Table Of Contents
What Is The Full Form of ERP?
The full form of ERP stands for Enterprise Resource Planning. ERP is a process of integrating basic processes such as Finance, HR, Manufacturing, and Supply Chain into one single integrated system. ERP is a system that helps organizations to run their operations by integrating the basic operations systematically and smoothly.
ERPs are the industry's future as the industry is going all out on software and automated operations. It derives many benefits to the organizations in decision-making, cost reduction, time reduction, automation of processes, centralized data, and effective integration of Departments.
Full Form Of ERP Explained
The full form of ERP software is Enterprise Resource Planning. It is a software solution which in integrating and managing the core process of any business along with its important data. This process is used so that the operation can be streamlined to make it centralized and unified. It leads to enhanced co-operation and improves the level of efficiency across all departments and functions.
An ERP system comprises different enterprise resource planning applications that talk to each other and share a database. ERP uses the centralized database for various business processes, reduces manual interventions, and simplifies business workflows. The full form of ERP software denotes some systems typically containing dashboards where users can look at the real-time data collected across the business to measure productivity and profitability and plan its course of action. It is not just the database. It is an integrated system synchronized with the data of an organization’s various departments.
Types
There are basically four types of ERP software which are as follows -
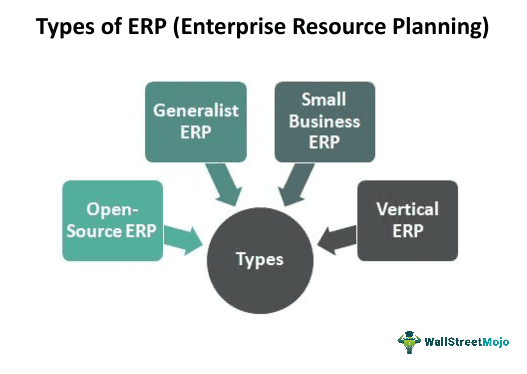
#1 - Generalist ERP
Generalist ERP is those ERPs that are strong in customization and integration to match the organization’s changing needs. These ERPs adapt to the processes of the industries very soon. There is also a high demand for these types of ERPs in the market.
Open-source ERPs increase usability and user adoption as these ERPs can establish a highly customized process. But still, these open-source ERPs are a small fraction of the ERP market.
#3 - Small Business ERP
These ERPs are modularized with pared-down features. Instead of delivering a fully integrated system, this enterprise resource planning serves one or two business processes and leaves out the others.
#4 - Vertical ERP
These ERPs are those who are Industry-specific ERPs. Often the vendors of these ERPs are Startups or smaller companies trying to focus on a niche, such as supermarket distribution, construction, or retail fashion.
Examples
We can identify a number of examples of ERP existing in the market.
- An example of a Generalist ERP is NetSuite ERP.
- An example of Open source is Odoo ERP.
- PeopleSoft is an example of small- business ERP.
- Microsoft Dynamic AX is an example of Vertical ERP.
The above are commonly used systems that are available for use in today's business environment.
Components
There are five main components full form of ERP system that is enterprise resource planning, which is explained below:
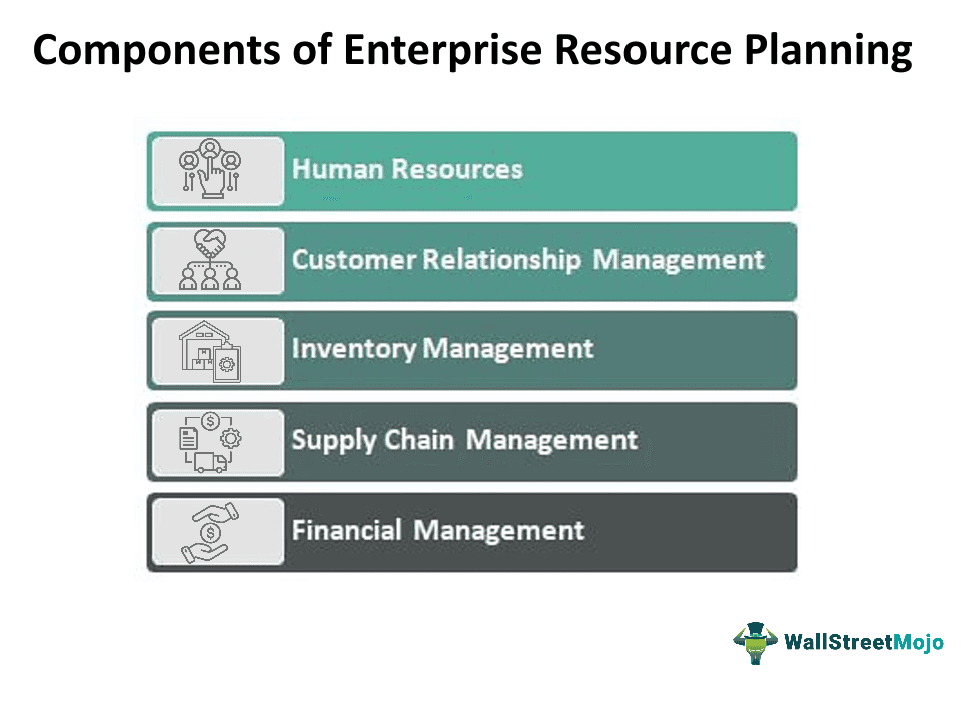
#1 - Human Resources
The priority for every organization should be first to manage all the employees. The HR ERP component should handle the whole structure of the employees’ management, from onboarding to off-boarding and from benefits to timekeeping.
#2 - Customer Relationship Management
The second most priority should be to manage the customers and leads because, without them, any business's survival would be of utmost difficulty. CRM ERP allows the organization to keep track of all the customers and leads within the software. The CRM ERP even helps in optimizing sales as well as marketing efforts.
#3 - Inventory Management
Inventory management is one of the most collaborative components of full form of ERP system. This component's main process is managing order fulfillment and stocking in the warehouse. Inventory management works simultaneously with the Supply chain management components.
#4 - Supply Chain Management
The ERP’s supply chain management component is the most crucial because it is difficult to determine an efficient supply chain. There is a requirement for the best SCM features in the software to optimize the supply chain and collect data in real time.
#5 - Financial Management
Since every business involves the process of money in and out from one to another, whether to customers, debtors, creditors, paying employees, or paying for transportation. The financial management component works with all of the components in the ERP system.
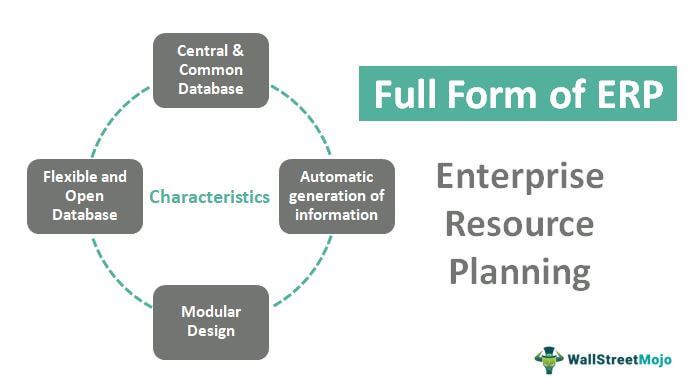
Characteristics
Some important characteristics of the process are mentioned below:
- Central & Common Database - Implementing ERP in an organization, requires a Common and centralized database. All the data is entered and stored only in one place and then utilized by all the departments. And this centralized database becomes one of the main characteristics of ERP.
- Automatic Generation of Information - An ERP provides a business with the business intelligence tools such as executive information systems (EIS) and decision support systems (DSS) to allow manufacturing operations to make more effective decisions about their overall production process.
- Modular Design - The ERP system incorporates all business models, such as manufacturing, financial, accounting, and distribution. All the modules take care of their functions, but the ERP software integrates them to provide a seamless data flow between the various modules.
- Flexible and Open Database - ERP software is dynamic and flexible as it needs to evolve as per the organization's changing needs as the organization needs are continuously changing. Therefore, the ERP also evolves with the changing needs of the organization.
Advantages
Let us look at some of the advantages of the concept.
- Reduction in Time and Costs of litigations.
- Elimination of unnecessary operations and data.
- Accurate and timely access to reliable information.
- Optimization of Business processes.
- The ability to share information between all components of the organization.
Disadvantages
Some important disadvantages of the concept are given below:
- The system can be difficult to use.
- Reduction in sharing internal information between the departments can reduce the efficiency of the software.
- The installation of Enterprise Resource Planning software is costly.
- The benefits are seen over some time and not immediately.
- Success depends on the workforce's skills and experiences, including education and how to make the system work properly.
ERP Vs CRM
Both the above are two different types of softwares commonly used in the business environment. However, there are a lot of differences their meaning, usage, purpose. Let us identify the differences.
- An ERP system is integrated software that incorporates data from all the departments and processes it to use in the organization. In contrast, CRM is a part of that process that includes the customer modules' data for higher sales and profit-generating opportunities.
- ERP software is the software’s superset, whereas CRM is just a subset of computer software.
- ERP mainly performs back-office activities, whereas CRM performs front-office activities.
- ERP’s main objective is to reduce the organization’s operating costs, whereas the main objective of CRM software is to increase the organization’s sales.
- The ERP software is Enterprise Oriented software, whereas the CRM software is customer-oriented.
