Table Of Contents
Present Value Definition
Present Value (PV) is today’s value of money you expect from future income and is calculated as the sum of future investment returns discounted at a specified level of rate of return expectation.
This concept is used in the valuation of stocks, bond pricing, financial modeling, and analysis of various investment options. The investor calculates a present value from the future cash flow of investment to decide whether that investment is worth investing in today. The expected cash flow of the future is discounted at a discount rate, which is the expected rate of return calculated inversely with future cash flow. Inflation reduces the value of money in hand since the price of goods and services rises due to inflation, which means the amount worth today might not be equally worth tomorrow. PV calculations make sure the inflationary impact is calculated from either the inflation rate or the expected rate of returns.
How to Find Present Value?
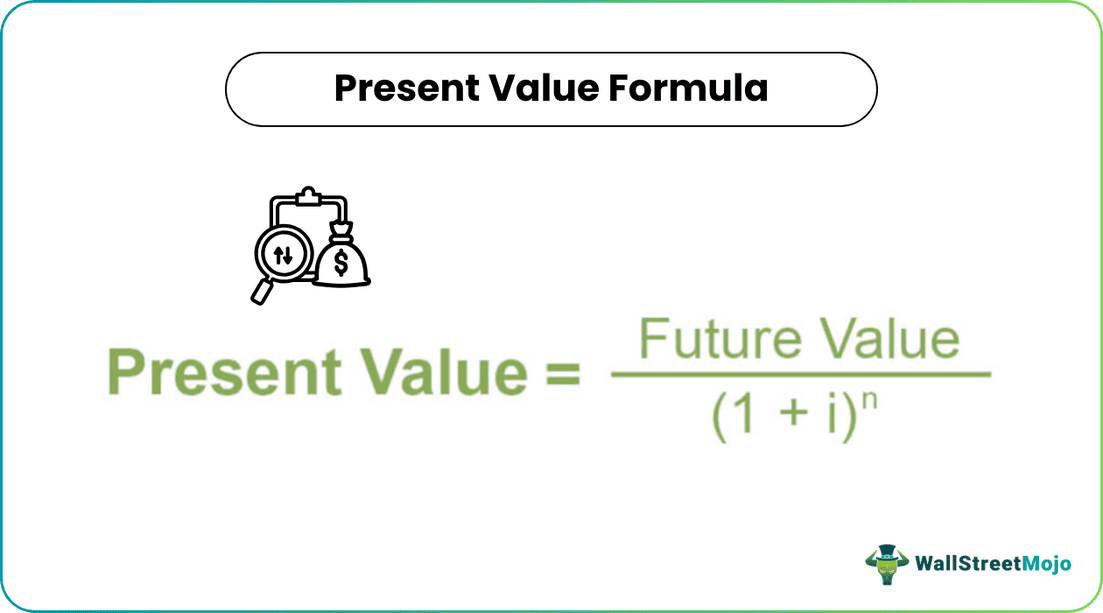
PV = Future Value / (1+i)n
- i = interest rate
- n = investment period
Step #1 - Put expected future value of the investment in a formula
Step #2 - Put Expected rate of return on your investment
Step #3 - Number of the period you are investing
Examples of Present Value
Example #1
Mr. X wants $10,000 after three years. The interest rate available on a specific investment, which he is interested in, is 4% per annum. How much he should invest today to receive the desired amount.
Solution
Given,
- Future Value = $10,000
- Interest = 4% per annum
- Period = 3 years
Calculation of Present Value can be done as follows,

- = $10,000 / (1+0.04)3
- = $8,889.96
i.e., Mr. X should invest $8,889.96 amount today to get the desired amount in 3 years.
Example #2
Mr. A has $100,000 in hand from his savings; he wants $200,000 after ten years. He has three options, i.e., either.
- Bank deposit at a rate of 4% per annum compounded quarterly.
- Government bonds at 3.85% for ten years.
- Invest in a Hedge fund with expected returns of a minimum of 8% per annum. Which investment option is best to achieve his goals?
Calculation of Present Value for Option A can be done as follows,

=$200000.00/(1+1%)40
= 134330.63
Similarly, we can calculate PV for Option B and Option C

Looking at the table above, the answer seems quite simple: an investment in option C, i.e., hedge funds give more returns, which help Mr. A to achieve his future investment returns. In contrast, investment options of bank deposits and government bonds will need an additional investment of $34,330.64 and $37,077.12 on the current amount in hand to achieve the desired return of $200,000.
At first, the choice seems simple to Mr. A to select investment option C. Still, investment in hedge funds also involves the risk of loss that needs to be considered, which means there is no guarantee that investors will earn expected future returns. While Option A and B, which are bank deposits and investment in government bonds, may not provide expected returns but include very low risk on investment.
Depending on Mr. A Financial condition, risk capacity decisions can be made. While a conservative investor prefers Option A or B, an aggressive investor will select Option C if he is ready and has the financial capacity to bear the risk.
Importance
- Important for analysis: For every business, it is important to understand future cash inflow or outflow from business; PV calculation becomes necessary when you expect a certain level of future cash flow.
- Fundamental concept: To calculate the value of various investments like bonds, stocks, bank deposits, insurance, and pension funds, you need PV calculations.
- Time-value of money: level of interest rate, inflation, and periods helps in making an investment return you expect in the future from your investment. What is the current value of future worth that helps make investment decisions?·
- Inflation effect: They make sure that the inflation effect on money is calculated over time by considering either the inflation rate or discounting the expected rate of return from future cash flow.
Benefits
- Investment Decision: This method helps in making investment decisions since it calculates the current value of future cash flows in investment. If the investor does not have enough to invest from which he expects future cash flow, he would prefer to select other investment options.
- Purchasing Power: Money worth today is more than the money worth tomorrow, which means a value of $100 today might not be equal to $100 after a year because inflation reduces the value of money. Present considers inflation and provides details on whether today's investment is enough for future cash flow.
- Discount Rate: The rate of return on investment is called a discount rate. In other words, a combination of the time value of money, which reduces over a period, and interest rate, which raises the value of your investment. A discount rate is used to calculate the PV of the investment in case of a settlement by discounting future value.
Limitation
- No guaranteed expected return: We calculate the PV by assuming interest rate over investment, but in reality, many investments cannot guarantee the rate of returns according to expectation, e.g., in the case of bank deposits, banks can change interest rates, which depends on other economic factors as well. Except for government bonds where risk is less and expected returns are given, no other investment can provide exact present value.
- Inflation vs. Interest: If the inflation rate is higher than the interest rate on investments, then investment becomes worthless. Suppose the value of money you hold today is higher than tomorrow people prefer to spend it today than invest in tomorrow.
Present Value vs Future Value
| Basis | Present Value | Future Value |
| Definition | The current Value of Future Cash flow is called the Present Value | Future cash flow resulting after a certain period on today's investments is known as Future Value |
| When | It focuses on value at the beginning of a period | Future Value focuses on Value at the end of the period |
| Rate | Interest rates and discount rates both need to consider in the calculation of PV | Only the interest rate is considered while calculating future value. |
| Decision | It is important to make a decision today regarding a particular investment. | Future Value provides a number that will receive in the future, which does not affect decision-making today. |
| Methods | Discounted | Compounding to get resulted amount on a future date |
| Views | It is required to get a certain future value. | Future value provides the value of the current investment in the future. |
Conclusion
Present value calculation helps make many investment decisions for the business and individuals; However, the exact value cannot be calculated because of changing interest rates on many investments and inflationary effects; this calculation still helps in estimating individuals' money worth in terms of their future expectations.
Since the present value is calculated at the beginning of the period while making investment decisions, it includes some assumptions regarding inflation and the rate of returns on investment, which should be realistic and proper analysis; a comparison of various investment options is necessary to find the right plan to invest in.

