Table Of Contents
Outsourcing Definition
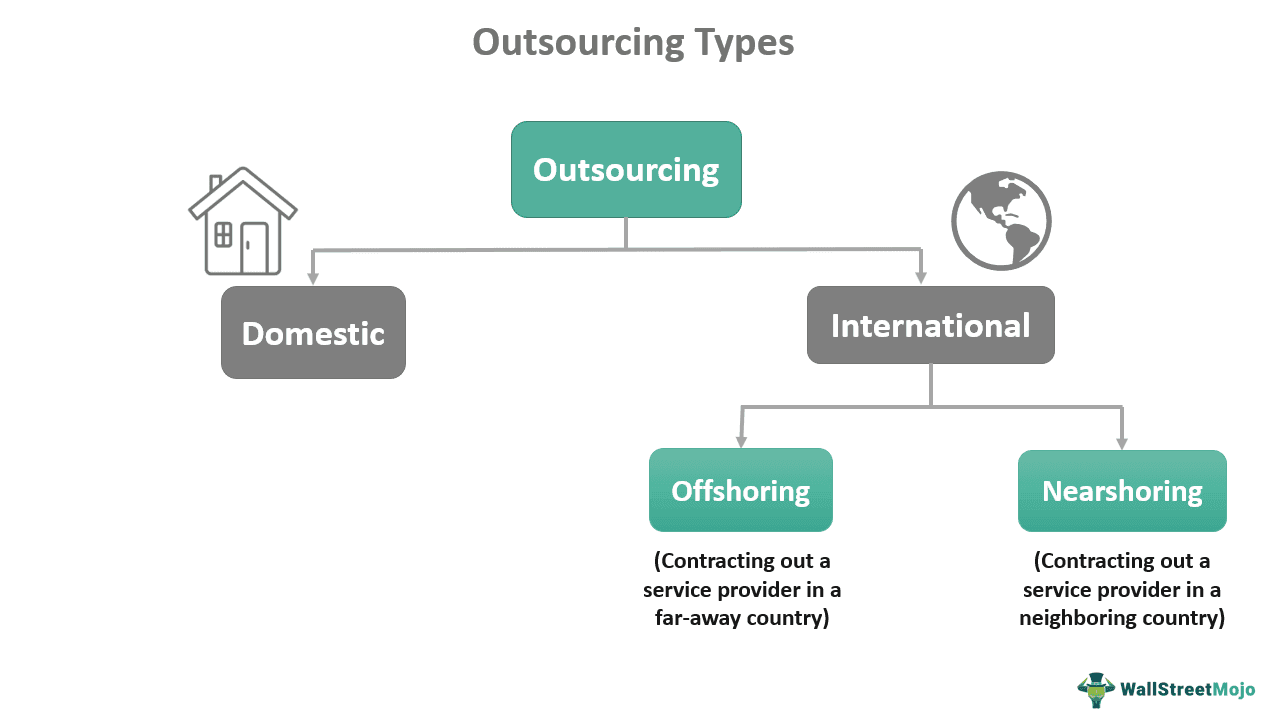
Outsourcing refers to contracting out specific business processes to a third-party or specialized service provider, i.e., an individual or company. Companies select external resources to perform tasks, services, or projects that they had previously handled on their own. It could be either domestic or international (offshoring and nearshoring).
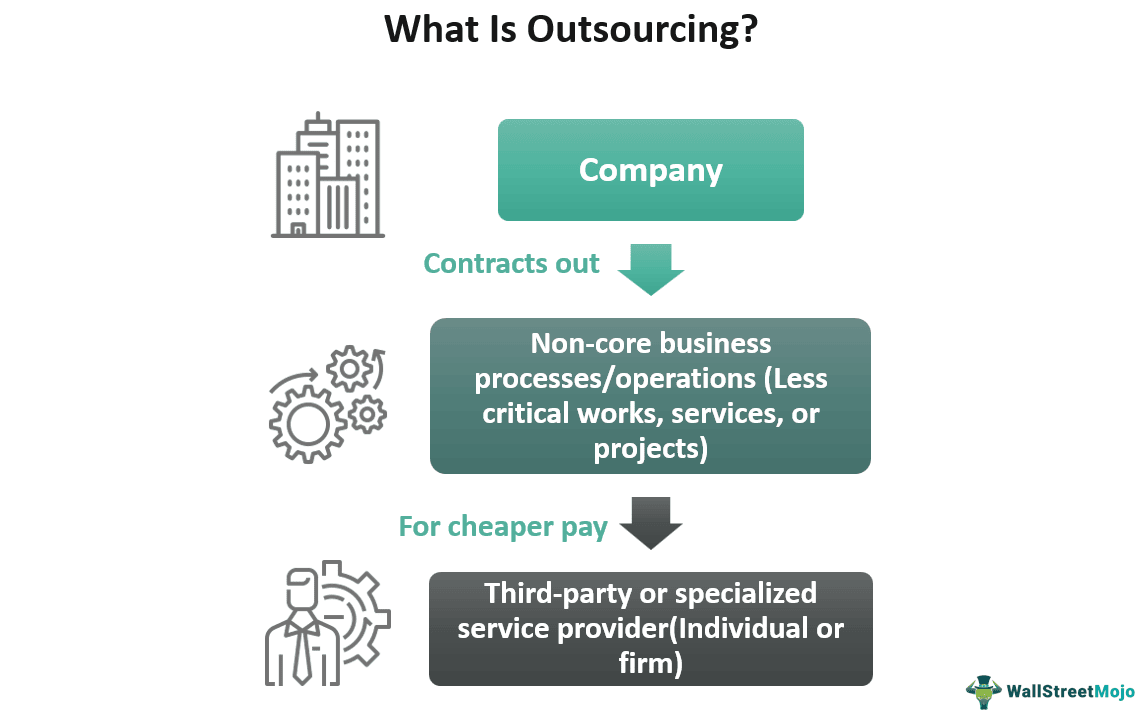
Opting for this strategy allows a company to focus on its core business operations while entrusting non-core or less vital activities to the contractor for cheaper pay. Furthermore, it leads to lower operating, overhead, and labor costs and higher efficiency, productivity, and competitiveness. It also saves
Key Takeaways
- Outsourcing is the strategy of delegating in-house work or parts of business processes to external resources, including individuals and organizations, to achieve better outcomes.
- It lets a company concentrate on its core business operations while allocating non-core tasks to a contractor for a lower fee.
- It is an effective way to achieve better outcomes and results in lower operating, overhead, personnel costs, and increased efficiency, productivity, competitiveness.
- Contracting out can sometimes become challenging due to communication barriers, risk of losses, data security, and quality issues.
How Does Outsourcing Work?
Outsourcing is the process of contracting an individual outside the organization or an external workforce to accomplish specific activities on time. It helps lower the workload and to achieve successful results. It begins with the company signing a contract with the contractor. This could include various areas like sales outsourcing, where companies delegate sales tasks to specialized service providers, improving efficiency and scaling their operations.
For example, 1840 & Company is a popular BPO partner that businesses turn to for sales outsourcing, offering dedicated sales teams to handle lead generation, prospecting, and closing.
This third-party, specialized service provider is responsible for carrying out business processes delegated to them. Based on the selection of the party, it can be domestic and international. It is further subdivided into offshoring (contracting out a business in a far-away country) and nearshoring (contracting out a business in a neighboring country).
When a corporation receives a large project, it usually divides it into teams and sets a deadline to complete it. Even yet, if the workload is heavy, the organization will look for small businesses or freelancers to help with some of it. These outsourcing companies or individuals will finish a part of the project and submit it to the larger organization. Their only point of contact here will be the company, not its clients.
However, the workload is not the only reason to outsource, and there are many others. One of the most common reasons for outsourcing is because the company believes they do not have the right workforce or specialized team for specific activities after taking on a project. A company can undertake the duties, but sometimes they outsource them to businesses known for producing better outcomes to meet a goal.
Contracting out primarily focuses on cost-cutting strategies as an organization cannot always be in the process of continuous hiring. With that said, many external factors can impact the industry. For example, the work-from-home scenario due to the COVID-19 pandemic has created a crisis in the Indian outsourcing business. However, contracting out still seems to have a bright future.
Steps To Business Process Outsourcing
Outsourcing definition suggests that these are contract-based jobs performed based on remunerations discussed before contracting out. It enables freelancers and small firms worldwide to participate in exciting projects and collaborate with more prominent and famous clients. However, a firm should consider the following steps before opting for contracting out its specific business operations to an external service provider:
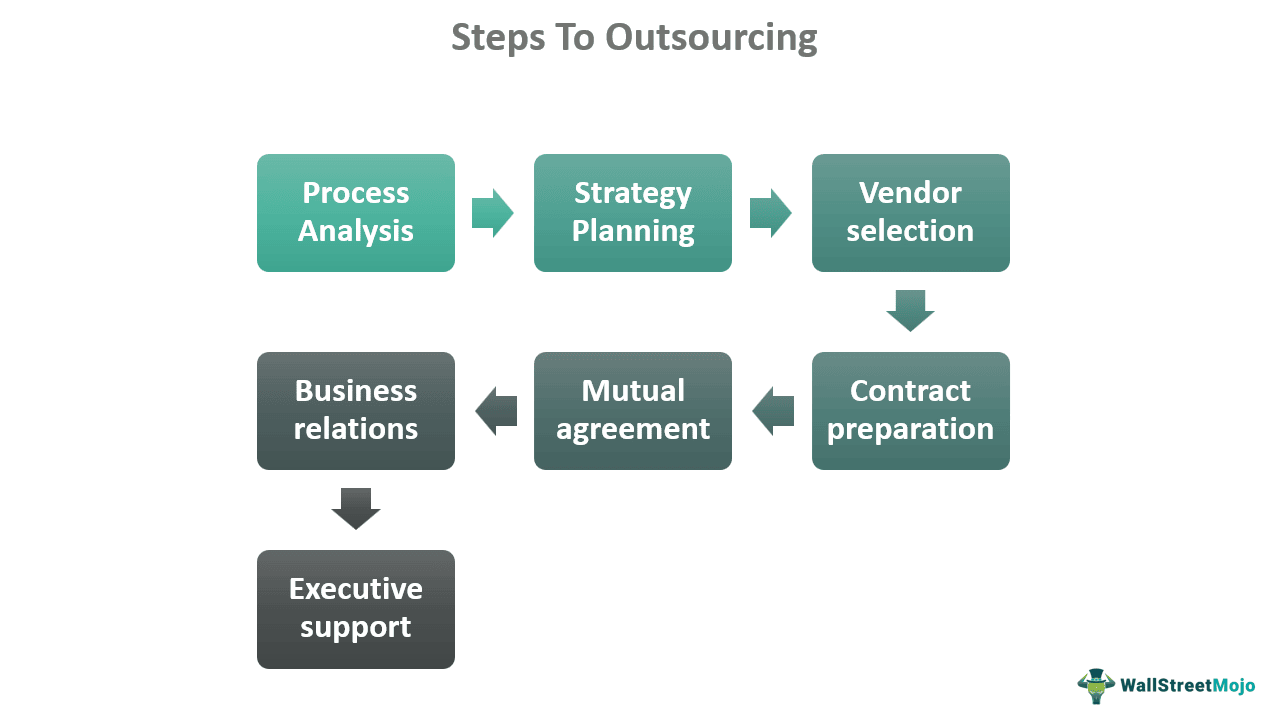
- Analyzing tasks, projects, processes, or services
- Planning strategies and communicating them with stakeholders
- Selecting the right vendor to meet the goal
- Structuring subcontract and vendor agreements
- Agreeing on a timetable for the contract implementation
- Maintaining business relations with the service provider
- Providing required business support
Outsourcing Examples
Let us look at the following outsourcing examples to understand how it works:
Example #1
A Canada-based women's apparel company finds it challenging to manufacture designer wedding dresses at affordable costs. It is because of rising labor costs and raw material prices. So it contracts out part of its production process to a specialized clothier based out of India. Both parties sign a contracting-out agreement to proceed. The Indian contractor completes the quality production at a cheaper cost and ships dresses to the Canadian firm. It, thus, results in increased profits for the latter.
Example #2
Pfizer Inc., a pharmaceutical firm based in the United States, said in May 2020 to outsource its medicine production in the wake of the large-scale production of an experimental COVID-19 vaccine. Pharmaceutical behemoths, including Catalent Inc. and Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., are among the company's existing network of outsourcing companies. Pfizer believes that relocating some production will help prevent supply chain interruptions for its other medications, including vaccines and injectable treatments.
Advantages
Contracting out contributes to the global free-market economy as it enables businesses to allocate resources to result-oriented contractors. The outsourcing benefits include:
#1 - Cost and Time Efficient
It reduces operating costs by removing the need for businesses to invest in new workers, equipment, or technology. It also allows them to focus on more critical aspects of their businesses while getting results for less crucial tasks on time.
#2 - Specialized Services
One of the key reasons a company opts for contracting out is to select the workforce outside the organization with a history of expertise and proven results. It further helps the business expand its talent pool.
#3 - Reduced Workload
One of the benefits of outsourcing is that it takes off the excessive workload for less critical tasks from the in-house employees. It, thus, indirectly helps companies focus on their employees working on core business operations.
#4 - Risk-Sharing
Since more than two entities involve in completing a task, project, service, or process, they equally share the responsibility and risk through meaningful partnerships.
#5 - Competitiveness
Companies can utilize internal resources for core competencies by contracting out time-consuming business processes and operations to external resources. It will, thus, improve their efficiency and competitiveness within the industry.
Disadvantages
The decision of business process outsourcing to an external service provider has a few drawbacks, such as:
#1 - Risk of Losses
When a company contracts out work, it becomes reliant on the contractor for completion, updates, and clarity on the project. It means they will have to face the consequences if the external service provider suffers a financial loss.
#2 - Lack of Communication
Offshoring and nearshoring can pose communication challenges to a business when outsourcing services, projects, or processes. Factors like language and time zone differences could cause the project delay or make it difficult to track its progress. It may also lead to the loss of managerial control of outsourced activities.
#3 - Threat to Job Security
In-house employees may become concerned when they learn their company is contracting out some of their tasks. It will eventually impact their morale and production. There have been cases of job losses, especially in the manufacturing industry.
#4 - Quality Issues
Every organization has a reputation for quality work and standards, but outsourcing is more likely to cause specific quality issues. If it becomes a recurring problem due to the profit-driven nature of the contractor, the company may lose goodwill, projects, and business. Similarly, understanding regulatory standards in a foreign country is equally crucial to contracting out.
#5 - Data Security
A company may have to share sensitive information with the out-house firm, which becomes a matter of confidentiality and data privacy. So if a data breach happens on the contractor side, it could pose a data security threat to the business that is contracting out.
