Table Of Contents
What Is Purchase Order Financing?
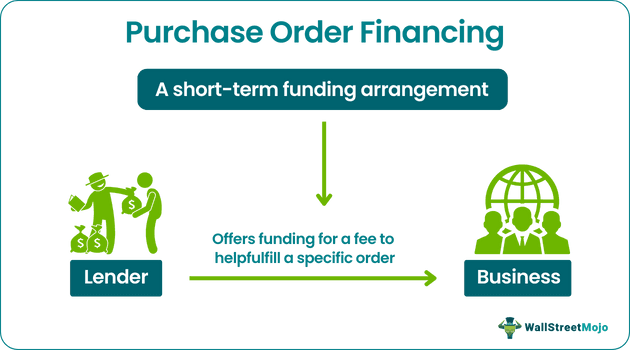
Purchase Order Financing, also called PO Financing, is a financing agreement where a lender makes funding available to a business to enable it to cover the costs of fulfilling a purchase order for a fee. Businesses that do not have the funds to fulfill a large order or have exhausted their working capital typically apply for such funding.
It can also be helpful for businesses with seasonal or cyclical cash flows, as it allows them to access the necessary funds to fulfill orders during slow periods. However, PO financing can be more expensive than other forms of financing, as lenders often charge higher interest rates or fees to offset the risks associated with this type of financing.
Key Takeaways
- Purchase Order Financing (PO financing) is a financial arrangement where a lender advances funds to a company to help it cover the costs associated with fulfilling a specific purchase order.
- It enables businesses to accept and fulfill large orders that they may otherwise not be able to deliver due to insufficient funds or a paucity of working capital.
- While PO financing is advantageous due to cash flow optimization, reduced inventory shortfalls, etc., it introduces certain challenges like reduced cost-effectiveness, complex paperwork, and lower profitability compared to other funding sources.
- PO financing is designed to finance the cost of fulfilling specific purchase orders while factoring focuses on providing immediate cash through the sale of outstanding invoices.
How Purchase Order Financing Works?
Purchase Order Financing is a type of short-term funding that helps businesses fulfill customer orders by providing them with the necessary funds to purchase the supplies and inventory needed to fulfill an order.
PO financing involves various steps and works in the following manner:
- A business receives an order from a customer but does not have the funds necessary to purchase the supplies or inventory required to fulfill the order.
- The firm approaches a purchase order financing company or lender and provides them with the details of the purchase order.
- The lender reviews the purchase order and evaluates the creditworthiness of the customer and the likelihood of the order being fulfilled successfully.
- If approved, the lender pays the supplier or vendor directly (the typical amount is 80 to 100% of the order value) to help the business secure the supplies or inventory required to fulfill the customer’s order.
- The business completes the order and delivers the goods to the customer. It bills the customer (by raising an invoice), and the customer pays the lender per the invoice.
- The lending entity deducts its financing fee as agreed upon while entering the purchase order financing agreement and remits the remaining amount to the business.
Three parties are involved in this process. They are the business, the lender, and the customer. The lender makes funds available to the business based on the creditworthiness of the customer and the likelihood of the order being fulfilled successfully.
This type of financing can be particularly useful for small firms that have limited cash flows or credit history, as it allows them to take on larger orders and grow their business without incurring significant debt.
Examples
Let us study some purchase order financing examples to understand the concept better.
Example #1
Suppose a small clothing manufacturer, ABC Clothing, receives a large order from a major retailer for 10,000 units of a new clothing line. However, ABC Clothing does not have enough funds to purchase the fabric and other materials needed to fulfill the order. They approached a purchase order financing company, XYZ Financing, for financial assistance.
XYZ Financing evaluates the creditworthiness of the retailer and the chances of the order being completed and delivered on time. They approve the order, and XYZ Financing agrees to make $100,000 available to ABC Clothing for the purchase of the necessary materials. The terms of the financing agreement state that XYZ Financing will receive a fee of 2% of the order value, which is $2,000 in this case.
XYZ Financing pays $100,000 to the suppliers of ABC Clothing. The suppliers provide the necessary materials, enabling ABC Clothing to manufacture the required apparel. ABC Clothing delivers the goods to the retailer. The company raises an invoice, and the retailer pays XYZ Financing $150,000 for the order.
XYZ Financing then deducts its fee ($2,000) and credits the remaining amount to ABC Clothing’s account. With the help of purchase order financing, ABC Clothing was able to fulfill a large order and grow its business without accumulating debt.
Example #2
King Trade Capital (KTC) is a well-known purchase order financing company in the US. According to a report published on the company’s own website in March 2023, King Trade Capital extended PO financing worth $8 Million to a popular sorbet brand. The company’s sorbet products initially became popular across restaurants and expanded to grocery chains later. Their delicious products are now in demand among big box retailers, too.
Seasonal order fulfillment is particularly important to this company due to the nature of its products. To meet seasonal orders, where the company needs to distribute its products through cold storage facilities to various customers, it opted for PO financing from KTC. Using this facility, they were able to fund their production and distribution, grow their customer base, and make considerable profits.
Advantages And Disadvantages
The advantages and disadvantages of purchase order financing have been discussed in this section.
Advantages
- Sales and market share boost: It allows businesses to take on larger orders that they may not have been able to fulfill otherwise due to a lack of funds. This gives sales a boost, and a rise in market share becomes possible.
- Improved cash flows: By providing the necessary funds to purchase inventory and supplies, purchase order financing can help businesses increase their cash flow and maintain a healthy cash position.
- Quick funding support: It is a form of unsecured financing, which means that businesses do not have to put up collateral to secure the funding. It helps companies with limited credit history secure the funding they need.
- Targeted and flexible solution: Unlike traditional loans, purchase order financing is a short-term financing solution that allows businesses to fulfill specific orders without taking on long-term debt. It helps businesses stay away from long-term financial obligations that may hamper their ability to adapt to changing market conditions or seize new opportunities as they come.
- Reduced stockouts: Since companies have access to inventory and other supplies through swift and adequate PO funding, the risk of stockouts declines dramatically.
Disadvantages
- Fairly costlier than traditional methods: It can be more expensive than traditional financing options such as bank loans or lines of credit. Lenders charge fees for their services, which can be higher than other financing options.
- Short-term funding solution: It is designed to help businesses fulfill specific orders, and the funding is typically tied to a specific transaction. This means that it may not be suitable for businesses that need ongoing funding for daily operations.
- Increased complexity: The process of obtaining purchase order financing can be more complicated than other financing options, as it involves multiple parties and requires detailed documentation.
- Limited availability: PO financing might not be available for all industries. Also, securing purchase order financing for startups may be challenging.
- Impact on profit margins: Since companies are required to pay the lender a fee, their profits might be affected, particularly if the profit margins are tight.
- Supplier apprehensions: Some suppliers or vendors may not be comfortable dealing with PO financing companies for their payments.
Purchase Order Financing vs Factoring
The differences between purchase order financing and factoring are enumerated in the table below.
| Basis | Purchase Order Financing | Factoring |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | It is designed to help businesses fulfill specific orders by providing the necessary funds to purchase inventory and supplies. | It is designed to help businesses improve their cash flow by selling their outstanding invoices to a third-party lender at a discount. |
| Parties Involved | It typically involves three parties: the business, the lender, and the customer. The lender provides the funds to the supplier for the inventory and supplies. Upon successful completion of the order, the invoice raised by the business is cleared by the customer. The lender receives the customer’s payment, deducts the specified fee, and transfers the remaining amount to the business. | It typically involves three parties: the business, the factoring company, and the customer. The factoring company takes the responsibility of securing payments from customers/debtors. |
| Repayment | The business raises the invoice. The customer pays the lender based on this invoice. The lender transfers the money to the business after deducting their fee. | The factoring company collects payments directly from the business's customers, who then become the factoring company’s debtors because their invoices were sold to the factoring company. |
| Creditworthiness | It is based on the creditworthiness of the customer placing the order. | It takes the creditworthiness of the business's customers into account. However, it also assesses the invoice quality and general stability of the business selling the outstanding invoices. |
