Table Of Contents
Rolling Forecast Meaning
A rolling forecast is a financial modeling tool used by management that helps the organization continuously forecast its state of affairs over a set time horizon; for example, if it is prepared for the twelve-month rolling period, it takes into consideration the next twelve months for the forecast as soon as the actual data of one month is finalized.
The implementation and preparation of such a model is a tough task. However, at the same time, it has its exclusive advantages, which are an essential part of any business entity in today’s cut-throat competition where information is passing at light speed, and correct decisions at the right time can do wonders.
Rolling Forecast Explained
Rolling forecast takes into consideration historical data to figure out the numbers applicable for a future date. From financial reporting to budgeting, the rolling forecast method is used to serve various purposes.
With the development of a computerized accounting system, it is easy and quick to prepare the rolling forecast numbers and books of accounts as all the departments are interlinked through ERP – Enterprise Resource Planning systems. However, an organization must always monitor and analyze the rolling forecast numbers with actual financial results to implement changes. Also, the simulation process should be run with the maximum variable. This helps understand the impact of changes in one variable on final numbers.
According to one survey, the rolling forecast is being used by 42% of the organization, while the rest are being seen switching to the static forecast method, which is prepared once a year without any frequent changes made. Thus, based on the requirement and after careful analysis, an organization should move to a rolling forecast model from a static budget or vice-versa.
As we explore this topic, it’s interesting to note how a deeper understanding can enhance practical budgeting skills. For those looking to expand their expertise, consider checking out this Financial Planning & Analysis Course, which delves into this further."
Components
To understand what a rolling forecast is, it is important to be aware of the elements or factors it considers. Here is a list of a few of them:
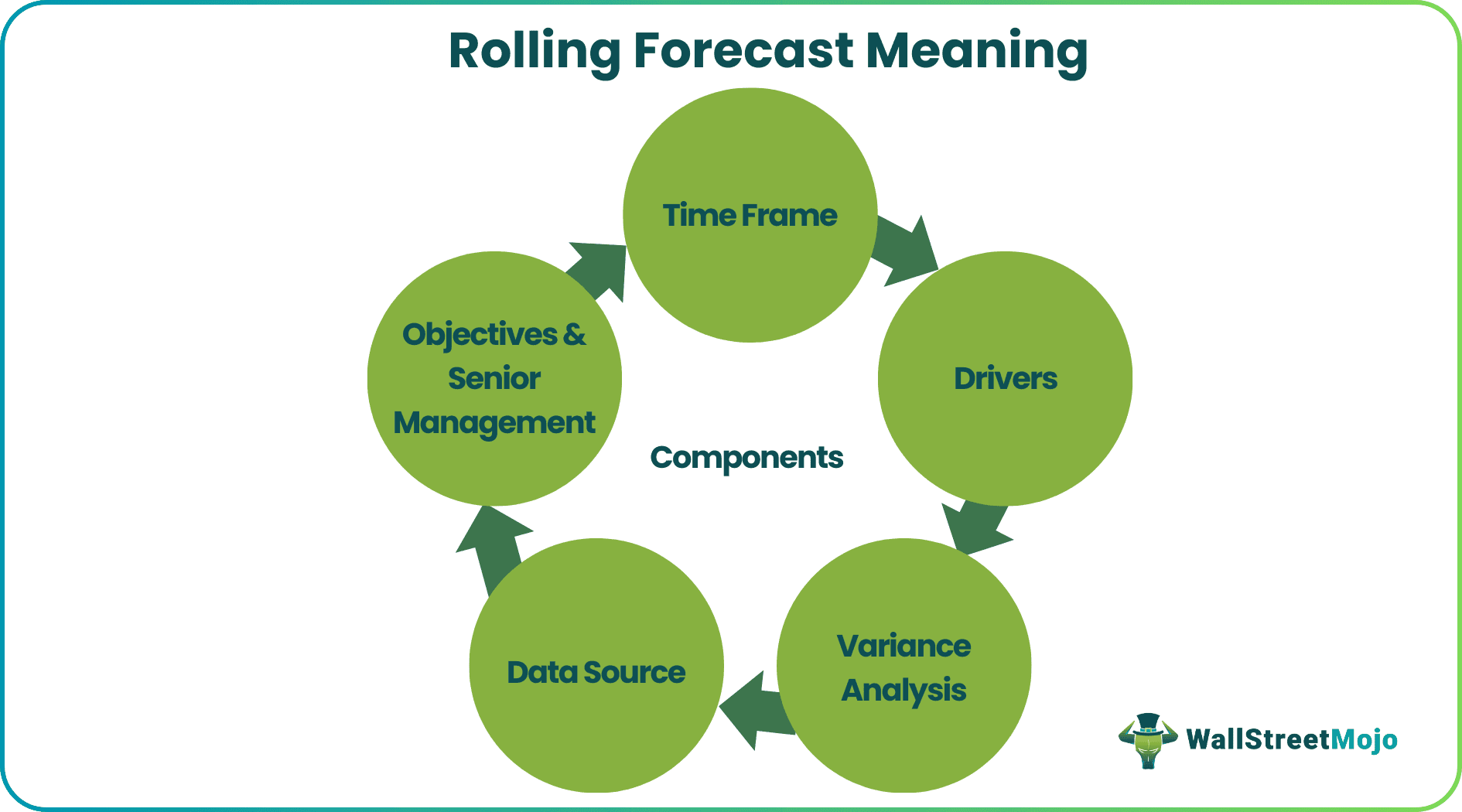
#1 - Time Frame
While preparing a rolling forecast model, any business must decide whether they want to update the forecast data weekly, monthly, or quarterly as analyzing the actual results with the forecast and then updating the next period forecast is a time-consuming and daunting task. In most cases, this is prepared over twelve months.
#2 - Drivers
The forecast must include the drivers and not just the numbers of total revenue or expenses. Let us understand this as follows:
If a car-making company wants to do a rolling forecast of its revenue. It must include the quantity and sales price of the model, which is selling the most and creating maximum revenue.
So next time, when there is an increase in revenue, it should be able to explain whether the increase is due to an increase in selling price or extra quantities sold. Similarly, if there is a decrease in revenue, it should explain whether the decrease is due to discounts offered or fewer quantities sold.
#3 - Variance Analysis
After the books of accounts are prepared for a month, the results must be compared with forecasted numbers. Depending on the outcome of variance analysis; appropriate changes should be made in the next period forecast. For example – if a Telecom company has forecasted that it has to pay a tower rental fee of $25,000 each month and because of integration and recent acquisition, it has stopped taking services from that tower. This $25,000 should be excluded from the next month's forecasted expenses.
#4 - Data Source
The data source must be free from bias when the forecast is prepared. For example, it should be included after an in-depth analysis as bonuses of senior leadership are tied to their department performance. A biased leader might provide a very conservative number for the forecast and then exceed the forecasted figures in actual results, which will lead to unethical practices. Also, the forecasted numbers must not come from someone who does not understand the complete process and might make some forecasted figures impossible.
#5 - Objectives & Senior Management
The rolling forecast model involves a lot of analysis, frequent changes in the forecasted numbers, and quick decision-making. Therefore, this model needs the support of its senior management for successful implementation. Plus, it should be aligned with organizational objectives.
Example
Let us consider the following rolling forecast example to understand how it works:
- Please consider the below tables in a continuation that shows the numbers from January 2019 to March 2020. If we believe that X Ltd. has prepared a rolling forecast for twelve months, then X Ltd. will initially prepare forecast data for the Jan – Dec 2019 period.
- As soon as the financial reports are ready for Jan 2019, they should be compared with forecasted data, and variances should be considered for future periods inputs.
- After Jan 2019 actual results, the table will show the forecast numbers for Feb 2019 to Jan 2020 period. Similarly, once the actual numbers for Feb and March 2019 are out, the rolling forecast model shows the forecast of Mar 19 to Feb 20 after Feb results and the forecast of Apr 19 to Mar 20 after Mar 19 results.
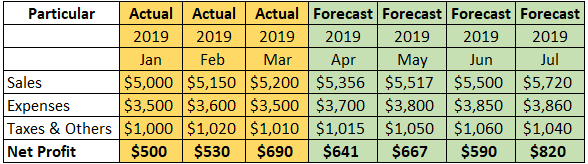
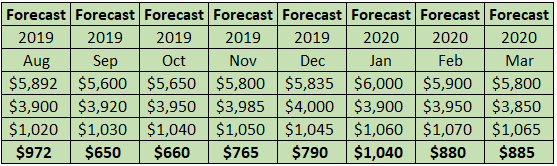
For detailed calculations, please refer to this excel sheet.
Advantages
- It considers monthly changes, which are essential for risk assessment.
- Helpful to senior leadership in decision making
- It helps in setting up a proper Financial Planning & Analysis team
- Highlights the key factors and changes every month.
- Does not create pressure to prepare the complete yearly forecast after the year-end. This is because the next 12 months' forecast numbers are always available.
- It keeps track of essential drivers that are critical to any organization's success.
Disadvantages
- It is a time-consuming process
- Many organizations find it challenging to implement
- Frequent changes are challenging to process period over period

