Table of Contents
What Is A Health Insurance Marketplace?
The Health Insurance Marketplace is a government-operated information source that assists individuals, families, and small businesses in comparing health insurance plans. Users can enroll in or change plans, access tax credits, and obtain information about health care insurance, ensuring clarity and informed decision-making.
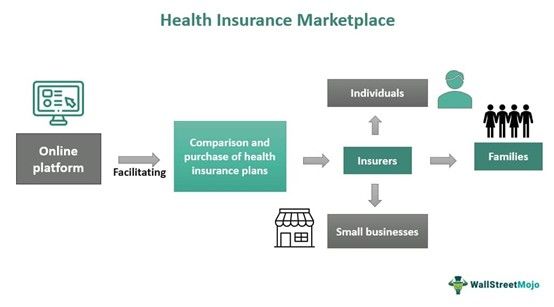
It provides a user-friendly insurance knowledge platform for individuals and small businesses to explore and evaluate different health insurance choices. , it enhances affordability in the health insurance sector by fostering transparency and competition. Moreover, eligible individuals can access premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, enhancing the affordability and availability of health insurance coverage.
Key Takeaways
- The Health Insurance Marketplace is a government-operated platform aiding families, small businesses and individuals in comparing and accessing health insurance plans.
- It simplifies plan selection, providing essential benefits and cost transparency.
- Through one application, users can determine eligibility for premium tax credits and cost-sharing reductions, enhancing affordability.
- Eligibility criteria include U.S. residency, citizenship, or lawful presence, with exemptions for those incarcerated.
- The Marketplace ensures patient protections under the ACA, including coverage for pre-existing conditions.
- It offers diverse plan options, promoting competition and improved service quality, ultimately encouraging population health and financial security against medical expenses.
Health Insurance Marketplace Explained
The Health Insurance Marketplace is a knowledge-sharing online setup that simplifies finding suitable health coverage tailored to individual needs and budgets. All plans are comparable based on price, quality, and other requirements, offering standardized essential health benefits, including doctor visits, prescriptions and preventive care. Through one application, eligibility for free or low-cost coverage via Medicaid or CHIP, or savings on Marketplace plans, is determined. Compliance with minimum health coverage requirements is mandatory for all U.S. residents and the platform helps identify the most suitable one.
The Health Insurance Marketplace, established under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), facilitates access to affordable health insurance for individuals and families. The federal government operates it in most states; some states manage their marketplaces. Eligibility for free or low-cost coverage is determined through premium tax credits, with most applicants qualifying for financial assistance.
These credits are income-based and consider family size and coverage criteria. All Marketplace plans cover important health benefits, including outpatient care, hospitalization, prescription drugs, and preventive services. They also provide pediatric services, rehabilitative services, laboratory services, and other emergency services. Additionally, comprehensive coverage options like dental and vision insurance are available through select plans offered by insurers.
The health insurance marketplace categorizes plans into four metal tiers: bronze, silver, gold, and platinum. These tiers vary based on premiums and out-of-pocket expenses such as deductibles, coinsurance, and maximum out-of-pocket limits. There are a number of marketplaces to choose from such as Virginia health insurance marketplace and NYS health insurance marketplaces.
Exploring insurance options can help you find coverage that fits your unique needs. For those interested in comparing a range of insurance products, resources like SuperMoney make it easier to review and select policies from top providers.
Types
There are two basic types of health insurance marketplaces:
- Federal marketplace: The federal marketplace, operated by the federal government at healthcare.gov, is the main platform most states use to offer health insurance plans.
- State-run marketplaces: State-run marketplaces, available in over a dozen states, have their platforms. Users can input household income to determine subsidy eligibility and compare plans, with each state providing cost estimates for available options.
How To Qualify?
To be eligible for enrollment in health coverage through the Marketplace, individuals must:
- Reside in the United States: If considered a U.S. "resident" for tax purposes, eligibility for Marketplace coverage applies. Understanding the IRS criteria for U.S. tax residency is hence crucial. Marketplace insurance extends coverage for healthcare services rendered by domestic healthcare providers, necessitating consideration for those residing abroad.
- Be U.S. citizens, nationals, or lawfully present individuals: A U.S. national is a citizen or someone with permanent allegiance to the U.S. Typically, U.S. nationals who are not citizens are individuals born in American Samoa or born abroad with at least one American Samoan parent.
- Not be punished in jail or prison.
Under the Affordable Care Act, in short, the ACA application through the Health Insurance Marketplace ensures specific patient protections:
- Insurers are barred from denying coverage based on gender or pre-existing conditions.
- Coverage for essential health benefits is not subjected to lifetime or annual limits.
- Young people can remain on the insurance plan of their families until they are 26.
Examples
Let us look into a few examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose Daisy, a self-employed individual, uses the Health Insurance Marketplace to find a suitable health insurance plan. Daisy browses through various government health insurance marketplace sites. Virginia health insurance marketplace and NYS health insurance marketplaces are such examples. She finds that she qualifies for a premium tax credit based on her income level, which helps reduce the premium costs of her chosen plan.
Daisy carefully compares different plans, considering factors like coverage, deductibles, co-payments, and network providers, and selects a plan that aligns with Daisy's healthcare needs and budget. She also learns about the Medicaid program, which provides health insurance coverage to low-income individuals. If her household income falls below 138% of the federal poverty level, she may qualify for Medicaid, which offers minimal or no-cost health insurance. By understanding her financial situation and exploring available options, Daisy makes an informed decision and enrolls in a comprehensive health insurance plan.
Example #2
APTC is a feature listed on the Department of Insurance and Financial Services of Michigan's government site.
The Advance Premium Tax Credit (APTC) is a federal government tax credit aimed at reducing the monthly cost of a health plan obtained through the Marketplace. Individuals with household incomes ranging from 100 percent to 400 percent of the federal poverty level may qualify for this credit. Eligibility is determined annually by the Marketplace. If eligible and utilizing the APTC to reduce monthly premium payments, individuals must reconcile the credit when filing federal taxes.
Benefits
Some of the benefits of the Health Insurance Marketplace are:
- Access to diverse health insurance options from multiple insurers.
- Transparent plan comparison detailing coverage specifics and expenses.
- Availability of premium tax credits along with cost-sharing reductions for enhanced affordability.
- Assistance and guidance for individuals navigating the healthcare landscape.
- Simplified enrollment in Medicaid and Children's Health Insurance Program (CHIP) for eligible candidates.
- Protection against exclusions based on pre-existing conditions.
- Comprehensive coverage of essential health benefits, encompassing preventive care, prescriptions, and mental health services.
- Flexibility to select plans tailored to individual healthcare requirements and financial capacities.
- Increased competition among insurers, potentially resulting in competitive pricing and improved service standards.
- Promotion of population health by encouraging obtaining health insurance.
- Financial safeguards against high medical bills and unforeseen healthcare expenses.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

