Table Of Contents
What Are Plant Assets?
A plant asset, also known as a fixed asset, is an asset whose benefit is spread out for more than a year, helping businesses generate revenue and carrying out the main operations for which it has been established.
As it involves heavy investment, proper controls should be put in place to secure the assets from damage, pilferage, theft, etc. Controls should be monitored by the top management regularly, and if there are any discrepancies, they should be corrected immediately to prevent further loss to the company as a whole.
Plant Assets Explained
Plant assets fall under the fixed asset category and can be used in the business for more than one year. They are used for manufacturing and selling the goods and services of the company.
Such assets are always tangible. They carry a monetary value used to earn revenue and profit for the enterprise. They are usually land and building, plant and machinery that may be fixed or movable, or any other equipment that can be categorized as the same. They are recorded at cost and are depreciated over the estimated useful life, or the actual useful life, whichever is lower.
If required, the business or the asset owner has to book the impairment loss. In that case, the estimated realized value of the asset is less than the actual depreciated cost appearing in the books.
Accounting
Let us look at the method of accounting and plant asset management.
To be classified under the category of this kind of asset, it should be of tangible nature, which means that it should have the feature of being seen or touched. The next plant assets characteristics is that it should be able to provide benefit to the business for more than one year. If the benefit is less than a year, it will fall under current asset.
Next, the business must ensure that it is used for the business purpose and not kept as inventory for selling later on. Thus, for accounting and plant asset disposal, they are recorded at cost, and are depreciated over the estimated useful life, or the actual useful life, whichever is lower. Finally, if required, the business or the asset owner has to book the impairment loss. In that case, the estimated realized value of the asset is less than the actual depreciated cost appearing in the books.
Types
They can be categorized into several categories, depending upon the organization's requirements. But, broadly speaking, the most common examples of fixed assets are:
- Land - The land is the only asset that is not depreciated; its value remains intact over the business tenure.
- Land Improvements - When the expenditure incurred is related to enhancing the usability of the land. It should be booked as a plant asset, and if it is practically feasible to estimate the useful life, it should be depreciated.
- Buildings - are one of the most common examples of plant assets or fixed assets. They can be either purchased or taken on lease, depending upon the fund availability with the company.
- Machinery - These are the assets that help the company produce something. They are installed in the factories, and the wear and tear are larger in such cases due to the usage.
- Office Equipment - Inverters, racks, tables, chairs, etc., fall under this category, and they need to be grouped for convenience purposes. It is not an exhaustive list, and the company can further categorize its assets depending on its requirements and accounting policies.
Thus, for plant assets accounting, it is necessary to understand and have a clear idea about the above types of assets.
Examples
Let us look at some examples to understand the plant asset management.
A company acquires the land from the third party for $10,000. But due to the hilly area and crooked path, leveling is being done, which costed the company for around $3,000. After leveling, now the company is planning to use this as a parking space, and for this, it installs fences amounting t0 $9,000 around the perimeter.3
As per the practical scenario, fences would last for the next 30 years.
| Particular | Debit | Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Acquisition of Land | ||
| Land | 10,000 | |
| Cash/Bank | 10,000 | |
| Levelling of the Land | ||
| Land Improvements | 3,000 | |
| Cash/Bank | 3,000 | |
| Parking Lot | ||
| Land Improvements | 9,000 | |
| Cash/Bank | 9,000 | |
| Depreciation Entry | ||
| Depreciation | 300 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 300 |
The last entry would be posted every year for the next 30 years, resulting in nil value at the end of the useful life. This explains the examples of plant assets accounting.
Depreciation
Depreciation is the wear and tear of the asset, which occurs due to its daily usage. In loose terms, the difference between the salvage value and the actual cost of the asset is known as depreciation. There are different ways through which a company can provide for reducing the cost of the asset.
- #1 - Straight Line Depreciation Method - Also known as the fixed installment method, this model suggests putting an equal charge for depreciation in each of the accounting periods.
- #2 - Written Down Value Method - Also known as the declining balance method, this model uses a fixed percentage of the depreciation and applies it on the net balance to derive the charge. In the initial years, the charge would be greater, and as time passes, it gets reduced, that's why it is known as reducing balance method.
- #3 - Sum of Years Digit Method - This method propagates to charge the depreciable amount of an asset to a fraction in different accounting periods. It works on the assumption that in the initial years, the benefit would be more as the machine is new, and as it moves towards the obsolescence, the benefit derived would be less, resulting in less charge and less burden on the profitability.
Other methods are - Double Declining Balance Method, Insurance Policy Method, Unit Production Method, etc. It would depend upon the company accounting policies, management, and expected usage of the asset, to opt for the suitable depreciation method.
Examples Of Depreciation
Let us try to understand the depreciation and plant asset disposal methods.
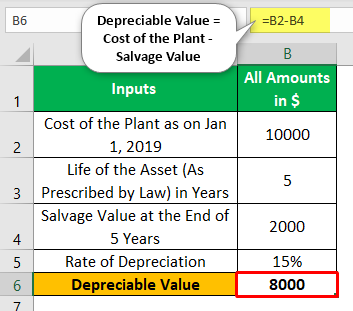
Depreciable Value = Cost of the Plant - Salvage Value
Hence, in this case, it would be 10,000(-) 2,000 = 8,000.
#1 - Straight Line Method
Here, points to be noted with respect to depreciation are –
- Depreciation remains constant every year.
- At the end of the asset life, the residual value remains in the books.
| Year | Value as on January | Depreciation | Value as on December |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 10000 | 1600 | 8400 |
| 2020 | 8400 | 1600 | 6800 |
| 2021 | 6800 | 1600 | 5200 |
| 2022 | 5200 | 1600 | 3600 |
| 2023 | 3600 | 1600 | 2000 |
#2 - Written Down Value Method
Observe the movement from the table-
- Depreciation is higher in the initial years and is in the falling stage as the year passes.
- It is not constant as it was observed in the straight-line method.
| Year | Value as on January | Depreciation | Value as on December |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 10000 | 1500 | 8500 |
| 2020 | 8500 | 1275 | 7225 |
| 2021 | 7225 | 1084 | 6141 |
| 2022 | 6141 | 921 | 5220 |
| 2023 | 5220 | 783 | 4437 |
#3 - Sum of Digit Method
Sum of Digits is calculated in the following manner –
1+2+3+4+5 = 15
| Year | Value as on January | Remaining Useful Life | Depreciation Fraction | Depreciation Expense | Value as on December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10000 | 5 | 0.333 | 2667 | 7333 |
| 2 | 7333 | 4 | 0.267 | 2133 | 5200 |
| 3 | 5200 | 3 | 0.200 | 1600 | 3600 |
| 4 | 3600 | 2 | 0.133 | 1067 | 2533 |
| 5 | 2533 | 1 | 0.067 | 533 | 2000 |
How To Calculate?
Investment in plant assets comes under strategic planning and occupy the major budget of the companies. Capitalization of plant assets should include the following:
| Particular | Values |
|---|---|
| Purchase Price | XX |
| Cost Incurred to make the Asset Ready for use | XX |
| Capitalization Rate | XX |
The cost incurred would include legal fees, commissions, borrowing costs up to the date when the asset is ready for use, etc., are some of the examples.
Plant Asset Vs Current Asset
Let us try to understand the difference between plant assets characteristics and current assets.
- The former can be used for more than one year but the latter is used for less than one year.
- Some example of the former is plant, machinery, land building, etc, whereas examples of the latter is inventory, accounts receivable, cash, etc.
- One of the plant assets characteristics is used to manufacture the goods and services, whereas the latter is used up during the manufacturing process as raw material.


