Let us look into a few differences between the concepts:
Table of Contents
What Is Revenue Analysis?
Revenue analysis is the process of understanding the revenue arising from all activities in a company. It involves reviewing the sources of income generated by the business. The resultant revenue could be from income, sales of goods and services, costs, and other variables.
Examining revenue and their current sources can provide companies with a better understanding of their financial health. It gives a clear picture of whether they are achieving their targets and what is lacking in their efforts to achieve them. Additionally, they also provide insights on potential sources of revenue.
Key Takeaways
- Revenue analysis is the process of examining the revenue through the evaluation of financial data. It gives insights into the business's financial health and performance.
- The process involves analyzing sales, costs, and other factors that are associated with revenue generation.
- It includes competition analysis, customer behavior analysis, and financial statement analysis.
- The benefits include assessing business viability, making data-driven decisions, identifying investment opportunities, and optimizing pricing and revenue techniques.
- Sales and revenue analysis help streamline operations and improve efficiency. This helps the companies build a sustainable future by correcting their mistakes.
Revenue Analysis Explained
Revenue analysis is the comprehensive analysis of financial data to examine the revenue flows generated from business activities. This includes analysis of revenue sources from every relevant department, product, and segment. The analysis looks into various streams that bring in income. It includes sales, marketing efforts, and customer success. It takes a unified approach to analyze revenue-generating operations across various departments.
This financial assessment strategy is performed to gain key insights into the business proceedings. This includes an estimation of the strategies employed, how successful they are, and the steps required to meet the expectations. It reveals how much money is spent on running the business, whether the revenue matches expenses, and if there is a profit. The analysis may include understanding customers, the product, and the cost of goods sold.
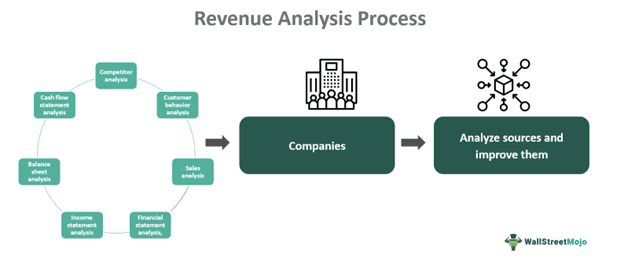
Additionally, it may involve understanding and evaluating marketing strategies and overhead costs. Various tools may be employed for it, such as competitor analysis, customer behavior analysis, sales analysis, financial statement analysis, income statement analysis, balance sheet analysis, and cash flow statement analysis.
Companies can define the goal of the analysis to begin the process. This helps them to save time and not deviate. They can then identify data sources, analyze data, and interpret results according to their set goals. The analysis can take various forms, such as analyzing growth in revenue, revenue by sectors, geography, products, channels, or decline, if any.
Types
Some of the different types of analysis are given as follows:
- Sales revenue analysis: It examines the total revenue generated by the business at different intervals. The analysis may focus on different products or customers as the need arises.
- Customer revenue analysis: The analysis examines the revenue generated from customers and breaks them into categories of different factors. They can be based on demographics, purchase period, or products purchased. Questions on who, what, when, where, and why are answered here.
- Product revenue analysis: The analysis examines how the products in the market are performing and intends to find the best-performing ones. The strategies of the products are either implemented on the rest after looking into why it worked or finding new strategies to find why it didn't work.
- Revenue trend analysis: This analysis covers the business revenue movements over time. The fluctuations are analyzed, such as the peaking and dipping of sales, the seasonality factor, and the sale periods.
Examples
Let us look at a few examples to understand the topic better:
Example #1
Suppose Company A is a SaaS company aiming to increase its profits. Its revenue is generated by three departments: sales, marketing, and customer success teams. It uses a revenue analysis dashboard to determine the average revenue per user and the impact of new feature releases. This helps the company understand the current situation and plan for the future. Moreover, understanding these metrics helps the company optimize its pricing, improve customer retention, and enhance operations and resource handling.
Example #2
Suffolk is a constituency in England. The city projects the revenues for its citizens for the fiscal year as part of the budget development project. The revenue analysis report document of 2013-2014 states that its primary revenue sources were local taxes, fees, and state, federal and other funding. The document provides a detailed breakup of the streams. The document is let out so that the citizens are aware of what comes in and how it is utilized for the functioning of the government.
Benefits
Given below are some of the benefits of revenue analysis:
- Business viability estimation: The analysis helps in assessing the profitability that a business yields and the sustainability of the business model. It provides insights into the long-term success of the current techniques. If it indicates the need for optimization, then it is time to rethink strategies.
- Planning ahead: Sales and revenue analysis support decisions that are data-driven, and this helps to plan. The decisions made include finding the product market fit and ideal target customers. They help maintain profitability and drive innovation to be competitive, which is possible through gaining insights into future expectations.
- Potential areas of investment: It helps identify the successful areas and its value proposition. The analysis of trends, sales data, and strategies helps discover new opportunities. It is done by enhancing existing products and services, optimizing sales processes, improving areas of efficiency, reducing costs, and streamlining operations. Furthermore, it also provides insights on pricing based on customer demand and market dynamics.
- Other benefits: The analysis also helps track performance over time and allocate resources for the optimal functioning of the business.
Revenue Analysis Vs. Cost Analysis
| Aspect | Revenue Analysis | Cost Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Concept | It focuses on the examination of revenue sources. | Cost analysis focuses on the cost and expenses associated with generating revenue. |
| 2. Purpose | It aims to optimize the revenue sources. | It aims to reduce costs to improve revenue and the surrounding efficiency. |
| 3. Essence | The sales and marketing teams use it to make decisions on product mix, pricing, and growth strategy to understand profit margins. | Cost analysis is used to make decisions on budgets, resource allocation, and cost reduction. Accounting departments often use them. |

