Table Of Contents
What is Seller Financing?
Seller financing is an agreement between the buyer and seller of the real estate. Instead of a financial institution, the seller manages the mortgage process and provides a loan; the buyer makes an initial down payment of the principal amount of the property price. The remaining amount is through monthly payments with some percent of interest charged on the loan.
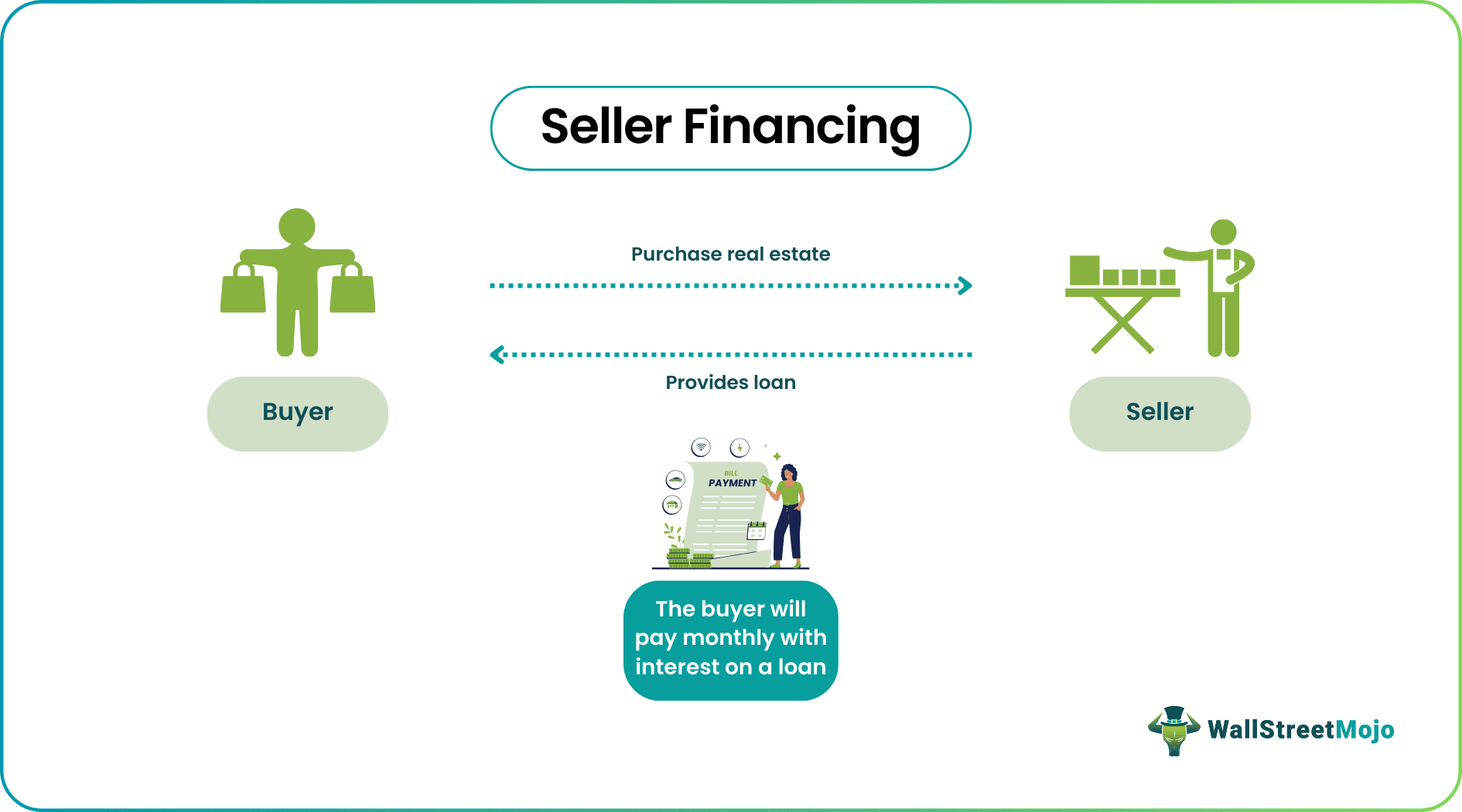
Also referred to as owner financing, these seller financing homes are provided at much higher interest rates than other financial vehicles. Therefore, it is a lucrative business model for the sellers of the real estate sector. Also, this is most suitable for individuals with a low credit score or irregular income as conventional mortgages might not be made available to them.
Key Takeaways
- Seller financing refers to an agreement between the real estate buyer and seller. The seller manages the mortgage process and provides a loan Instead of a financial institution.
- The initial down payment from the buyer is equal to the principal balance of the purchase price. The remaining sum is paid back over time in equal monthly installments plus a percentage of the loan's interest.
- Examples of seller financing are all-inclusive mortgages, rent-to-own agreements, second mortgages or junior mortgages, wrap-around agreements, and land contracts.
How Does Seller Financing Work?
Seller financing is a transaction between the buyer and seller in a real estate deal. Instead of conventional financial institutions like banks providing loans, the seller provides the mortgage loan after the buyer has paid the initial amount towards the purchase of the property.
Seller financing homes are better for individuals with irregular income or lower credit scores. Many factors come into consideration in the approach for the negotiation in such types of contracts, building trust between buyer and seller and understanding the legal requirement to be fulfilled in such agreements.
Instead of using it as a tool for financing, this option should be suitable only if it fits into your investment strategy over a period.
It is important to complete such contracts through legal attorneys with important points like price, interest rate, accruing interest, date of payment, maturity date, and due on sale clause.
Types
Before understanding how to use the seller financing calculator, it is important to understand the different types of such facilities. Let us do so through the discussion below.
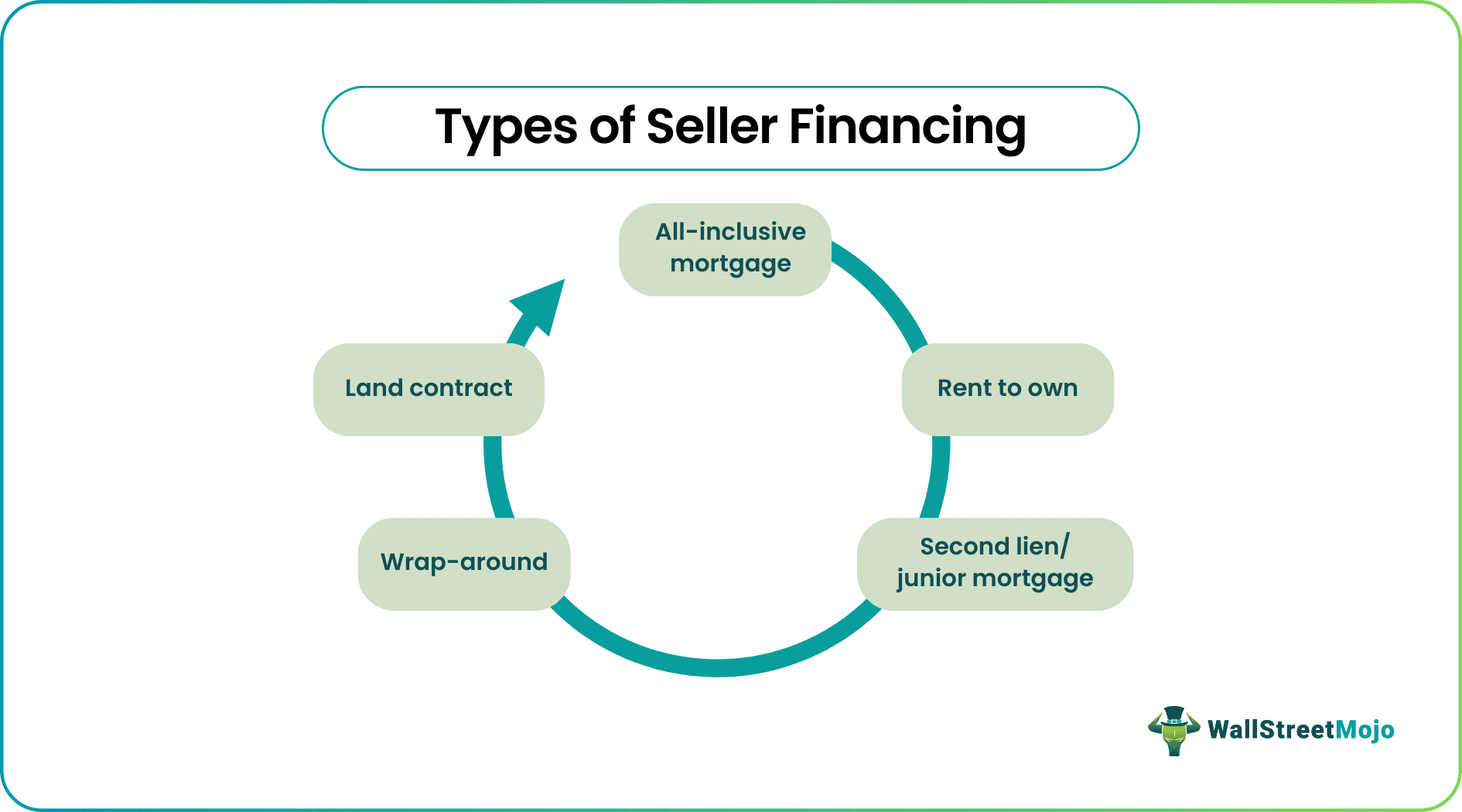
- All-inclusive Mortgage: In this, an owner sells the home to the buyer for an all-inclusive trust deed and bears a promissory note for the entire home price balance in compliance with a less down payment, if any.
- Rent to Own: The buyer has the option but not obligation to buy property from the seller, but the buyer gets the right to own the house with the down payment while also paying regular monthly rent. At the end of the given term of a contract, the buyer can pay off the balance amount of the contract to the seller. In such agreements, sellers often charge a decent amount of non-refundable down payment if the buyer decides not to buy. In other cases, the buyer gets protection with a record of the lease contract by which the seller cannot sell the property to anyone else.
- Second Lien/ Junior Mortgage: Often, the seller feels risk in making a seller-financing contract with a buyer, so instead, the buyer gets an option to take a second mortgage, i.e., for the major part of financing is done from a bank and the seller financing does remaining. In this type of contract, the Buyer makes two payments, i.e., first to the bank and second to the seller. This type of contract reduces the risk of a buyer getting a default.
- Wrap-Around: Wrap-around mortgage is a good opportunity for the seller to earn a better rate of return. Suppose the seller has a mortgage that he did not completely pay off. In that case, he sells property with a seller financing option. He can charge a higher rate on the property price, less down payment, maintain continuous payment to his mortgage from a bank and earn an extra return rate. E.g., Mr. X bought a house with a mortgage of $200,000 at a rate of 4.5%. The current value of the home is $250,000. So, he makes a seller financing contract with a new buyer by taking a down payment of $50,000 and the remaining $200,000 with an interest rate of 7.5%. Such agreements are mostly done through escrow companies, ensuring that the payment process remains clear.
- Land Contract: – In this type of contract, the title of the ownership is not transferred to the buyer but gets equitable interest in a property. Only after making the final payment of the signed contract does the buyer receive a legal transfer of the ownership from the seller.
Examples
Let us understand how a seller financing calculator and its impact on the price of the property with the help of a couple of examples.
Example #1
Mr. X is selling his house for $250,000. Mr. Y is self-employed and unable to get a good credit score because of irregularity in his income. Therefore, Mr. Y cannot take the loan in the traditional method. However, Mr. X runs a background check on Mr. Y and can develop confidence in his overall profession. Therefore, Mr. X and Mr. Y get into an agreement where Mr. Y agrees to pay a down payment of $50,000 and the remaining $200,000 in EMI over 20 years with an additional interest of 6%.
Solution:
Below is given data for calculation of payment: -

The measure of EMI is as follows: -

- = /
- EMI = 1432.86
Total Payment:-

- Total Payment = $343886.9.
In the above example, the buyer and seller enter into a contract without involving other financial institutions. Important factors required: -
- The seller owns the property. (Zero debt / very low amount of debt which one can settle on the closing of this deal)
- The seller intentionally completes all required legal documents for transfer to the buyer.
- The contract between buyer and seller where the buyer agrees to pay as per terms of the seller-financing agreement.
Example #2
In March 2023, the Arizona’s Attorney General accused two companies for fraud relating to seller financing.
Deed and Note Traders and 881 Homes were involved in misrepresenting and deceiving their customers into buying homes that were already under defaulted payments in mortgage by these companies. Therefore, the interest rates were higher than the buyers expected.
In relation to this case, the Arizona Attorney General’s office has informed that the two companies have agreed to pay $375,000 towards reinstitution and fees. Additionally, the companies will pay $25,000 towards civil penalties.
Benefits
Let us understand the benefits of seller financing homes from the perspective of both the buyer and seller in detail through the explanation below.
For the Buyer
- Less Paperwork: Although the seller still needs to show complete trust in you to enter into such an agreement, less paperwork and procedures make it easy.
- Negotiable: Unlike a bank or any other financial institution, the buyer can negotiate on amount terms, conditions, and interest rates.
- Lower Cost: Without an institutional lender, there are no processing charges, admin charges, or originating charges.
- Faster Closing: No bureaucracy, repetitive process, inspections, etc.
For the Seller
- Sellers may sell property in the same condition without costly repairs or modifications needed by conventional lenders.
- Familiar investment: A mortgage secured by the property you owned for a time is much more comforting than any other unfamiliar investment.
- Regular Income: Continuous income without worrying about owning and managing a property.
- In case of default, the seller gets to keep down payment plus ownership of the property.
- Tax Advantage: Selling in installments defers capital gain on the property, which helps save a high level of taxes.
- Higher Returns: The seller financing contract provides higher returns over a period than a one-time, long-term capital gain.
Drawbacks
Similarly, it is important to understand the drawbacks from the perspective of both the parties involved in the transaction. From the seller financing calculator above, we have understood that the interest rates are higher than most other loan facilities. Let us understand other details through the detailed discussion below.
For the Buyer
- High Rate of Interest: In many cases, the interest rate in seller financing is more elevated than in banks.
- Understanding of Terms: Clauses like ‘due on sale,’ which banks can foreclose if the seller still has not paid the complete mortgage. The buyer needs to read and understand all the terms and legal meanings in the contract.
- In case of default, if a buyer cannot secure financing, he can lose all money paid in down payment and monthly payment with the house.
For the Seller
- Risk analysis: The seller needs to analyze the risk involved in seller financing and make necessary decisions regarding involvement.
- Trust on Buyer: Banks make a certain process to qualify for the loan for a reason. In the case of the seller, the financing seller has to find a way to believe in the ability and reliability of the buyer.
- Default: In case of default, the process of foreclosure must be processed by a seller if the buyer does not move out.
- Repair Cost: The seller might have to make repairs and property changes if a buyer defaults.
