Table Of Contents
What is the Chart of Accounts (COA)?
A chart of accounts (COA) lists all the general ledger accounts that an organization uses to organize its financial transactions systematically. Every account in the chart holds a number to facilitate its identification in the ledger while reading the financial statements.
COA helps companies prepare, maintain, and monitor their financial accounts as per the standard accounting norms. It facilitates stakeholders to interpret a company's financial performance with ease.
Table of contents
- What is the Chart of Accounts (COA)?
- A chart of accounts (COA) is an accounting tool that tabulates all the accounts recorded in the company's general ledger to keep track of its financial transactions.
- It helps in the quick identification of a business's expenses and revenues.
- COA usually has four columns which are account number, account description, account type and financial statement.
- The account number corresponds to the respective ledger entry. It can be three to seven digits depending upon the company's size, divisions, and departments. A small business will usually have three numbers.
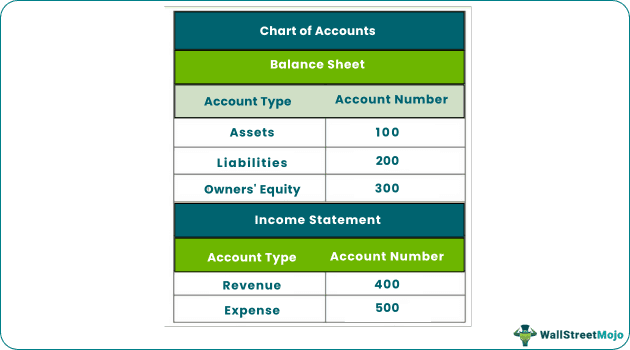
- The COA generally features five account types: asset, liability, equity, income, and expense. The first three account types affect the balance sheet, the last two impact the income statement.
How Does Chart of Accounts Work?
Chart of Accounts gives a consolidated view of the financial transactions affecting a company's balance sheet and income statement. Depending on the size of an organization, a firm can have multiple entries for expenses and income in an accounting year.
For instance, a large-scale company could have several entries for expenses that it doesn't separately mention in the income statement. A chart of accounts can help the company list all the costs recorded in its general ledger in one place. This will enable the directors and shareholders to quickly identify the source of expenses and revenues when going through the financial statements.
The COA will include balance sheet entries of assets, liabilities and owner's equity, and income statement's expenses and revenue. The chart of accounts numbering will indicate the location of the listed account in the ledger.
Components of a COA
In accounting, a chart of accounts usually has four columns:
Account Number
The account number is the unique code allotted to each account. It depicts the numbering of the COA. For example, the account number 120 represents that this account belongs to the asset class. A person can look up additional details related to the account in the ledger using this number.
Account Type
The account type depicts the nature of each account. There are five primary types of accounts, i.e., asset, liability, equity, income and expense. However, it can be reduced to four in small organizations, while in large corporations, it can also be more than five.
Assets: It comprises fixed assets, intangible assets, inventory and current assets like cash, trade receivables, etc. All the asset accounts contain account number starting with 1.
Liabilities: The COA liability category involves long-term and short-term borrowings, trade payable, interest payable, and other current liabilities. All the liability accounts contain the account number starting with 2.
Equity: It includes equity share capital, preference share capital, and reserve & surplus. All the owner's equity entries contain the account number starting with 3. Assets, liabilities and equity are related to the balance sheet.
Revenue: It involves sales revenue, interest received, income from scrap, or any other earnings. All the revenue accounts contain account number starting with 4.
Expenses: The COA expense category comprises the cost of goods sold, rent, electricity, salary and wages, and any other business expense. All the expense accounts contain number starting with 5. Expenses and revenues are related to the income statement.
Account Description
It represents the name of the account. The account description should be kept precise but capable of including multiple relevant accounts under a large account. For example, "cash receivables" will be mentioned under the type of asset.
Financial Statement
Under this column, we mention the financial statement impacted by the accounts. The asset-liability and equity accounts affect the balance sheet, whereas the income and expense accounts reflect changes in the income statement.
How to make a COA?
Initially, a company needs to decide the structure of its COA, the account types and the numbering pattern. It can derive the name of accounts from its general ledger. If the firm wants to include all the expenses to provide a complete understanding of where it is spending the finances, it can customize its COA. However, the chart should be in line with the standard accounting norms.
A small business entity can have an account number of just three digits like "118", where the first digit signifies the account type . Since 1 is the code for assets, 118 belongs to the asset class. The other two digits, "18", show what the asset is.
A large organization can have an account number of many digits. For instance, "5030"; where "5" is the code for expense, and "030" corresponds to the sales department's employees commutation cost.
Chart of Accounts Example
PQR Enterprises is a firm engaged in the manufacturing of plastic containers. Given below is the company's categorization of accounts under the COA.
Below is a sample chart of accounts list for the above company -
| Account Number | Account Description | Account Type | Financial Statement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | Cash | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 1005 | Accounts Receivable | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 1009 | Inventory | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 1014 | Plant & Machinery | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 1011 | Land & Building | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 2001 | Short-Term Borrowings | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 2005 | Outstanding Fee | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 2009 | Accounts Payable | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 2013 | Interest Payable | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 2014 | Payroll Payable | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 3003 | Equity Share Capital | Equity | Balance Sheet |
| 3009 | General Reserve | Equity | Balance Sheet |
| 3010 | Retained Earnings | Equity | Balance Sheet |
| 4001 | Sales Revenue | Income | Income Statement |
| 4005 | Sales Return and Allowances | Income | Income Statement |
| 4008 | Interest Received | Income | Income Statement |
| 5004 | Raw Material | Expense | Income Statement |
| 5009 | Salary and Wages | Expense | Income Statement |
| 5013 | Office Rent | Expense | Income Statement |
| 5015 | Electricity Expense | Expense | Income Statement |
| 5020 | Miscellaneous Expense | Expense | Income Statement |
Importance of Chart of Accounts
We can say that a COA has the same role in a company's financial analysis as a map has in reaching the destination. It, therefore, makes it easy for the user to locate a particular account with the help of its account number.
The COA is customizable; hence, it serves the need of every business organization. A COA is a financial tool that provides an extensive understanding of cost and income to anyone who goes through the company's financial health.
For example, the Cambodian government had decided to use a unified chart of accounts (COA) to monitor how the money was being spent on welfare initiatives. The unified COA will throw light on each source of expense and earning. Such data will prove helpful to policymakers in cutting down unnecessary costs.
COA Best Practices
A company can undertake the following suggestions mentioned below to create and maintain an effective COA:
- Customize the COA by adopting a suitable pattern for account numbering based on your company's size, departments, structure and operations. Remember that the best chart of accounts structure is the one that serves your managerial accounting purpose.
- Use a standard COA as per the norms set forth by the GAAP and tax authorities. Avoid making changes to the format; otherwise, it will cause confusion and error.
- Design your COA to suit the business needs for the upcoming years. This will result in the creation of a more consistent, comparable and helpful index.
- Keep an eye on the unnecessary accounts whose amount you can transfer to the larger accounts. This step will aid you in keeping the COA list short and accessible.
- Many large corporations use accounting software like SAP to make their COA. A chart of accounts is created as an excel spreadsheet, with many using an online template such as Quickbooks' for ease. Chart of Accounts
FAQs
A chart of accounts is a tool that lists all the accounts in the general ledger with unique numbering to help locate them in the relevant accounting book. Stakeholders can refer to the COA and balance sheet, and income statement to find the source of expense and earnings.
Below is an excerpt of a chat of accounts example
| Account Number | Account Description | Account Type | Financial Statement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | Cash | Asset | Balance Sheet |
| 2001 | Accounts Payables | Liability | Balance Sheet |
| 3001 | Owner’s equity | Equity | Balance Sheet |
| 4009 | Interest Received | Income | Income Statement |
| 5004 | Raw Material | Expense | Income Statement |
In SAP, the categories of a COA are as follows:
1. Operating COA: It comprises accounts used to record regular business transactions, i.e., expenses and revenue accounts.
2. Group COA: It consists of standard accounts applicable at the corporate level by all the business units.
3. Country-Specific COA: Useful for MNCs, this COA is used to maintain accounts as per the legal requirements of a particular country.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to what is a Chart of Accounts (COA) and its definition. Here we discuss the list of categories of accounts chart based on balance sheet & PL Statement with the help of examples. You can learn more from the following articles -

