Table Of Contents
What Is A Risk-Weighted Asset?
Risk-Weighted Assets are the minimum amount of capital that a bank or other financial institution must hold to cover an unexpected loss arising out of the inherent risk of its assets and not get bankrupt. Risk-Weighted Asset calculation enables a comparison between two different banks operating in two different regions or countries.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision has formulated the Basel Accord that provides recommendations on risks related to banking operations. These accords, namely, Basel I, Basel II, and Basel III, is to ensure that banks and financial institutions have the required amount of capital to absorb the unexpected losses.
Risk-Weighted Asset Explained
Risk-weighted assets, commonly abbreviated as RWAs, represent a method for evaluating the potential financial risk associated with a bank's assets. This assessment is essential for determining the amount of capital a financial institution needs to hold as a buffer against unforeseen losses. It is known for embodying the prudent approach financial institutions adopt to assess and manage risk.
The calculation of the risk-weighted asset ratio involves assigning varying risk weights to different categories of assets based on their perceived risk levels. Higher-risk assets, such as loans to less creditworthy borrowers, receive higher risk weights, necessitating a greater allocation of capital to cover potential losses. Conversely, lower-risk assets, like government bonds, carry lower risk weights, requiring less capital.
Regulatory bodies, such as central banks, often mandate financial institutions to maintain a minimum level of capital adequacy in relation to their risk-weighted assets. This regulatory framework, known as Basel III, aims to enhance the stability of the global banking system by ensuring that banks possess sufficient capital to withstand financial shocks.
By employing the risk-weighted assets framework, financial institutions can more accurately reflect the potential risks in their portfolios, fostering a more resilient and stable banking sector. This approach not only safeguards the interests of depositors and investors but also contributes to the overall health and integrity of the financial system, reinforcing trust in the markets. In essence, understanding risk-weighted assets is integral to comprehending how financial institutions prudently manage risk and maintain a robust financial foundation.
Formula
Let us understand the formula that shall act as the very basis for risk-weighted asset calculation through the detailed discussion below.
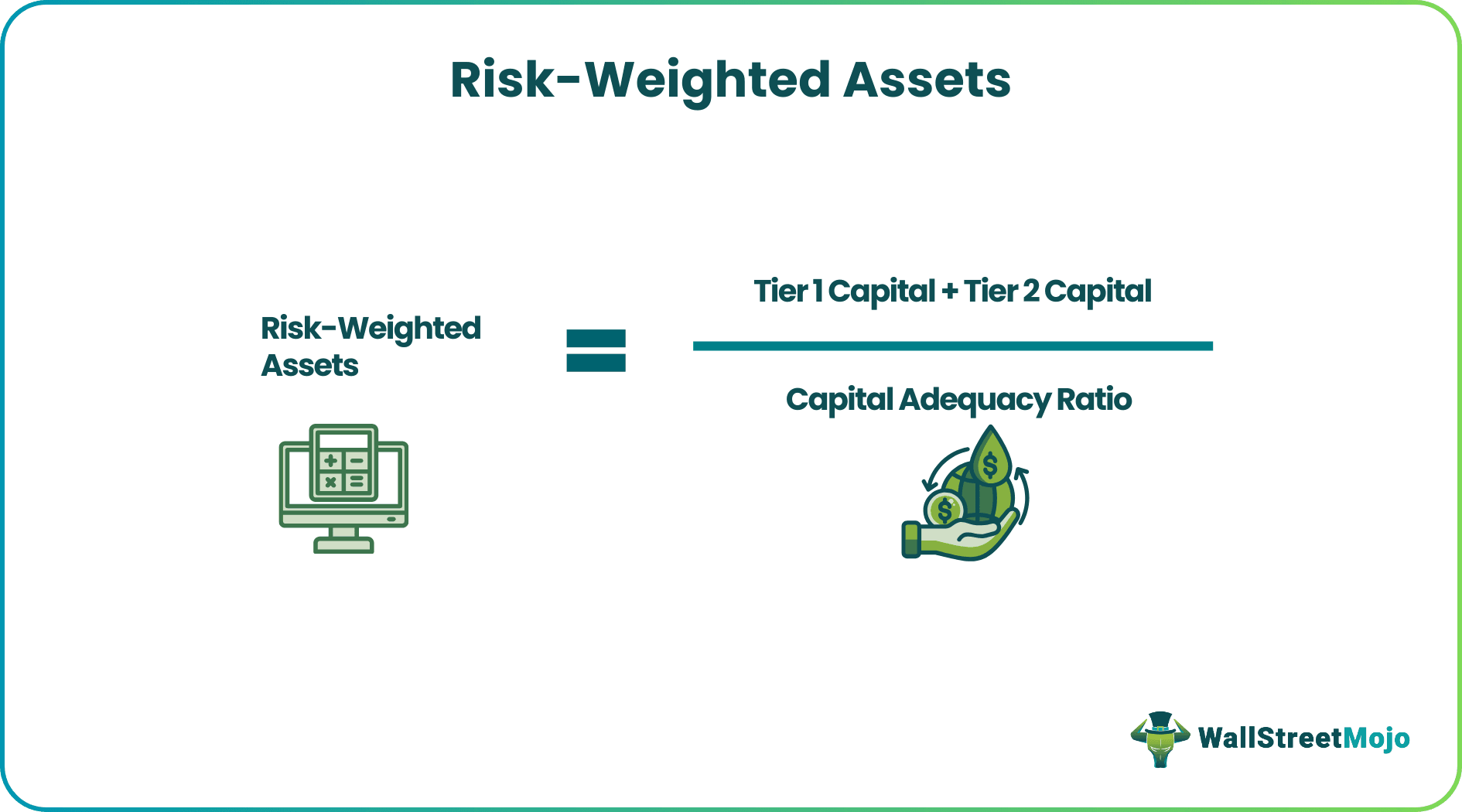
Capital Adequacy Ratio = Tier 1 Capital + Tier 2 Capital / Risk-Weighted Assets
Therefore,
Risk-Weighted Assets = Tier 1 Capital + Tier 2 Capital / Capital Adequacy Ratio
- Tier 1: Capital is a bank's core capital used at times of financial emergency to absorb losses without impacting daily operations. It includes audited revenue reserves, ordinary share capital, intangible assets, and future tax benefits.
- Tier 2: Capital is a bank's additional capital used to absorb losses when winding up an asset. It includes revaluation reserves, perpetual cumulative preference shares, retained earnings, subordinated debt, and general provisions for bad debt.
A bank or a financial institution with a higher Capital Adequacy Ratio indicates that it has sufficient capital to meet unexpected losses. Inversely, when the capital adequacy ratio is low, it indicates that the bank or the financial institutions stand a chance of failing in case of an unexpected loss, which means additional capital is required to be safer. An investor will look to invest in a business with a higher Capital Adequacy Ratio.
Examples
Now that we understand the intricacies of risk-weighted asset ratio, let us apply the theoretical knowledge to practical application through the examples below.
Example #1
The below table has information regarding Tier 1 and 2 capital for Bank A and Bank B.
It also gives the Capital Adequacy Ratio for these two banks.
| Particulars | Bank A | Bank B |
|---|---|---|
| Tier 1 | 1000000 | 1500000 |
| Tier 2 | 2500000 | 3100000 |
| Capital Adequacy Ratio | 8 | 7 |
Calculation of the Risk-Weighted Assets.
The risk-weighted average can be calculated as below:

Example #2
Bank A has the below portfolio, Calculation of the risk-weighted for the loans (assets)
| Particulars | $ | Risk Weight (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Government Securities | 20000 | 0 |
| Shares | 2000 | 125 |
| Secured Loans | 15000 | 0 |
| Corporate Loans | 50000 | 50 |
| Other Loans | 2000 | 100 |
| Cash Balance | 5000 | 0 |
| Balance with Banks | 1000 | 20 |
| Other Assets | 6000 | 100 |
The risk-weighted asset can be calculated as below:

Advantages
Let us understand the advantages of risk-weighted asset calculation through the points below.
- Ensures that banks and financial institutions have a minimum capital maintained to be safe during uncertainty.
- Encourages banks and financial institutions to review their current financial condition and highlights any red flags in case of minimum capital requirement.
- The Basel Committee on Banking Supervision helps banks achieve capital adequacy goals.
- It reduces the risk of foreseeable risks
Disadvantages
Despite the various advantages mentioned above, there are a few factors of the risk-weighted asset ratio that prove to be a disadvantage. Let us understand them through the explanation below.
- It is backward-looking, meaning; it assumes that security that has been risky in the past is the same as the securities that will be risky in the future.
- Banks must hold more common stocks since they need to find less risky assets with returns.
- The Basel II regulatory framework assumes banks to be in the best position to measure their financial risks, whereas, in reality, they might not be.
- Regulatory requirements have made it mandatory for banks at a global level to follow the Basel framework, which requires additional efforts on the bank’s front. Although the process is streamlined, it requires a lot of manual effort.


