Table Of Contents
What Is A Merchant Bank?
A merchant bank is a financial institution that provides banking and financial solutions to High Net-worth Individuals (HNIs) and large corporations. They provide services like underwriting, fundraising, issue management, loan syndication, portfolio management, and financial advice.
Merchant banks don’t just serve the general public; they facilitate multi-national companies in cross-border trade. A merchant banker plays varied roles for clients—banker, financial advisor, broker, lender, consultant, debenture trustee, underwriter, and portfolio manager. The banks do not provide regular banking services like a checking account.
Key Takeaways
- Merchant banks are institutions that provide various services like asset and wealth management, loans and capital for business enterprises.
- Besides, they help with fundraising for mergers, acquisitions and expansion and other advisory services. They help their clients structure large international transactions
- They provide services which are different from retail and investment banking and do not provide services to the general public.
- Some of the world's largest merchant banks include Rothschild & Co, Barclays Capital and JP Morgan which started as a service bank early on.
- The main risks associated with a merchant bank include the cost of using their services and the potential for conflicts of interest.
Merchant Banks Explained
Merchant banks offer financial services to wealthy individuals and mid-sized corporations. They underwrite securities, raise venture capital, and raise funds. They do not provide basic banking services.
Among all the services, the focus is on financial advice. These banks primarily earn from the fee paid for advisory services. In addition, the bank invests depositors' assets in financial portfolios—based on expected returns and risk-taking capacity.
Now, let us understand the brief history—merchant banking started in the 17th and 18th centuries—in France and Italy. By the end of the 18th century, these banks became popular in Europe; they facilitated distant payments, currency exchange, and issued bills of exchange. The US introduced such banks in the 19th century—JP Morgan and Citi Bank.
Features
The following are the characteristics that differentiate merchant banks from other financial institutions:
- These banks serve huge corporations and high net-worth individuals instead of the general public;
- They are innovative and have a loose organizational structure;
- Despite high liquidity measures, their profit distribution is low;
- Since they have many decision-makers, the decision-making process is prompt;
- They offer services at domestic and international levels;
- These banks possess strong databases and high-density information;
- They make money in the form of fees and commissions.
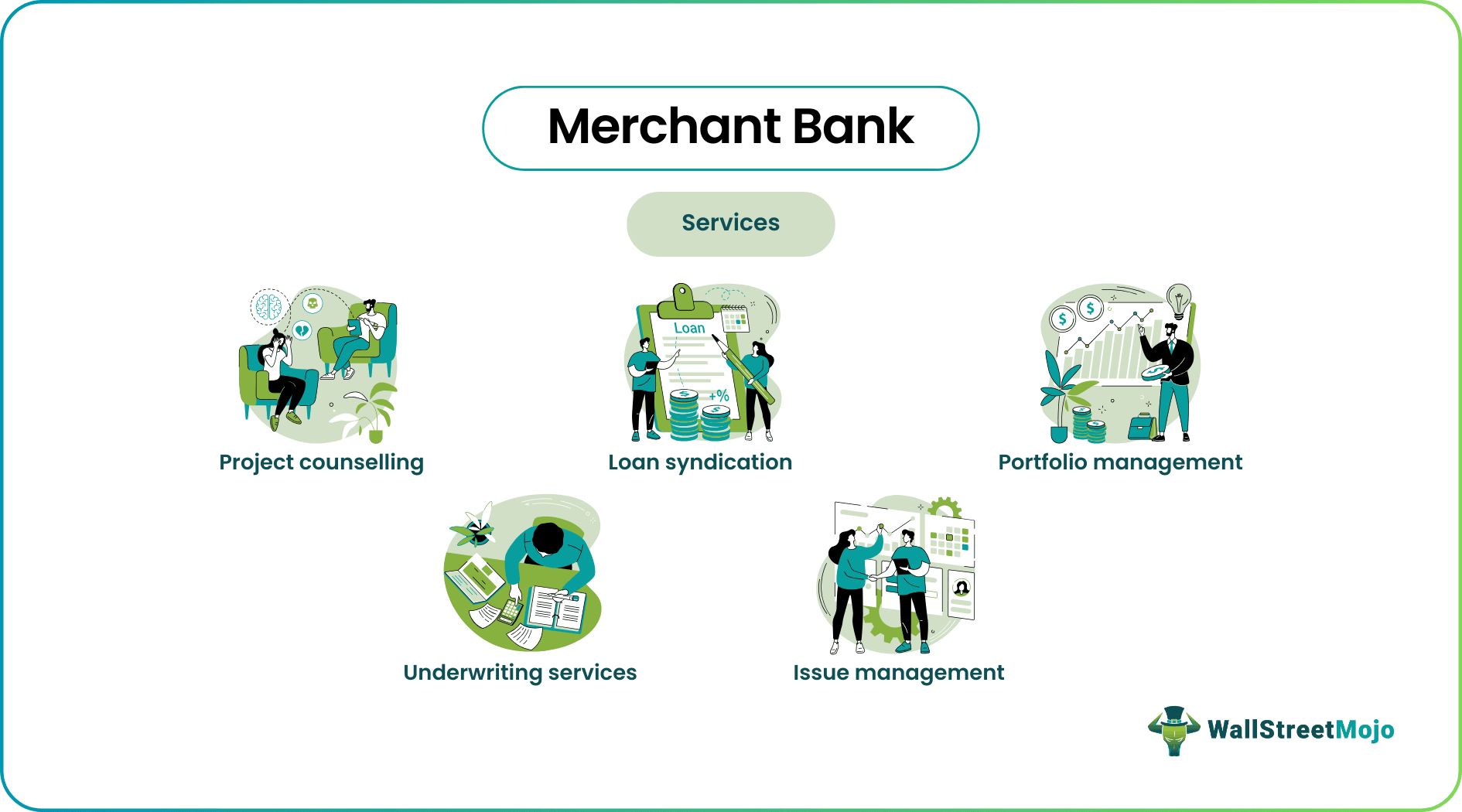
Merchant Bank Functions
The banks extend a variety of services and charge a fee. The services differ from those offered by regular banks.
Let us understand each service in detail:
- Project Counselling: Merchant bankers assist their clients at every stage of the project—idea generation, report creation, budgeting, and financing. This is especially the case with new entrepreneurs.
- Leasing Services: The banks extend leasing facilities—clients lease assets and equipment to generate rental income.
- Issue Management: High net-worth individuals employ merchant banks to issue equity shares, preference shares, and debentures to the general public.
- Underwriting: The banks also facilitate equity underwriting. They assess the price and risk involved in particular security and initiate public issues and distribution of stocks.
- Fund Raising: Through various facilities like underwriting and securities issuance, bankers help private companies generate capital from international and domestic markets.
- Portfolio Management: On behalf of clients, these bankers invest in different kinds of financial instruments.
- Loan Syndication: They finance term loans to back projects that need funding.
- Promotional Activities: Merchant banks are financial intermediaries that promote new enterprises.
Examples
Some of the oldest banks offering merchant banking services include Citi Bank and JP Morgan.
Other institutions include Bank of America, Merrill Lynch, Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, Barclays Capital, Credit Suisse, Deutsche Bank AG, Evercore, Jefferies International Ltd, Lazard, RBC Capital Markets, SG CIB, Stifel, USBank, and UBS Investment Bank.
Merchant Bank Vs. Investment Bank
Both offer financial and advisory services to their clients, but their scope of operation is different.
Merchant banks work with private corporate entities that are not big enough to release an initial public offering (IPO).
On the other hand, investment banks work with bigger clients to release IPOs. Investment banks are large enough to expend time, effort, and money to raise capital via traditional channels—they serve institutional investors and the government. In addition, investment banks help companies with mergers, acquisitions, capital restructuring, and conducting investment research.
Merchant bankers facilitate private equity investments- they ensure the private placement of corporate securities in front of a preferred group of investors or institutions.
Merchant banks are usually fee-based while investment banks have a two-fold income structure. Investment banks usually charge advisory fees and success fees (percentage of the deal size, often 1–5%) for services like M&A.
You can read more about the differences between merchant and commercial banking in this article Commercial banking vs merchant banking.

