Table Of Contents
What is the Joint Probability?
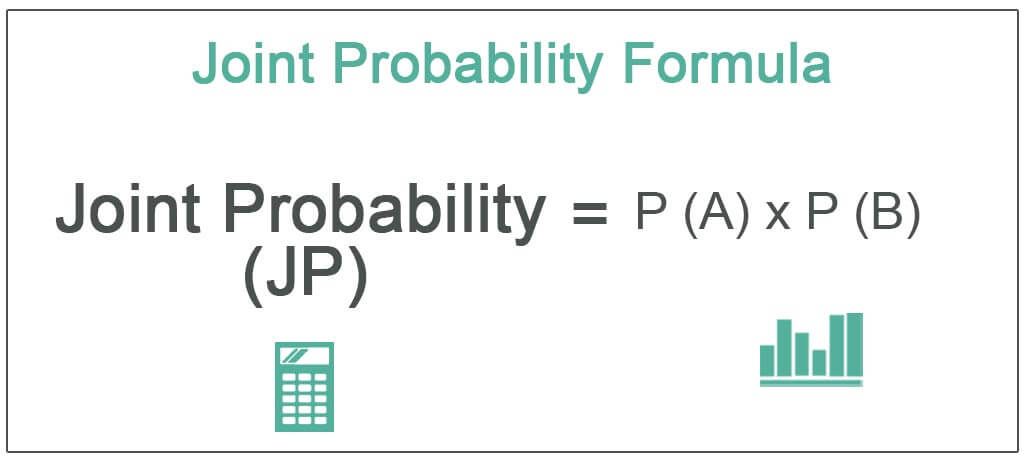
A joint probability is a possibility of occurring one or more independent events simultaneously, denoted as P (A∩B) or P (A and B). One can calculate it by multiplying the probability of both outcomes = P (A)*P (B).
Joint Probability Formula = P (A∩B) = P (A)*P (B)
Step 1- Find the probability of two events separately.
Step 2 – Both probabilities must be multiplied to calculate joint probability.
Key Takeaways
- A joint probability is the probability of one or more independent events occurring simultaneously and is represented as P(A∩B) or P(A and B).
- It can be calculated by multiplying the individual probabilities of the events: P(A) * P(B).
- A joint probability is used to determine the likelihood of multiple events coinciding, but it does not provide information about causation or influence between the events.
- Statisticians utilize joint probability to understand the probability of two or more events occurring together, considering their independent probabilities. However, it does not capture the relationship or influence between these events.
Examples of Joint Probability Formula (with Excel Template)
Example #1
Let’s consider a simple example. A bag contains 10 blue and 10 red balls if we choose 1 red and 1 blue from the bag on a single take. What will be the joint probability of choosing 1 blue and 1 red?
Solution:
- Possible outcomes = (red, blue),(blue, red),(red, red), (blue, blue)=4
- Favorable outcomes = (red, blue) or (blue, red) = 1
Use the below-given data for the calculation.
| Particulars | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of Red Balls | 10 |
| Number of Blue Balls | 10 |
| Probability of Choosing 1 Red and 1 Blue | 1 |
| Possible Outcomes | 4 |
Probability of choosing the red ball

- P (a) = 1/4
- = 0.25
Probability of choosing a blue ball

- P (b) = 1/4
- = 0.25

- =0.25*0.25

Example #2
You have a student's strength of 50 in a class, and 4 students are between 140-150cms in height. If you randomly select one student without replacing the first selected person, you select the second person. What is the probability of both being between 140-150cms?
Solution
Use the below-given data for calculation.
| Particulars | Value |
|---|---|
| Total no of students in class | 50 |
| No of students between 140-150 cms height | 4 |
First, need to find the probability of choosing 1 student in the first draw

- P(a) =50*4
- =0.08
Next, we need to find a second person between 140-150cms without replacing the selected one. As we already selected 1 from 4 the balance will be 3 students.
Probability of choosing 2 students

- P(b) =50*4
- =0.08

- =0.08*0.0612
Therefore, the joint probability of both students being 140-150cms will be:

Example #3
There was a survey with full-timers and part-timers in a college to find out how they choose a course. There were two options, either by the quality of a college or by the cost, of course. So let’s find the joint probability of both full-timers and part-timers choosing cost as the deciding factor.
Solution
Use the below-given data for the calculation.
| Particulars | Cost | Quality | Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fulltime | 30 | 70 | 100 |
| Part-time | 60 | 50 | 110 |
| Total | 90 | 120 | 210 |
Probability of full-timers in college:

- =30/210
- Full-timers = 0.143
Probability of part-timers in college:

- =60/210
- Part-timers = 0.286
The joint probability of full-timers and part-timers is calculated as follows:

- =0.143*0.286

Difference Between Joint, Marginal, and Conditional Probability
- JOINT PROBABILITY - It is the possibility of simultaneously occurring one or more independent events. For instance, if an event Y appears and the same time event X appears, it is called a joint probability.
- CONDITIONAL PROBABILITY - If one event occurs, then the other event is already known or true, called conditional probability. e.g., if event y has to be, then event X must be true.
Conditional probability occurs when there is a conditional that the event already exists or the event already given has to be true. One can also say that one event depends on another event's occurrence or existence.
- MARGINAL PROBABILITY - It simply refers to the probability of occurrence of a single event. It does not depend on another probability of occurring, like conditional probability.
Both conditional and joint probabilities deal with two events, but their occurrence differs. In conditional, it has an underlying condition, whereas in joint, it occurs simultaneously.
For example, if the price of crude oil increases, then there will be an increase in the price of petrol and gold. So if gold and petrol prices increase simultaneously, it can be said to be a joint probability. Still, we can’t measure how much one influences the other with joint probability. So instead, one can use conditional probability to measure how much one event influences the other.
Relevance and Use
When two more events occur simultaneously, the joint probability is used. Mostly used by statisticians to indicate the likelihood of two or more events occurring simultaneously, but it does not know how they influence each other.
We can use it to know the value of both events, but it will not show how far one event will influence the other.

