Table Of Contents
Privatization Meaning
Privatization refers to transferring ownership, operation, and control of a government or public entity to a non-government or private enterprise. The process is carried out to make sure the public firm or organization becomes more disciplined and more efficient with respect to the market's expectations. There are multiple ways in which privatization could be achieved.
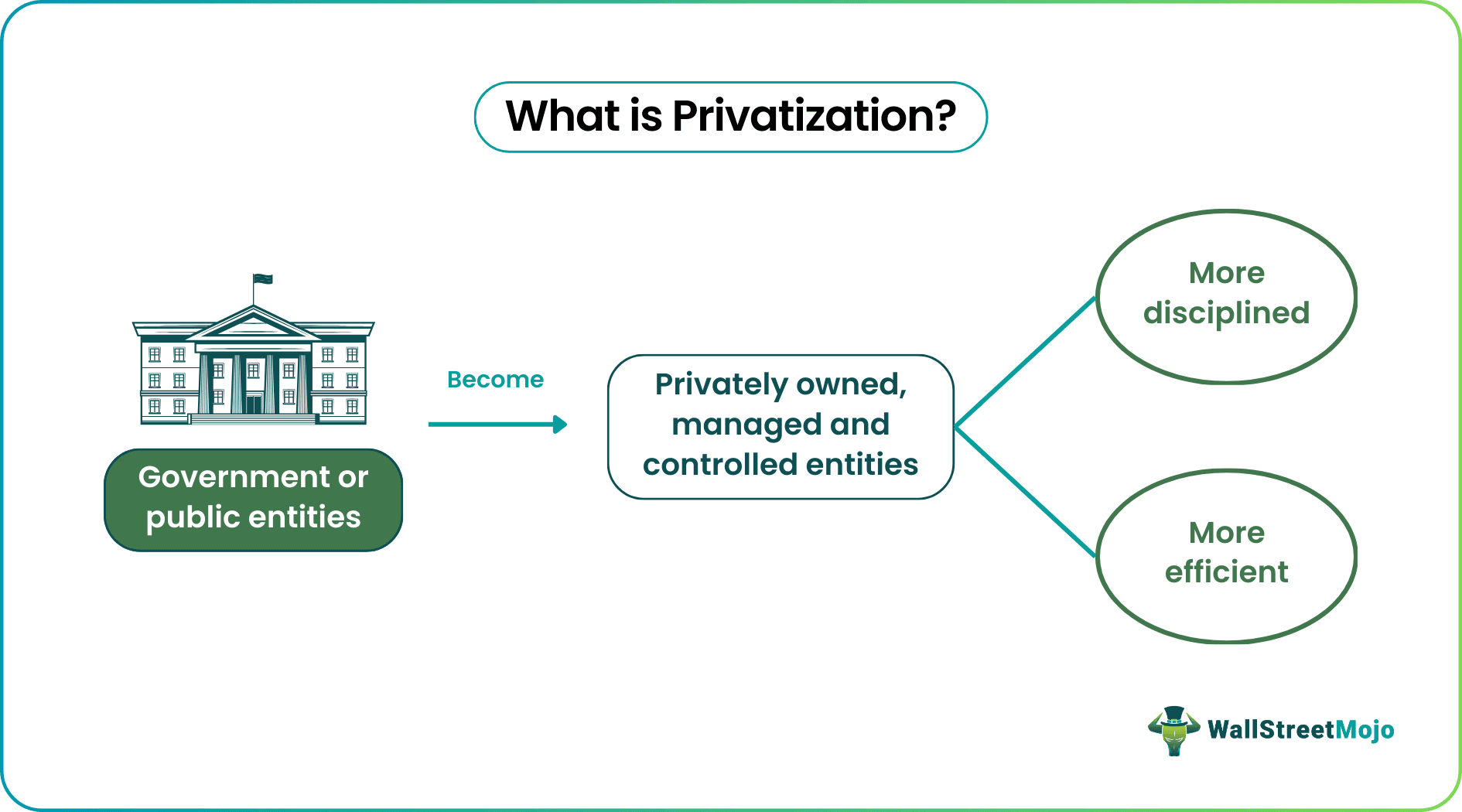
Table of contents
The concept, however, is not confined to government organizations only. Rather, private firms also undergo corporate privatization and turn into privately-held companies from publicly traded ones. As a result, the stocks of the companies become inaccessible to the general public.
Table of contents
- Privatization Meaning
- Privatization is a measure in which the ownership and management of public sector industries are moved to the private sector.
- It helps the government increase efficiency and quality of products and services by allowing private businesses to enter the sector and take control.
- Privatization can be achieved in multiple ways, including selling shares through public tender, auctions, outsourcing, asset divestiture, etc.
- From privatization in education to privatizing healthcare services, the process finds relevance and significance in almost all industries.
How Does Privatization Work?
Privatization finds relevance in either the public sector enterprise or private sector entity. The most common way of achieving it is by selling the stocks of the government-owned companies, thereby diluting their ownership and control of them.
The process is considered when a public sector entity is not performing as per expectations due to a lack of discipline. When such companies privatize, they are likely to become more disciplined, better maintained, and more efficient, maximizing profits and productivity.
Britain's Thatcher government introduced this concept of privatizing firms in the early 1980s, which has now been accepted as one of the most reliable tools of financial governance by more than 100 economies worldwide. It plays a vital role in facilitating market participation in allocating enough resources to the respective nations.
Privatization is important for any economy as it allows healthy competition for private businesses, resulting in fair pricing of goods and services. Also, when a particular sector is privatized, it leads to job creation as more and more business houses enter the industry. In addition, involving the private sector also improves the quality of goods and services.
A few major sectors hardly undergo privatization, given the confidentiality involved in the way they operate. These industries include atomic energy, defense, cigarette, railways, chemical fertilizers, hazardous chemicals, etc.
Reasons
Privatizing entities is a common scenario in many sectors. However, the most common is the privatization of banks, privatization of health care services, etc. Various reasons make governments decide to transfer their ownership, management, and control rights to the private entities. Let us have a quick look at those reasons:
- Improved efficiency
- Enhanced competition
- Better revenue generation
- No external influence
- Diversified functioning
Methods of Privatization
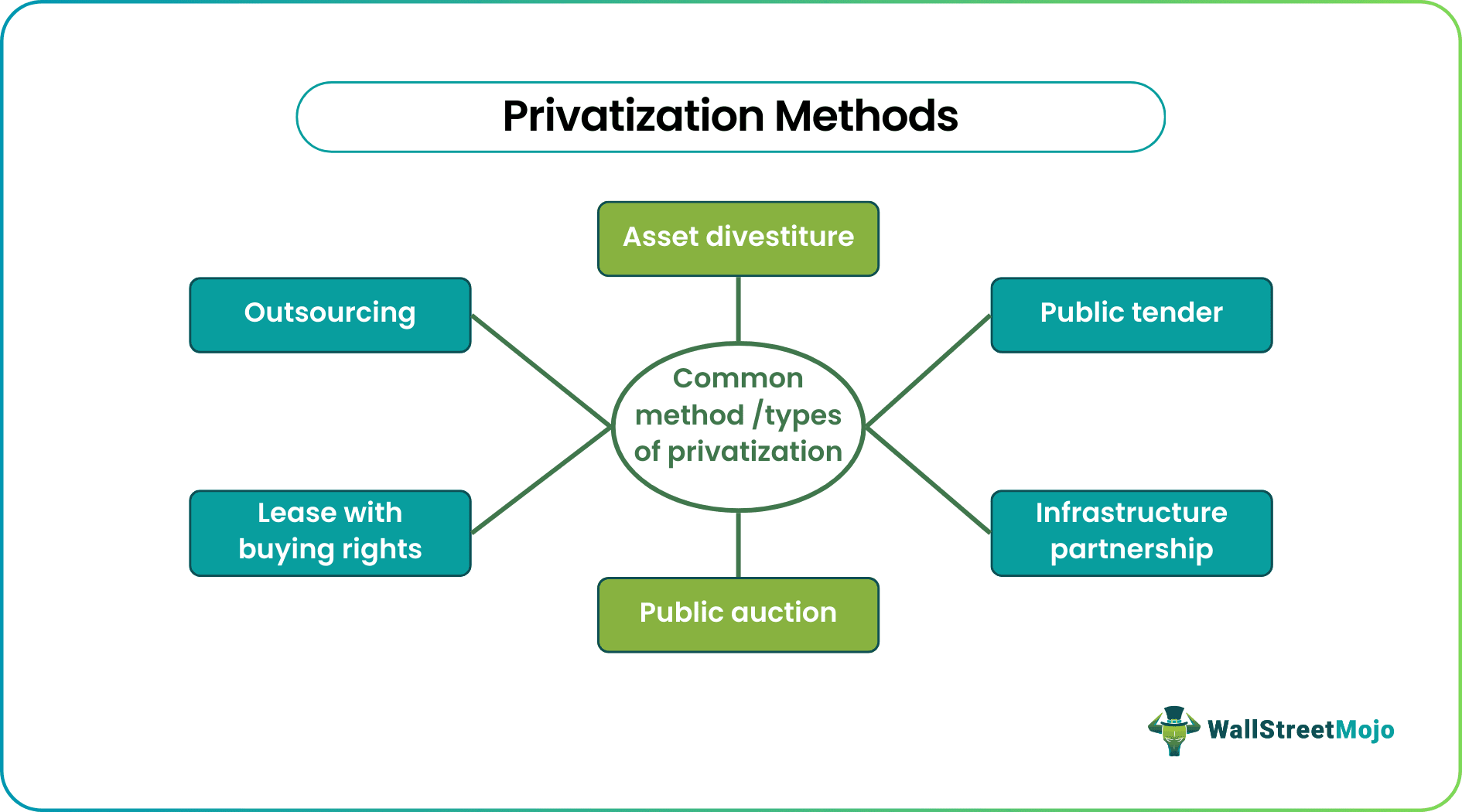
As soon as the governments decide to privatize firms, they start looking for the best ways of achieving it. There are multiple methods to achieve privatization successfully.
Asset Divestiture
The first on the list is asset divestiture. This is the process whereby the government or public sector operators raise capital by issuing the firms to private investors. There is no sale of shares in this case. As a result, the number of individual investors/shareholders increases in the economy.
Public Tender
Secondly, companies sell their shares to those with the highest bid presented through a public tender. In this case, government or public sector firms may or may not sell the entire business. Instead, they can choose to sell only a portion of it.
Infrastructure Partnership
The third privatization method is infrastructure partnership. As the name implies, this type of partnership between public-sector and private-sector firms leads to collaborations to handle infrastructure development, involving huge expenditure. In addition, it helps in risk-sharing, thereby ensuring no taxpayer gets overburdened at any cost.
Public Auction
A public auction is the next on the list. The governments or public authorities conduct auctions to sell off the firms at the highest possible rate to raise the maximum possible funds. The public-sector firms put the shares and long-term assets for sale during the process.
Lease With Buying Rights
There are instances where government lend properties to private owners for use. This is where a lease with buying rights can be a mode of privatization. There is a set of rules and regulations to follow in the process while the latter uses the public asset. However, the private owner has the liberty to buy the property in case it wishes to after paying the required amount.
Outsourcing
Last but not least is outsourcing. This is the method of privatizing firms where one firm operates and provides goods and services while the other is producing or manufacturing them. The government entities can outsource functions to private companies. The outsourcing process is one of the most cost-effective means of letting private firms enjoy control over the business.
For example, the government might conduct the maintenance of a building, but the decision to purchase or construct it would rest on the private firm to which the responsibilities have been transferred.
Impact
When privatization occurs, an economy witnesses its significant effects. As soon as the public sector firms get privatized, they are controlled by stronger management. While government organizations also have funds collected from taxpayers to operate, the private firms have to make sure they generate a net income sufficient to survive in the market. Thus, the controllers have stricter rules and standards to ensure consumer satisfaction. When they sell more, they earn more. Therefore, stronger management helps them be more efficient and more productive.
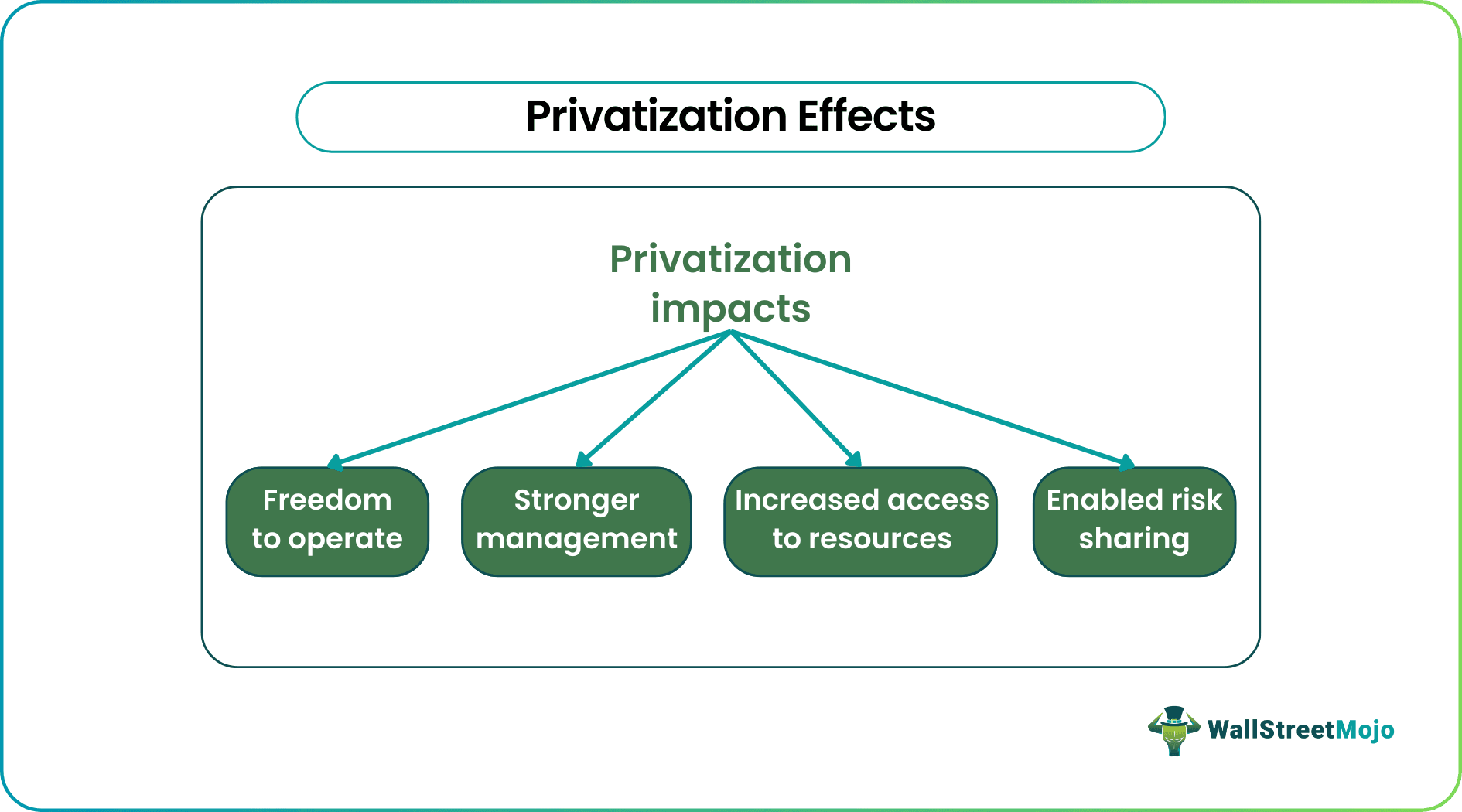
With privatization comes the freedom to operate fearlessly. When a firm is under governmental control, the decisions are, voluntarily or involuntarily, influenced by varied political, social, and economic factors. On the contrary, when the firms are privately-held, they operate the way they want in diversified markets. Moreover, there is no restriction on the use of resources. Rather, they get enhanced access to resources to produce the best output.
Above everything else, when the government firms become private, the latter still has the liberty to ask for funds from the public authorities. Especially, if the entities handle a project in partnership, the government has a private company to share the risks besides profits.
Examples
Let us consider the following examples to understand the concept and its functions well:
Example 1
The instance that led to the inception of the privatization process took place in the 1980s when Britain's Prime Minister Margaret Thatcher decided to politically privatize the commanding heights of the economy. Thus, she sold off British Airways, British Petroleum, British Airports Authority, British Telecom, and many other British housing projects. Furthermore, she preferred public share offerings over auctions to other firms. As a result, the United Kingdom witnessed a huge increase in the number of individual shareholders, which signified support for such a method of privatization.
Example 2
American States Water Company, through American States Utility Services, offers operations, maintenance, and construction management facilities to ensure proper distribution of water and efficient collection and treatment of wastewater across eleven military bases throughout the United States. The company has been doing it with respect to the 50-year privatization contracts with the country. As a result, it has been paying dividends to all shareholders since 1931, ensuring their share gets an increment every year.
Advantages & Disadvantages
The process has its own set of pros and cons. Let us a have a quick look at the disadvantages and advantages of privatization:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Resources are efficiently used | Private players may enter the market, establishing monopoly |
| Facilitates healthy competition | Less transparent |
| Risk-sharing with government | Higher cost to consumers |
| No political influence | |
| Enhanced productivity |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Privatization refers to the transfer of ownership, management, and controlling rights from government or public-sector authorities to private enterprises. From the education sector to banking institutions, governments can decide to privatize whichever entity they want if those do not perform as expected.
The government decides to privatize firms to improve their efficiency and productivity, help them work under stronger management, facilitate healthy competition, reduce their financial burden, diversify market operation, etc.
It can positively impact the economy, but it is not devoid of negative impacts. While it makes firms more efficient, productive, competitive, and profitable, the process might significantly increase the costs of goods and services for customers. Moreover, there are chances that individual investors or shareholders start acting privately, establishing a monopoly in the market.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to what is Privatization is & its meaning. Here we explain the reasons, types, methods, impact, examples & advantages of the process. You can learn more about from the following articles: -
