Table Of Contents
What is Liquidity in Accounting?
Accounting liquidity measures the company’s debtor’s ability concerning its debt payments. Usually, one expresses it in terms of the percentage of the current liabilities. For example, one can measure the current ratio as current assets divided by current liabilities, which is helpful for the company in knowing the liquidity of the company so that company does not face any liquidity crunch in the future.
Key Takeaways
- Accounting liquidity determines the company's debtor's capability regarding debt payments. Usually, one expresses it as the percentage of the current liabilities.
- It measures the capability to pay off outstanding debts if they become due utilizing its liquid obligations.
- It helps understand whether or not enough liquidity satisfies short-term obligations with the particular company.
- Different ratios determine the accounting liquidity, including the current, quick, and cash ratios.
- If the person has more liquid assets than their current liabilities or short-term obligations, it displays that their accounting liquidity is sufficient. Else, it can meet its obligations on time.
Accounting Liquidity Formula
Various ratios measure the accounting liquidity of a person, which are as follows: -
#1 - Current Ratio
The current ratio measures the ability of the company to pay the current liabilities, which are payable within the next year, concerning its current assets available, like cash, inventories, and accounts receivable. Therefore, the higher the current ratio, the better the company's liquidity position.
Formula to calculate the current ratio: -
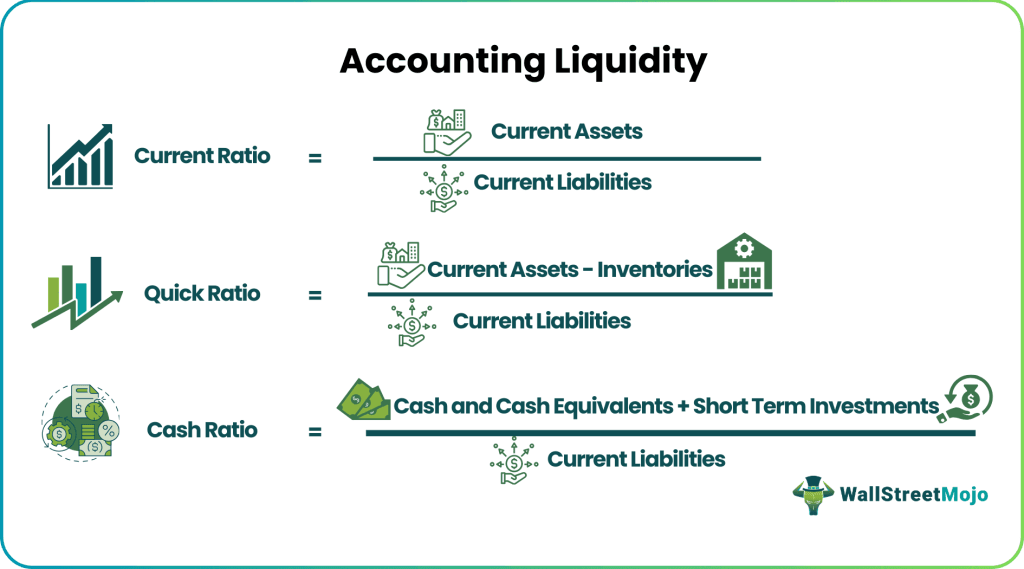
Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities
#2 - Acid-Test/Quick Ratio
The quick ratio measures the ability of the company to pay the current liabilities, which are payable within the next year, concerning its most liquid assets. Inventories and prepaid costs exclude from the current assets for calculating the most liquid assets.
Quick Ratio = (Cash and Cash Equivalent + Accounts Receivable + Short-term Investments)/Current Liabilities
Or
Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventories – Prepaid Costs)/Current Liabilities
#3 - Cash Ratio
The cash ratio measures the ability of the company to pay the current liabilities, which are payable within the next year concerning its cash or cash equivalents. The cash ratio defines the liquid assets strictly the cash or cash equivalents. It assesses the ability of the company to stay solvent if there comes any emergency, as even a highly profitable company sometimes can go into trouble if there is no liquidity to meet unforeseen events. Its formula to calculate the cash ratio: -
Cash Ratio = (Cash and Cash Equivalent + Short-term Investments)/Current Liabilities
Video Explanation of Accounting Liquidity
Example of Accounting Liquidity
Two companies, X Ltd. and Y Ltd. work in the same industry.
For X Ltd.:
- Current assets: $35
- Current liabilities: $10
- Inventories: $10
For Y Ltd.:
- Current assets: $12
- Current liabilities: $20
- Inventories: $6
Comment on the accounting liquidity of the two companies.
Analysis
For analyzing the accounting liquidity position of X Ltd. and Y Ltd., one may calculate the liquidity ratios from the available information where,
- Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities
- Quick Ratio = (Current Assets – Inventories)/Current Liabilities
For X Ltd.:


Similarly,
For Y Ltd.:


The current ratio of X Ltd. is more than that of Y Ltd., which shows that X Ltd. has a high degree of liquidity. Furthermore, the quick ratio of X Ltd. also points to an adequate level of liquidity even after excluding the inventories of $2 from current assets. That is because it has $2.5 cash for every dollar of the current liabilities.
Advantages of the Accounting Liquidity
There are several advantages of accounting liquidity for the company or an individual. Some of the benefits are as follows: -
- It helps determine whether the company has sufficient liquidity to meet its short-term obligations or not to plan its future course of action accordingly.
- It is easy to measure and calculate accounting liquidity.
- It is helpful for the company's management in assessing the company's performance.
- Banks, investors, creditors, and other stakeholders may use it as part of their analysis before providing credit or investing their money in the company.
Disadvantages
Limitations and drawbacks of the accounting liquidity include the following: -
- The accounting liquidity is calculated based on the figures, and there are chances that the company will manipulate these figures. In that case, the accounting liquidity calculated will not show the correct picture of the company's liquidity position.
- Accounting liquidity helps know whether sufficient liquidity to meet short-term obligations is there or not with the particular company. Still, it does not compare with the industry figures or competitors as these ratios may have different interpretations for different industries.
- Several ratios measure accounting liquidity and differ based on how strictly a liquid asset define in them. Each ratio defines liquid assets differently, so there is no concrete conclusion on which ratio best measures accounting liquidity.
Important Points
- Accounting liquidity is a measure of the ease with which a company or an individual can meet their financial obligations using the liquid assets available.
- Accounting liquidity measures the ability to pay off outstanding debts when they become due using its liquid assets.
- One can assess accounting liquidity by comparing the liquid assets present to the current liabilities or the short-term obligations due within one year.
- Accounting liquidity is one of the important measures used to know the ability of a person to pay off their current debt obligations due within the next year without a need to raise external capital.
- Different ratios measure the accounting liquidity, including the current, quick, and cash ratios. If the person has more liquid assets than their current liabilities or short-term obligations, then it shows that the accounting liquidity of the person is sufficient. Otherwise, it will be able to meet its obligations on time.

