Table Of Contents
What Is Growth Investing?
Growth Investing refers to capital allocation in potentially high-earning companies such as small caps, startups, etc., that grow much faster than the overall industry or mature companies. As the returns in such investments are high, the risk faced by such investors is higher too.
Investors usually pick stocks that have good future potential even though they might be small or new companies. They are mostly in sectors that are rapidly expanding, like new technology. Thus, along with the risk involved, there is also good probability of future returns if proper analysis is done.
Key Takeaways
- Growth investing is the appropriate capital leverage provided to certain small startups and budding companies, which have the potential growth to provide faster returns to their investors.
- Growth investing stocks are very important as it tends to give satisfactory returns, and the stock price movement is directly related to the company's profitability.
- The pitfalls of growth investing are that managers focus on future returns rather than the current numbers held by the company. Additionally, the safety margin is comparatively lower in small-cap or mid-cap organizations.
- Such kind of investing happens mostly in rapidly expanding sectors like technology.
Growth Investing Explained
Growth investing is investing in stocks of companies with good future growth potential, usually in any rapidly expanding sector. These companies have a better capacity to increase their profits and are in a better position to survive the competition.
If business strategy is strong, growth investing stocks show sudden rise in price within a limited time span. Companies with good growth potential will have a relatively higher earnings per share (EPS) and also a higher price earning ratio (P/E ratio) compared to their competitors.
High growth investing stocks are mostly of emerging sectors like virtual reality, artificial intelligence, robotics, and biotechnology and stocks that fall under this category show outperformance within a short time, in spite of being recent entrants in the market.
Strategy
There are many ways to identify growth investing companies.
- Stock performance – Investors can analyze the stock’s performance by keeping track of the price at which it is trading and the reasons for change if any.
- Return on equity – Understanding the return generated from the capital investors invest in the business with the aim of long term growth investing. If a return is good, the business is using the money wisely and expanding. This means it has good prospects.
- Profit margin – The profit margin helps to analyze whether the business can cover its costs and still has extra money for future expansion.
- Historical performance – This performance will show how the company is progressing.
- Peer comparison – High growth investing stocks usually perform better than their peers, giving high growth with high risk.
Growth Investing in Video
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the concept.
Example #1
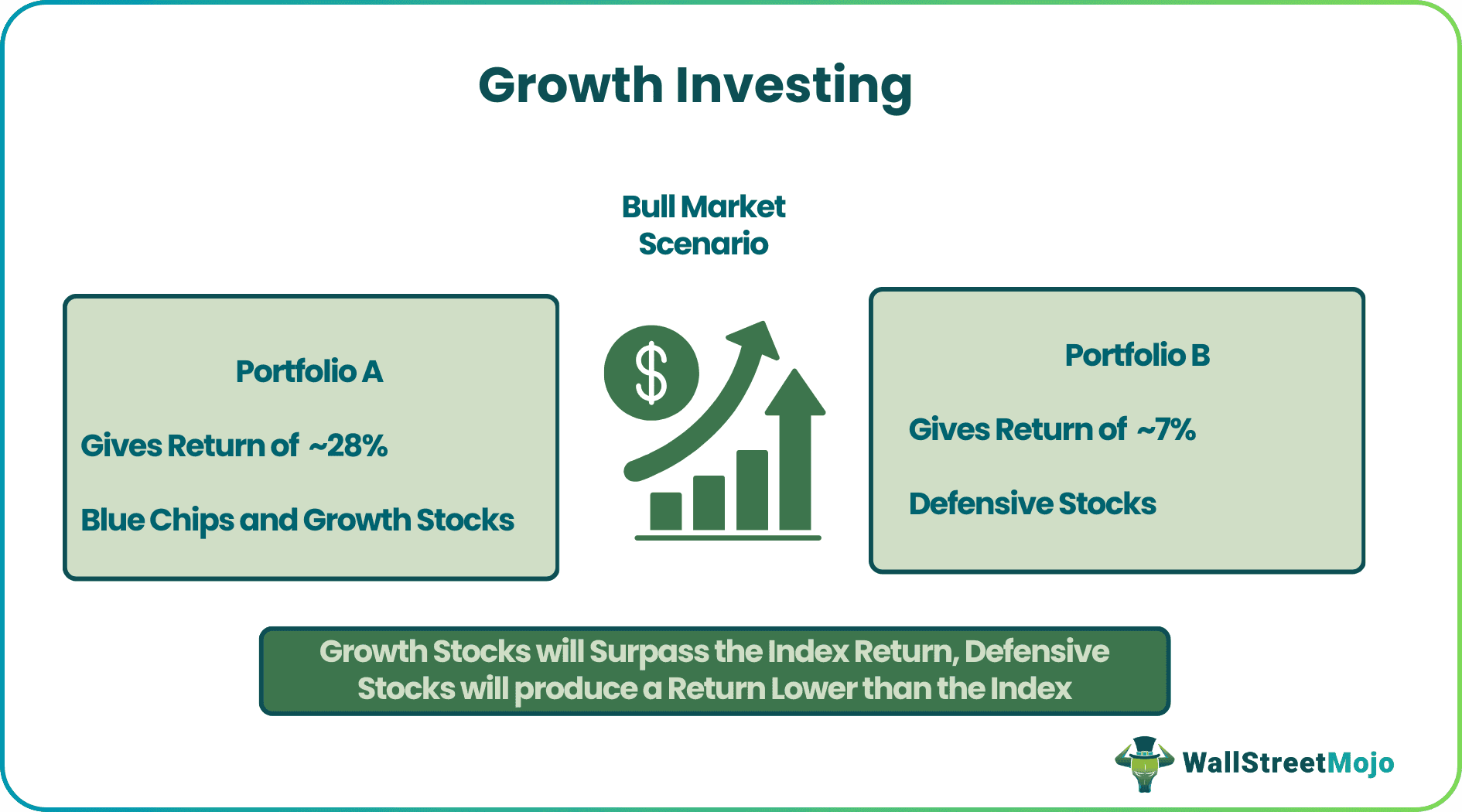
Portfolio A and Portfolio B consist of four stocks each. At the same time, portfolio A has given a return of ~28%, and portfolio B has generated a return of ~7.5% during the bull market scenario. Portfolio A consists of blue chips and growth stocks, while portfolio B consists of defensive stocks, whose profitability grows less than the GDP.
The index has generated a return of 13.5% during the period. Thus, we may conclude that during good times portfolio A will surpass the index return during a good bull market, while defensive stocks will generate a return that is less than the index.
Example #2
During the recession, we have seen that the price-to-earnings metrics tend to erode, irrespective of the quality of the stocks, because of the negative investor sentiment. Thus, richly valued blue-chip stocks become cheaper because the market will discount the overall sentiment and will drive the price lower. On the other hand, slow growers or defensive categories remain in the same range.
The reason is that irrespective of the market conditions, the price to earnings multiples or other valuation metrics remain low for these categories of stocks. So, during economic recessions or slowdowns, these slow growers resist the portfolio's drawdown.
Pros And Cons
Let us understand the pros and cons of growth investing companies.
Pros
- Growth Investing includes stocks that have the potential to provide high returns to investors. The potential of stock price movement is directly correlated with the profitability growth of the company. The higher the growth, the higher is the return.
- As the return is high, the risk to reward ratio and return on investment (ROI) remains on the higher side, which is profitable in case of long term growth investing.
- Capital appreciation is one of the primary aspects of growth Investment. Unlike other Investment methodologies, the return from this particular segment is the maximum. The primary focus remains on blue-chip, growth companies, stalwart, or market leader categories, not on defensive stocks.
Cons
- In the Growth investing approach, the fund managers concentrate on the future growth of the businesses and give the least focus on the valuation of the stocks like preference on the price to earnings, Enterprise value to EBITDA, or price to book of the stocks.
- In most cases, the focus is on the blue-chip, stalwart, market leader, or various small-cap or midcap categories where the higher valuation is on, the higher side.
- The risk is comparatively high compared to the other conventional approaches used in investing.
- The margin of safety is comparatively low in growth investing because funds are diverted towards growth companies that fall in the small-cap and mid-cap categories stocks. Due to the changing business scenarios, the profitability of these companies becomes volatile and impacts adversely on the stock prices.
- During the economic recession, this particular approach does not help retain the actual invested capital.
Growth Investing Vs Value Investing
Growth investing involves purchasing stocks that investors classify as having good future growth potential, whereas value investing is in stocks that are undervalued in the stock market. The primary differences between them are as follows:
| Growth Investing | Value Investing |
|---|---|
| Stocks are usually overvalued or fairly valued. | Stocks are usually undervalued. |
| The price earning ratio is generally high. | The price earning ratio is generally low. |
| Dividend yields are low. | Dividend yields are high. |
| They have high risk along with high return. | They have low risk with low return. |
| Volatility is high. | Volatility is low. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Growth investing includes high volatility stocks providing high returns, such as penny stocks, futures and options, foreign currency and real estate, etc.
A long-term investment perspective and a healthy risk tolerance are recommended for market participants because most growth funds are high-risk, high-reward investments.
Growth stocks are highly volatile as they do not offer dividends; the only way an investor may profit from their investment is by eventually selling their shares. If the company does not do well, it can lead to the downfall of the investor’s investment.
