Table Of Contents
Journal Voucher Meaning
A Journal voucher is a document of every financial transaction, having the necessary information such as the identification number of the voucher, date, description of the business transaction, amount of transaction, applicable taxes, a reference to other evidence, the signature of the maker and signature of the authorized person, used recording the transaction in the books of the organization.
Table of contents
- Journal Voucher Meaning
- A journal voucher is a document used to record financial transactions in the general ledger.
- It includes information such as the date of the transaction, a description of the transaction, the accounts affected, and the amounts debited or credited.
- Journal vouchers are used to make adjustments to accounts or to correct errors in accounting records.
- Journal vouchers provide a permanent record of financial transactions and are often used in conjunction with the journal to prepare financial statements.
Explanation
- Every transaction requires some sort of physical backup, which forms a base for it. The physical backup is nothing but the documentary evidence known as a journal voucher.
- It contains the information with the actual invoice as evidence. The third party gives the actual invoice. A voucher is taken as the base for recording the financial transaction into the books of accounts of the organization.
- Auditors generally scrutinize the voucher as a part of their audit procedures.
- Journal vouchers (also known as JVs) are used for transactions that do not relate to the material, cash, bank, and other day-to-day business transactions. It means JVs are used for a transaction such as depreciation, transfer entries, adjusting entries, provisions, accrual entries, purchase & sale of fixed assets on credit, write-off balances no more required, etc.
- These vouchers are easily traceable in any accounting system. Since these transactions are out of routine transactions, auditors vouch over these at priority.
Types
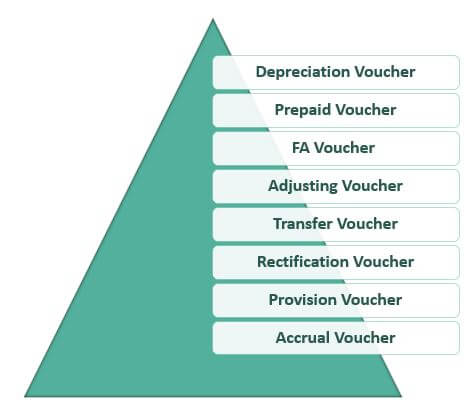
- Depreciation Voucher - For recording the depreciation expense for the year.
- Prepaid Voucher - For recording prepaid expenses;
- FA Voucher - For recording the purchase of fixed assets;
- Adjusting Voucher - For recording the closing entries.
- Transfer Voucher - For shifting of balances of one account to another.
- Rectification Voucher - For rectification of an error.
- Provision Voucher - For providing for an expense on an estimation basis.
- Accrual Voucher - For recording accrual income;
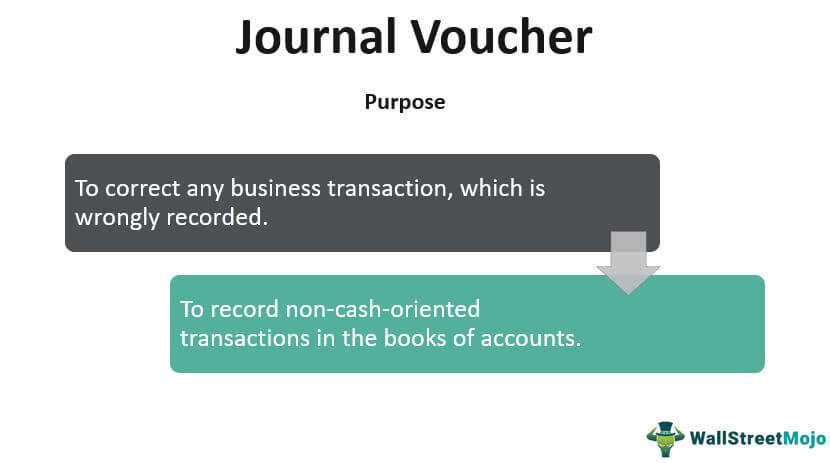
Purpose
- The primary purpose is to correct any business transaction which is wrongly recorded. Also, the dual purpose is to record non-cash-oriented transactions in the books of accounts.
- Every transaction does not necessarily involve an outflow. Hence, transactions such as the depreciation of tangible assets, amortization of intangibles, write off account balances, adjusting journal entries, etc., require the use of journal vouchers.
Features
- The journals are standardized
- Every journal voucher requires information on the following:
- Identification number
- Name of the counterparty
- Transaction amount
- Date of the transaction
- Debit & credit accounts with GL (General Ledger) Codes
- Documentary evidence
- Brief description of the nature of the transaction effected.
- Every journal voucher requires the approval of an authorized person.
Journal Entry Examples - Explained in Video
Example Format of Journal Voucher
#1 - Purchase of Machinery
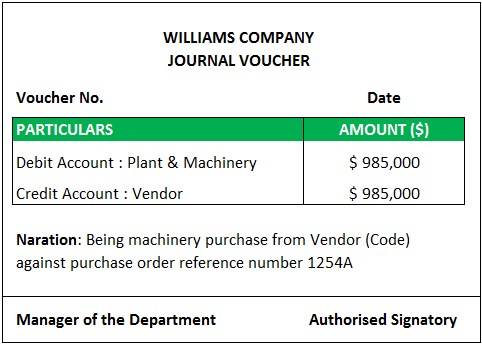
Explanation
The company purchased plant & machinery on credit. Plant & Machinery is a real account in nature (i.e., an asset for the organization). It is not usual for the organization's business to purchase the plant & machinery daily. Hence, a company cannot issue a purchase voucher. To prepare a document in the records, the company can use a Journal voucher containing all the above details. The invoice from the vendor is used as evidence for the said Journal voucher.
#2 - Provision for Outstanding Expenses
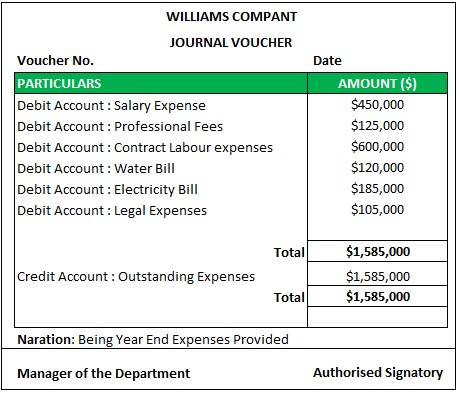
Explanation
At the end of every accounting year, the organization must make estimates for the expenses that will be relevant for the end part of the accounting period. Hence, provisions need to be made. However, the actual bill from the relevant parties (if any) is received in the next accounting period. The documentary evidence is not available. Thus, journal vouchers help serve the purpose. As evidence, a working is prepared wherein the basis of amounts is provided. The assumption is generally based on the management’s experience. Since actual payment is not made & the relevant vendor is not easily identifiable, the outstanding expenses (liability) account is credited in the books of account.
Documents Required for Preparation of Journal Voucher
- Debit Notes & Credit notes for any purchase return or sale return
- In case of any services supplied or procured, debit notes or credit notes
- Bill of the expense in case of prepaid or outstanding expenses.
- Documents for substantiating the correction of any error
- Trail mails can also be used as a basis for journal vouchers.
- Base working for the provisions.
Use & Importance
- It is used for recording the non-cash & non-trading types of transactions.
- It helps the auditors understand the impact of financial transactions in a business.
- It acts as evidence for future reference.
- It forms the basis of rectification entries.
Journal Voucher vs. Journal Entry
- The words “Journal voucher” and “Journal Entry” are interchangeable. However, there is a difference between the two. The former is the inception of any financial transaction & the latter is the effect given in the books of accounts.
- Journal entry is recorded in the journal, i.e., the primary books of accounts, while vouchers are the record documents kept as evidence for the journal entry.
- Journal entries can be simple (i.e., one debit and one credit) or compound (i.e., one or more debits and/or more credits). However, there is no such difference in journal vouchers. Any number of journal entries can be drawn from one journal voucher.
- The next step after the journal entry is posting the entries to appropriate ledgers. On the other hand, the next step of the journal voucher is recording the transaction in the system.
Advantages
- All business transactions are kept in the chronological order of their occurrence.
- It helps in the rectification of errors.
- It helps track the non-cash expenses easily.
- It helps close the books of accounts at the end of the year.
- It provides smooth backup for a reversal of entries.
- It helps comply with significant financial reporting standards prescribed by the relevant authority.
Disadvantages
- The most significant disadvantage is that it is incapable of giving all the information in case of large transactions.
- The voucher itself does not help keep track of all the financial transactions. There is a chance that a few transactions are missed out on being recorded. Here is where the role of the auditor comes into play.
- There is no actual cash flow involved in the transaction. Hence, if proper disclosures are not provided in the books of accounts, the reader of financial statements may not understand the impact of all such recordings.
Conclusion
Journal vouchers are the inception of the recording of any non-cash transaction. These have a material impact on the profits or losses of an organization. However, these entries serve the purpose of the accrual basis of accounting of the organization. Also, these transactions are ignored at the time of preparation of the cash flow statement.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Who prepares a journal voucher?
An accountant or bookkeeper typically prepares it. The accountant or bookkeeper ensures that all financial transactions are accurately recorded in the accounting system. After the voucher is ready, it must be approved by a supervisor or manager before the transaction can be posted to the accounting system.
How do journal vouchers differ from journal entries?
Journal vouchers and journal entries are used to record financial transactions, but some key differences exist. For example, journal vouchers are typically utilized for adjustments or corrections to accounts, while journal entries are used to record regular business transactions.
Is a journal voucher a source document?
A journal voucher is not generally a source document but a supporting document. It is prepared based on source documents and provides additional information and details about a transaction. In other words, this voucher supports a journal entry, a financial transaction record posted directly to the accounting system.

