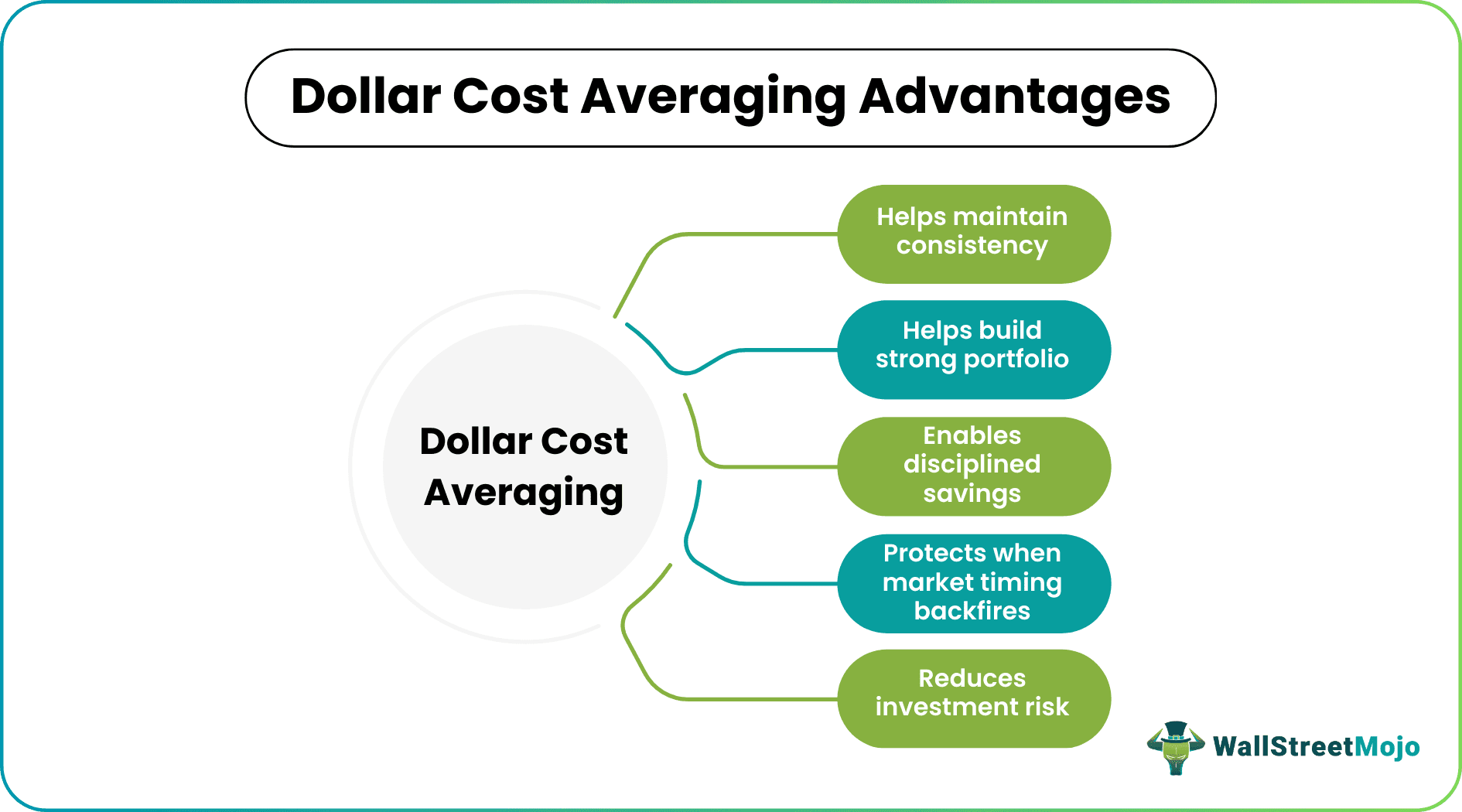
The unit cost averaging not only helps divide and reduce the risks associated with the deals but also lets investors remain consistent in making investments irrespective of the current market trends. Moreover, once the investors decide to spend a fixed amount on buying securities at regular intervals, they are subject to building a diverse portfolio.
In addition, when this averaging strategy is adopted, individuals get an opportunity to make an average saving per investment in the form of considerable returns. There are instances when people time the market and try to track the price movement for lump sum investment for higher returns. As a result, if the market deteriorates unexpectedly, the investors lose a lot of money. The unit cost averaging helps avoid such bad timing.
Limitations
Though this incremental averaging strategy offers many advantages, there are a few limitations that investors must be aware of.
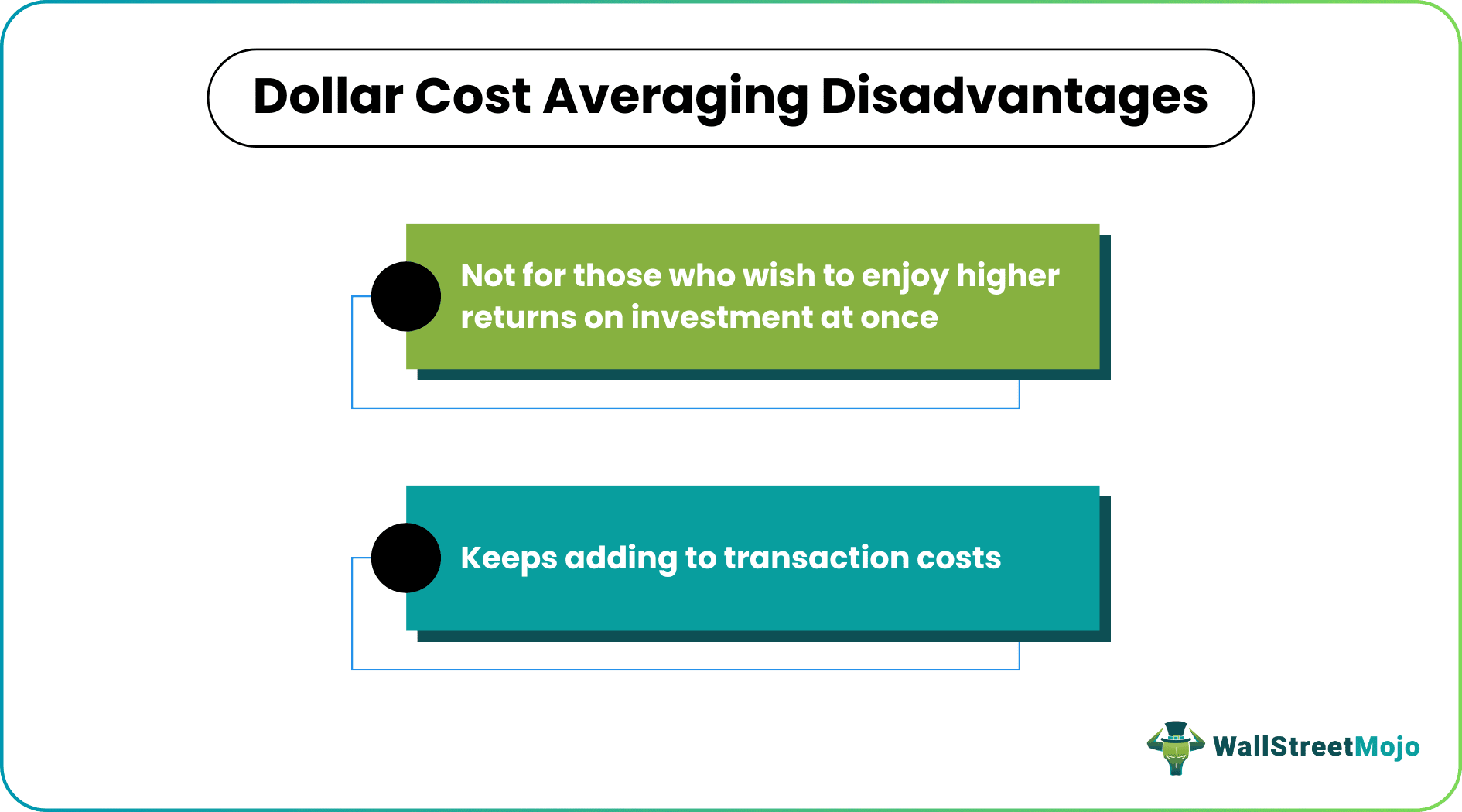
This investment strategy is fruitful only for those happy with lower returns over time. On the other hand, those who desire heavy returns on investments should spend a lump sum to buy securities. However, they must be ready to take higher risks in the latter case.
In addition, unit cost averaging tends to offer frequent returns on every investment that individuals make. This, in turn, leads to more transactions, adding to the transactions costs for the investors.
Dollar Cost Averaging vs Timing the Market
Timing the market or market timing refers to an investment strategy whereby investors predict the market's future price movements and decide when to buy or sell securities.
The future prediction might go wrong, leading to the buying and selling of securities at the wrong time. Investors might purchase stocks under the fear of an expected price rise in the future if the market goes up. They, however, forget that in such situations, there are equal chances of a drop in the stock prices. As a result, investors end up incurring huge losses.
On the other hand, a dollar or unit cost averaging strategy helps investors avoid a situation where market timings backfire. Instead, investors decide to invest a fixed amount at regular intervals to buy the same stock. This, in turn, ensures the division of risk among the portions of investment so that the market fluctuations do adversely affect investors.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Also known as unit cost averaging or incremental averaging, this strategy helps investors minimize risks on investment by letting them divide their investment amount in fixed proportions over time. As a result, even if the market is down, it won't affect all the investment but only a part of it for that particular tenure.
The unit cost averaging is a good idea if an investor cannot keep track of the market regularly but desires to be a consistent investor. Such individuals can decide on a fixed amount to invest in a security over a period. In addition, if they are willing to develop a habit of disciplined saving, this incremental averaging technique is of great help.
The technique works in the same way for crypto as well as stocks. Investors can choose a fixed amount to invest in the desired cryptocurrency over a period. Then, the investment would continue while guaranteeing the returns irrespective of the fluctuations in the market.
