Table of Contents
Fed Pivot Meaning
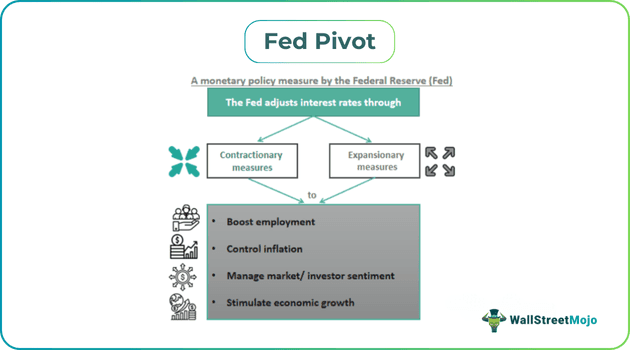
A Fed Pivot denotes the Federal Reserve's decision to shift from its existing monetary policy and undertake an expansionary or contractionary policy approach (as required) to correct situations causing economic instability. This helps maintain price stability and supports employment. To achieve this, the Fed uses monetary policy tools.
By making interest rate changes and bond purchases, the Fed can bring about significant changes in the country’s economic conditions. For instance, it can maintain the growth momentum, retain dollar value, and stop recession through such measures. Since the changes cause a considerable shift in the Fed’s monetary policies, it is referred to as a “pivot”. Studying the Fed Pivot history provides insights into the Fed's policy decisions.
Key Takeaways
- A Fed Pivot refers to the Federal Reserve (Fed) reversing its current monetary policy position, changing it to tight (or contractionary) policy from loose (or expansionary) policy and vice versa to stabilize the US economy in adverse economic conditions.
- It aims to maintain price stability and improve employment rates through interest rate adjustments and bond purchases falling within the purview of its monetary policy framework.
- The Fed lowers interest rates to inject liquidity into the markets to promote economic growth and control inflation.
- Such pivots have significant implications for every sector of the economy as they affect investments, consumer spending, and borrowing.
Fed Pivot Explained
A Fed Pivot is defined as the changes the Federal Reserve introduces to control inflation, promote employment, and accelerate economic growth. It involves tightening or loosening monetary policy by adjusting the interest rate to prompt a change in the direction the US economy takes from there. Minimizing unemployment and maintaining price stability while ensuring the country’s stock markets remain stable are some crucial objectives of such monetary policy measures.
As interest rates affect spending, borrowing, and investment activities in the economy, reducing or increasing these rates helps trigger economic growth. Some effects of such interest rate changes (increase and decrease) are:
- When interest rates are reduced, the cost of borrowing declines, and businesses, as well as individuals, can secure funds at relatively lower costs than otherwise.
- The lowering of interest rates typically leads to increased spending on products, goods, and services.
- Low interest rates may also result in increased investments in projects and other business activities.
- An increase in the interest rate will lead to opposite effects on consumer spending, borrowing, and investing, but it can attract foreign investment as investors are presented with the chance to earn higher returns than under normal conditions.
- A pivot may mitigate inflation, but it may have adverse effects on the banking sector. Any untimed or rapid pivot can negatively influence the global markets. It may also act as a trigger for volatile reactions.
Many investors and analysts believe that a pivot that goes from tightening to loosening, or vice versa, signals a shift in market sentiment. Tightening by the Fed has been known to result in a decline in stock market returns.
The Federal Reserve initiates a pivot when it identifies certain risks or patterns that could affect economic growth. For this, it monitors the economy closely and looks for adverse indications before making a pivot decision.
If the Fed believes that the US faces risks in terms of overheating in the form of inflationary pressures or increasing unemployment, it takes a contractionary monetary policy approach. It tightens the economy with an interest rate increase that slows economic growth and cools the economy by lowering the inflation level. The reverse happens when the Fed observes that the economy faces low inflation and high employment; it takes a loose or contractionary monetary policy approach. It does so by pumping extra liquidity into the economy and the markets to stimulate growth and prevent a recession.
After the Fed takes these actions, the corresponding effects take more than a week to several months to materialize. After achieving its goal, the Fed typically sticks to its monetary policy for a while to maintain stability and prevent market disruptions.
Examples
In this section, let us study some examples to understand the topic.
Example #1
A January 2024 Brookings post highlights the Fed’s actions in the wake of Covid-19. In response to the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020, the Federal Reserve made a significant shift by implementing large-scale asset purchases, commonly referred to as quantitative easing, to support financial markets and provide liquidity. As the economy began to recover, the Fed subsequently announced a pivot towards tapering, gradually reducing the rate of asset purchases.
This was a strategic monetary policy response initiated to adapt to the changing economic conditions and strengthen the US economy to ensure economic recovery.
Example #2
A December 2023 New York Times article raised questions about the Fed’s decision to pivot and lower interest rates at different junctures in the coming year. Investors believe the economy is likely to see a decline in borrowing costs with multiple interest rate cuts (the tentative plan is to cut interest rates thrice in 2024).
Experienced investors and analysts at Wall Street are not entirely convinced about the effectiveness of this decision, given their views on how the Standard & Poor 500 (S&P 500) has been moving. If this happens, global stocks and bonds are expected to perform well in a low-inflation environment. Europe’s central bankers, Wall Street experts, and analysts from various financial institutions have shown skepticism about how useful, effective, and timely these rate cuts will be in 2024 and beyond.
This Fed pivot 2023 article shows how various market forces, participants, and other players begin predicting the results of a Fed pivot after it is announced or anticipated. It also throws light on how these pivots affect decision-making across various sectors of the US economy and beyond.
Importance
After the 2008 financial crisis, the Federal Reserve implemented a series of interest rate reductions to stimulate economic growth. However, in 2015, a pivot began as the Fed embarked on a gradual path of interest rate hikes to restore monetary policy and mitigate inflationary pressures. From this, we can see that a pivot plays a key role in deciding the fate of an economy and its financial markets, making it significant in every aspect.
Below are some points that outline its importance.
- Effective monetary policy: The Fed uses the pivot to adjust its monetary policy to achieve its goals. It does so by pivoting strategically to impact economic growth, borrowing costs, and inflation rates, promoting economic stability.
- Economic stability: It stimulates economic stability and maintains it through suitable actions. These actions include managing economic downturns and inflationary pressures to reduce risks and encourage sustainable growth. As a result, serious recessions and periods of high inflation that may adversely affect businesses and individuals can be avoided.
- Investor and market sentiments: Financial markets and investors closely monitor the Fed's actions. In-depth knowledge about a pivot strategy boosts market confidence and impacts investor perspectives and actions. Consequently, overall market sentiments, asset prices, and interest rates are impacted, leading to smoother functioning and reducing uncertainty.
- Implications towards the global economy: Since the dollar as a currency is the gold standard of the global economy, the Fed’s decision to pivot at any given point in time directly affects its valuation. Hence, any change in the Fed’s views directly affects the global exchange rates, financial markets, and capital flows.
- Indication of policy shift: These pivots indicate a drastic shift in the monetary policy. A pivot changes market expectations, affects economic stability and growth, and impacts investment decisions. Hence, following Fed pivot news is crucial for making various business, commercial, investing, borrowing, and other decisions.
- Adjustment to strategy: By closely watching the Fed’s pivot and interpreting the policy shift, investors, businesses, and policymakers can adjust their strategies to their advantage.
