Table Of Contents
Insourcing Definition
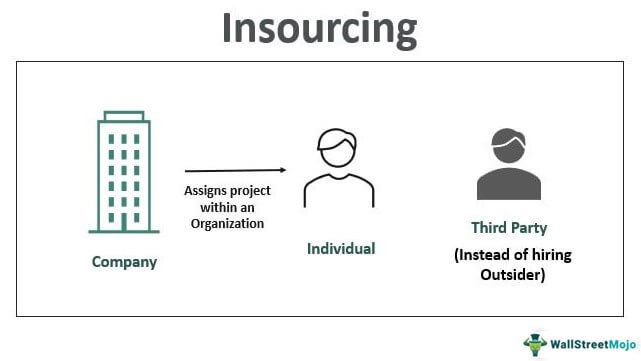
Insourcing refers to assigning a project to an individual or a department within the organization instead of hiring a third party or outsider. In other words, it uses internally developed company resources to perform vital projects rather than someone from outside the company.
Generally, insourcing offers a company better control over its decision-making process while enhancing the speed and precision of execution. However, in some cases, it may be more expensive than outsourcing because it often involves teething issues of setting up a new process or a different division within the organization.
Key Takeaways
- Insourcing means allotting a project to an organization's individual or department rather than hiring a third party or an outsider.
- It requires a process like understanding the different aspects of the existing contract, considering financial and non-financial factors,
- ensuring the current tasks can successfully perform the charges, and changing the organizational structure to back the new internal delivery.
- Insourcing saves time and provides speedy delivery, but outsourcing is only possible if it requires sufficient time. In addition, it gives opportunities to learn and hone skills.
- Moreover, it also helps internal employees understand the project quickly and efficiently as they work closely with the project leads.
How Does Insourcing Work?
The implementation needs to go through the following steps: -
- The management needs to understand the different aspects/ factors of the existing contract. These factors include whether the contract expires or has to be terminated, pricing, and other similar post-termination implications.
- The management should consider all the financial and non-financial factors associated with the transition from outsourcing to insourcing. It is to be noted that building a business case for introducing insourcing is not just a comparison of the costs of outsourced resources and internal resources.
- The management should ensure that the existing staff can do the tasks internally successfully. Hence, the team must be trained to prepare for upcoming challenges and develop operational capability.
- The company may need to change the organizational structure to support the new internal delivery. The structural change primarily includes redefining the job description, sizing, and training.
- One must prepare a detailed transition plan because outsourcing to insourcing represents a significant risk to the business.
Example
Let us take the example of a soft drink manufacturing company planning a new soft drink brand. Its marketing strategy primarily involves reaching a larger audience through social media campaigns. The company has a team with the technical expertise required to run the social media campaign. However, this team has never worked on social media campaigns for a new product launch. So, should the company outsource the project or hand it over to the internal team?
Given the high stakes of a product launch, the company may initially hire a third party for the social media brand for its new soft drink. However, once the social media campaign is up and running, the internal team can get it back, and that will be the process of insourcing in the end.
Reasons for Insourcing
- In today’s world, business expansion, coupled with the need to reduce cycle time, has necessitated the increased use of an agile workforce. Outsourced contracts slow down the process, so such time-sensitive projects are better handled internally.
- In some cases, it has been observed that the poor quality of the outsourcing resulted in problems that, in turn, led to huge losses. One can avoid such instances through insourcing as it offers better control.
- It has also been noticed that social capital and knowledge sharing are stronger when employees are in relationships within the organization. Trust plays a vital role in social capital and knowledge sharing.
Why is Insourcing better than Outsourcing?
- Insourcing saves time and facilitates speedy delivery, but outsourcing is impossible because it requires a longer time.
- The employees get opportunities to learn something new and hone their skills, while the employer can access the best internal talents.
- Internal employees can understand the project quickly and better as they work closely (physical presence) with the project leads. That is not possible in the case of outsourced projects.
Benefits
- It provides the opportunity to work closely with the team members.
- It significantly lowers the cost of employment.
- It offers the advantages of easy and smooth communication.
Limitations
- Sometimes, the newly appointed internal team may incur higher costs than offshore resources.
- It is difficult to identify a set of people appropriate for the new project at such short notice.
