Table Of Contents
What is Negotiable Instruments?
Negotiable Instruments are signed legal documents that guarantee paying a particular amount to a person or party at a set date or on-demand. It acts as an assurance of payment or repayment that the assignee expects. Based on the nature of the note, this document may or may not contain the recipients' names.
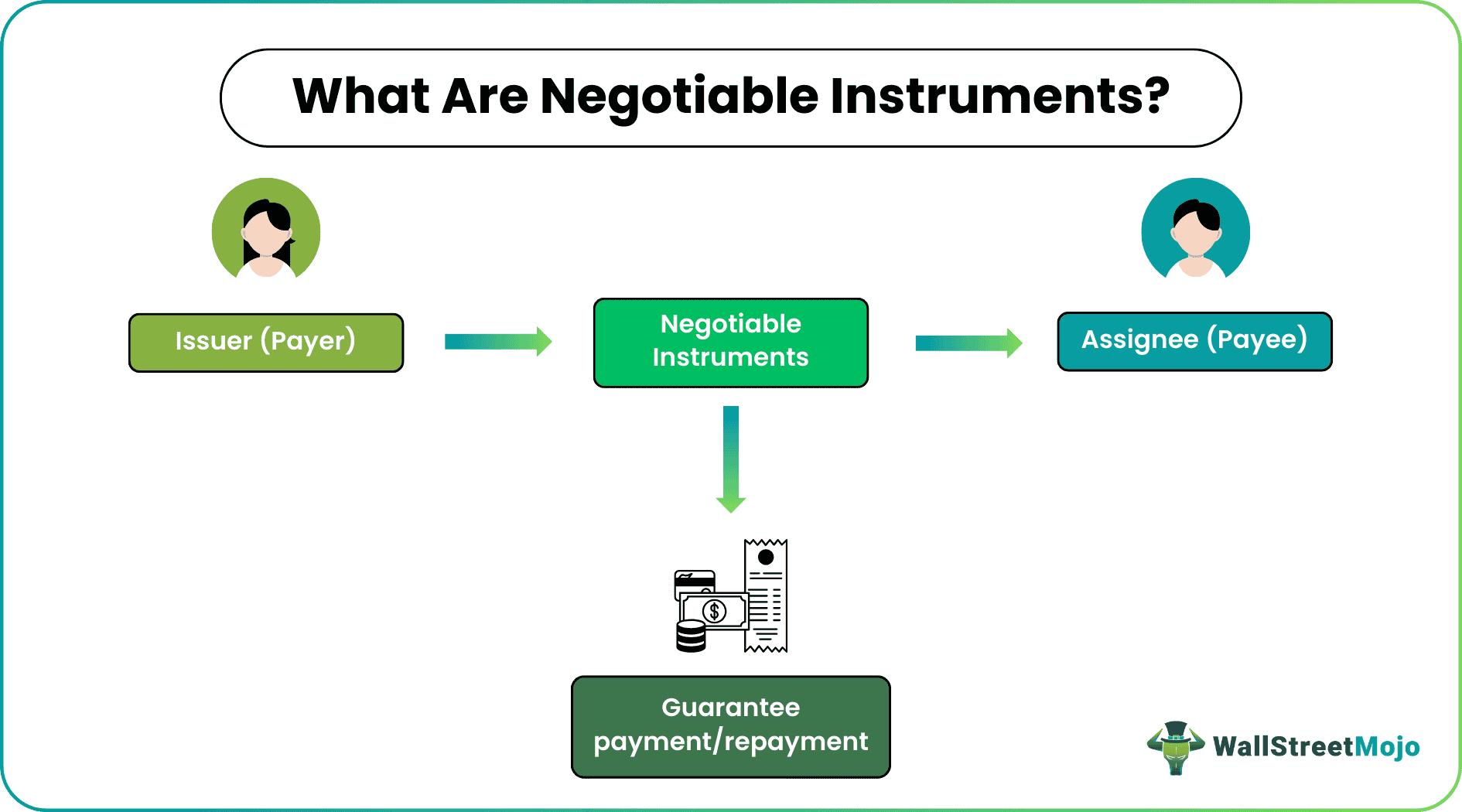
Negotiable instruments, unlike non-negotiable instruments, are transferable. Hence, they can move from one person or party to another until it reaches the final holder, who holds the complete right to use them. The one who issues them is a payer, whereas the one it is issued for is the payee.
Key Takeaways
- Negotiable instruments are written and signed legal documents that ensure a party pays or repays another party within a set period or on-demand.
- These are the safest modes of payment as they contain the name of the issuer and the name of the recipient on them.
- Such financial products are easily transferable, and individuals are free to either encash them or transfer them to consecutive payees.
- Some such instruments include – promissory notes, checks, Certificates of Deposit (CD), money orders, bearers bonds, etc.
Negotiable Instruments Explained
Negotiable instruments assure payment/repayment to an entity or individual. These legal documents are so prepared that the time of payment and the recipient's name are mentioned. Such instruments are written promises signed by payers and made to payees, per which the former guarantees to make the payment on the mentioned date or on-demand.
These are nothing but evidence of indebtedness, as the instrument holder has an unconditional right to recover the amount of money stated in the instrument from its maker. These instruments are used as a substitute for cash to safely transfer the payments between the merchants and have a risk-free business transaction.
These legal notes make individuals and entities trust each other with payments and repayments. They are negotiable as these notes or drafts involve two parties that agree to take forward a transaction. Though unconditional, these documents must have the assignee's name mentioned on them. Hence, the payment is made to the mentioned payee only.
Characteristics
These documents exhibit a wide range of characteristic traits. For example, some of the features of negotiable instruments include:
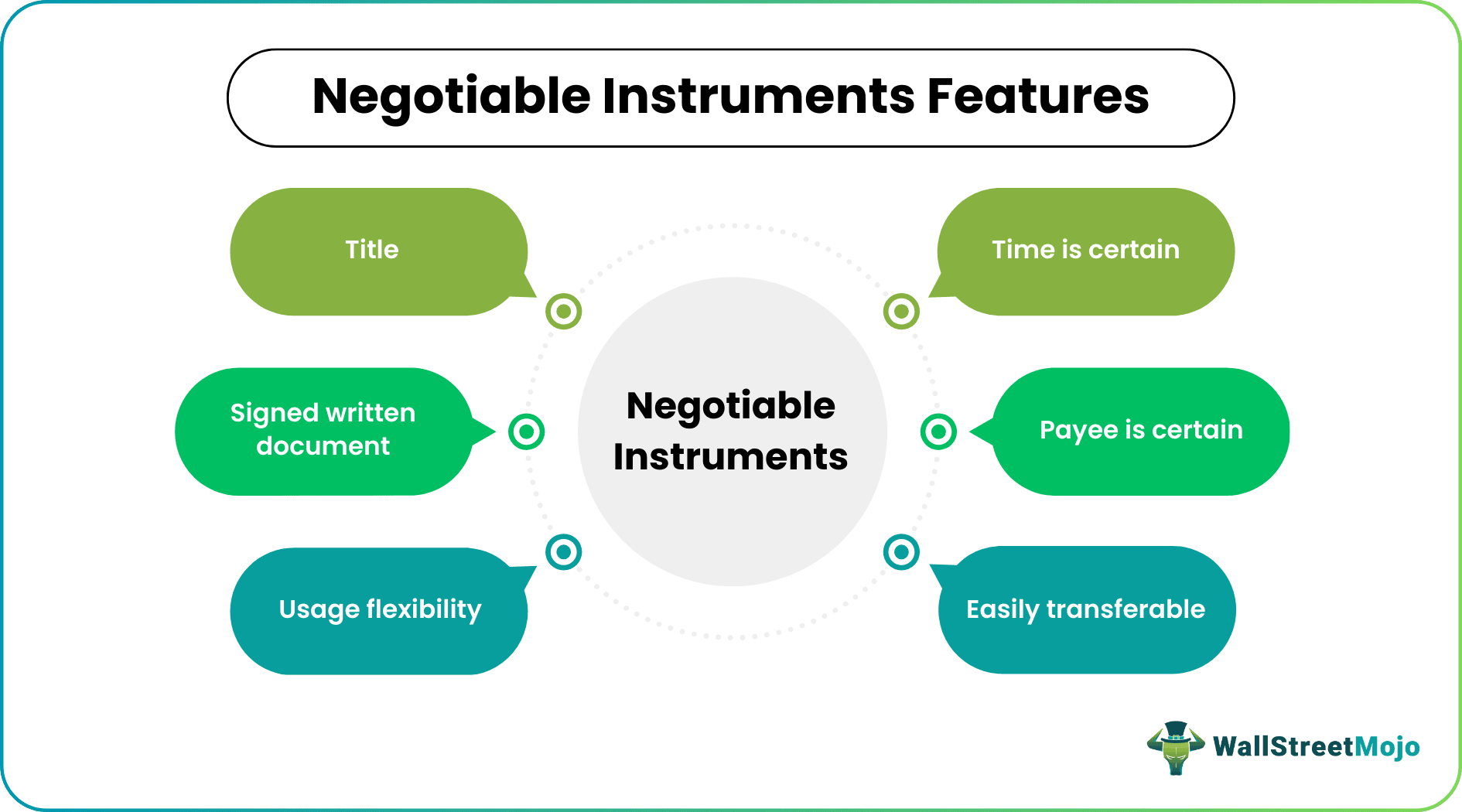
- It is a written document signed by the issuer.
- It is like a valid contract easily transferable from one party to another. The holder can transfer the document to another individual or entity without hassle. It is this feature that makes such instruments negotiable.
- As named on the instrument, the payee enjoys complete ownership of the legal document. This means the title gets transferred when the note is handed over to the consecutive parties.
- A negotiable instrument always mentions the payee's name, which signifies making the payment to a specific person or firm.
- In addition to the payee, the time is also predetermined and is certain. A payee can present the document to encash it or receive the payment as promised within the specified date or on-demand.
- There is flexibility as the payee can receive the funds in cash or transfer the document to another party for consecutive usage.
Types
These legal drafts and notes are available in wide varieties. Some of the widely found classification or kinds of negotiable instruments are as follows:
Checks
A check is a note containing the amount paid by one party to another party. It includes the bearer's name and account number from which the money would be debited. In addition, it also mentions the name of the payee. As a result, even if the check goes missing, no third party can misuse it. In short, checks are the safest mode of making payments or transferring funds from one party to another.
Though debiting the amount from one account and crediting the same in the other takes a bit more time, people still consider issuing a check for safety reasons. People and firms use various checks, like traveler's checks, personal checks, certified checks, cashier's checks, etc.
Promissory Notes
A promissory note means one party promises to pay a sum of rupees to another party whose name is mentioned on the note along with a fixed future date. Generally, it is used as short-term trade credit, , and the maker pays the due amount on or before the note's expiry. As a safe mode of transferring money, business people frequently use it to have smooth business transactions.
Individuals or firms can claim the outstanding funds after the expiry of the term in the event of non-payment of the promised money. It is also issued as a debt instrument, which corporations use to finance their short-term projects.
Certificates of Deposit (CD)
Banks and financial institutions offer Certificate of Deposit as a financial product. In the process, the customers deposit a certain amount and keep it safe for a fixed tenure while receiving a high-interest rate on the amount in return. The interest rate tends to increase constantly with the increasing deposit span. The individuals can withdraw the amount plus interest once the CD matures. However, in case of early withdrawal, one would need to pay the penalty.
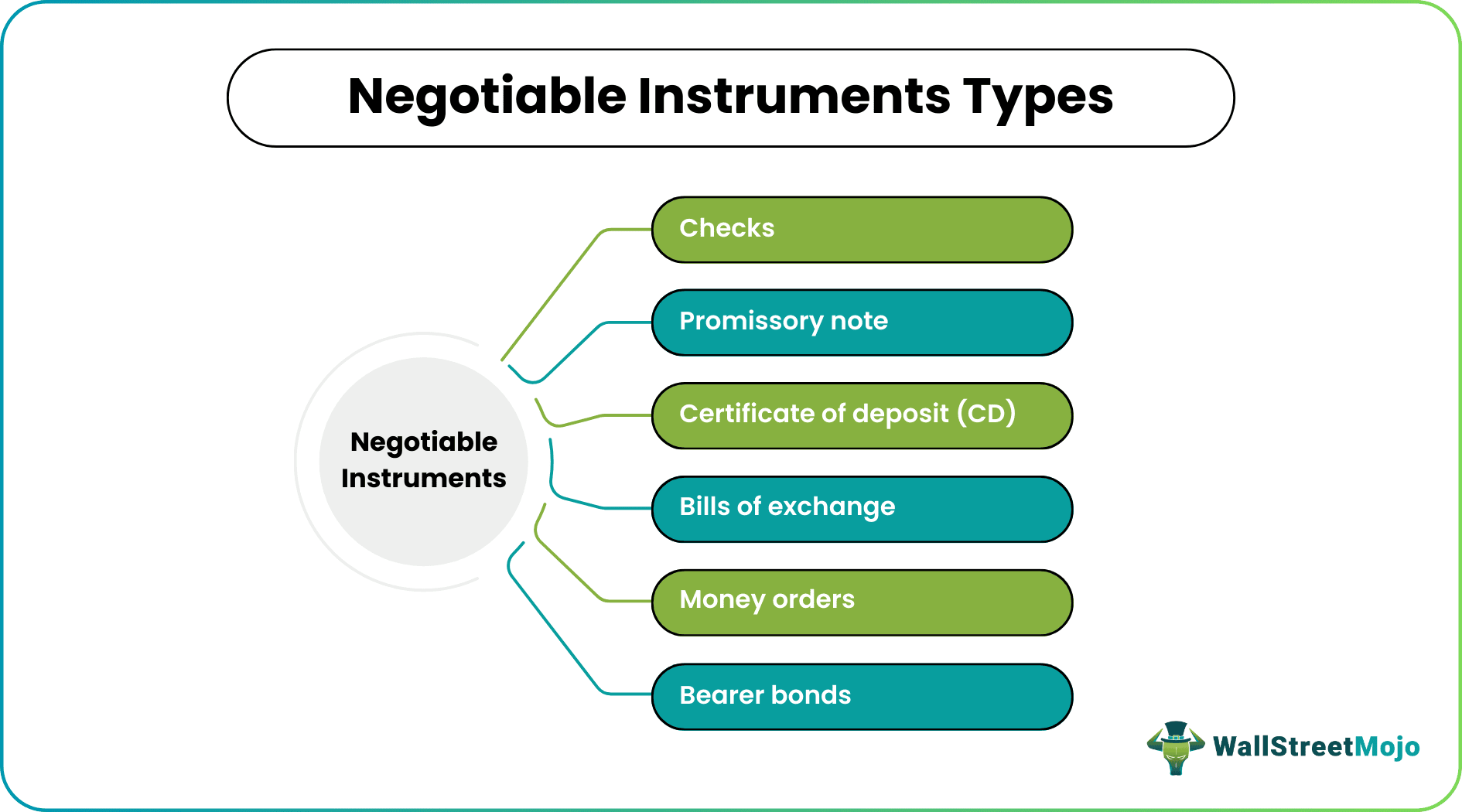
Bills of Exchange
Bills of Exchange are similar to promissory notes and can be used for national and international trade. Using this instrument, one party promises to pay the sum of money to another party or any other person on a fixed future date. The person it is endorsed for is the drawee, who has a valid claim on the bill writer or the drawer for the amount mentioned on the bill.
Money Orders
It is a substitute for the check for making payments on-demand. In a money order, the amount is specified. To process the money order, the payer has to pay the amount to a financial institution beforehand and a small processing fee. In return, the financial institution issues the money order. It has long been the traditional way of transferring money from one party to another with utmost security guaranteed. These are the best mode of money transfer for those who do not possess a bank account.
Bearer Bonds
These are the unregistered bonds issued by the Government or Corporate, and as the name suggests, the bondholder is entitled to get a coupon and principal payment thereon. The issuer doesn't keep the record of the original bond owner. Whoever has physical possession of the bearer bonds will be treated as the legal owner. Therefore, there is a huge risk of loss, theft, or otherwise the destruction of these bonds.
Examples
Let us consider the following negotiable instruments examples to understand the negotiable instruments definition better:
Example 1
Anne applied for a loan of $100,000 from a banking institution. The bank checks her credit scores and verifies her income and other proof to ensure she can repay the amount. However, in receiving repayment assurance, the bank asks Anne to sign a promissory note to ensure repayment in time.
In the event of default, despite all verifications, the promissory note will give the bank the right to legally claim the amount or take the borrower to the court of law to settle things further.
Example 2
In November 2023, the International Trade and Forfaiting Association (ITFA) released an addendum to the Digital Negotiable Instruments (DNI) Handbook. This addendum stated the need to enhance digital trade arrangements. The modification came following the enactment of the UK Electronic Trade Documents Act 2023, which advocated for the creation of electronic trade documents, including bills of exchange, promissory notes, and other types that already exist in their traditional forms.
Current Trends
Multiple nations have introduced certain laws to ensure the ethical usage of these instruments and also the security of the payee's rights. For example, India enforced the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881, to govern the practices of using the above instruments effectively, including the rights, duties, and obligations of parties involved in the transactions.
However, recently, India introduced The Negotiable Instruments (Amendment) Bill, 2017, to safeguard the rights of the payees in case of dishonor of checks.
While most of the negotiable instruments have already witnessed a downtrend and have become less preferred among individuals and entities, there are a few of them, the use of which is still trending.
Today, the virtual mode of transactions has become way more popular. Therefore, individuals and businesses tend to use online banking channels to ensure transactions do not take much time and occur instantly. Nowadays, people are more comfortable doing transactions through NEFT, RTGS, debit & credit cards, etc.
Though the time taken for transactions is less in the case of modern financial instruments, the security concerns are major. As a result, when the sum or amount to be transferred is huge, people still prefer using traditional money transfers, like issuing checks, money orders, etc.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Negotiable instruments, by providing an assurance for repayment from the payee, makes financial dealings easier to carry out without any stress. Though it offers a number of benefits, there are drawbacks as well that limit the advantages of these instruments. Let us have a look at the merits and demerits of these financial vehicles in brief:
Benefits
- These instruments improves the liquidity in the market by making credit options easily accessible to people and business entities.
- Including a negotiable instrument in the business arrangement is safe and secure as it is legally protected and enforceable.
- Due to the legal bindings, the individuals and business entities involved in the dealing try their best to obey it and hence the risk of default is insignificant.
- As the name suggests, these instruments are negotiable in nature. Hence, the parties involved have the liberty to keep the terms and conditions per their mutual agreement, be it in terms of the maturity date or payment terms, etc.
- These are convenient to be transferred to another party when the situations change and the parties can change their financial arrangements, accordingly.
Limitations
- Negotiable instruments are delicate and hence they are required to be handled with extreme care. If stolen or lost, they may lead to significant losses for the parties involved.
- These are a bit complicated as the verification requires signature matching. Though it makes the process even more secure, the parties involved might not have that patience to stick to or choose this option when other alternatives are found.
- Undoubtedly, the issuer and the assignee are legally bound to obey the agreement, but there are still possibilities of default or dishonor of the negotiable instruments.
Difference Between Negotiable and Non-Negotiable Instruments
Negotiable and non-negotiable instruments are two options that individuals and business entities can opt for to leverage the credit mechanisms in the market. Though the objective of both are same, they differ in many ways, which have been mentioned below:
- While the negotiable instrument offer flexible terms and can be transferred to another party, a non-negotiable vehicle cannot be transferred to anyone else.
- The payment, in case of the former, is made to the bearer who holds the instrument at that point in time. For non-negotiable options, the payment is done to the original holder of the instrument only.
- The former is usually preferred in commercial dealings, while the non-negotiable instrument is used in personal or private agreements.
- Legal protections are stricter in case of negotiable instruments, while the non-negotiable instrument might not necessarily be governed by legal laws and regulations.
