Table Of Contents
What Are The Types Of Financial Models?
The different types of financial models are unique techniques commonly used in any business to analyze and forecast financial performance, which will have a future impact on the entire business operation.
Financial models are used to represent the forecast of company’s financials based on its historical performance as well as future expectations with the purpose of using them for financial analysis and the most common types of financial models include Discounted Cash Flow model (DCF), Leveraged Buyout model (LBO), Comparable Company Analysis model, and Mergers & Acquisition model. These different types of financial models act as a guide to understanding where the business may stand in the competitive financial market.
Key Takeaways
- Different types of financial models are used by financial analysts, corporate managers, and investment bankers to make informed decisions.
- The more commonly used financial models include Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model, Accretion/Dilution M&A Model, Initial Public Offering (IPO) Model, and so on.
- The accuracy of each model relies on the quality and relevance of the input data and assumptions.
Types Of Financial Models Explained
The various types of financial models in Excel are mathematical processes and tools that evaluate and predict the condition of the business going forward, which can be used as a guideline to frame policies and strategies related to finance, marketing and sales, production, pricing, and any other resource related procedures within the business.
Here is the list of the top 4 types of financial models
- Discounted Cash Flow Model (DCF)
- Leveraged Buyout Model Comparable
- Company Analysis Model
- Mergers and Acquisitions Model
Such models are extremely important for any company because they help in decision making related to different processes within the business. Activities like risk assessment and management, corporate finance, merger, acquisition, portfolio management, budgeting, real estate investment, etc derive their inputs from the analysis made in such models.
These types of financial models in Excel are created mainly in excel format or any special software that are available for this purpose. There are various types of inputs used which are derived from historical data and financial statements. Different assumptions, variables, and mathematical formulas and equations are used based on some principles to create the model. It is important to maintain the reliability and accuracy of information used and projected in them, which again depends on the skill and knowledge of the model creator.
These types of financial models for startups or any other type of business have gained wide importance in the financial market due to the ever-changing business landscape which also involves a lot of risk and uncertainty. They help in streamlining the company operations to make it smooth and stable through proper strategies so that it can survive any market downturn.
Let us discuss each one of them in detail as given in the article below.
Top 4 Types Of Financial Models
Let us look at what are the four types of financial models commonly used.
Given below are 4 different kinds of models commonly used in the financial market. We will study types of financial models for startups or any other types of business in detail. It will help us understand how they contribute to business strategies and help in utilizing the available resources in an optimum way.
#1 - Discounted Cash Flow Model
This is perhaps one of the most important types of financial model that is a part of valuation methodologies. It utilizes the projected free cash flows expected to be extracted and discounts them to arrive at a Present Net Value (NPV), which aids in the potential value of an investment and how quickly they can break even from the same.
This can be expressed with the below formula:
DCF = CF1/(1+r) 1 + CF2/(1+r) 2 +…….. + CFn/(1+r) n
where CF1 = the cash flow at the end of the year
r = Discounted rate of Return
n = Life of the project
In the NPV calculation, we shall assume that the cost of capital is known for calculating the NPV.If NPV is positive, then the project is worth considering; it is a loss-making option.
This financial model is used in equity research and capital market areas.
#2 - Leveraged Buyout Model

A leveraged buyout (LBO) is acquiring a public or private company with a significant amount of borrowed funds. After the purchase of the company, the Debt/Equity ratio is generally greater than 1 (debt constituting a majority of the portion). During the ownership, the firm’s cash flows are used for servicing the debt amounts and the interest.
The overall return realized by the investors is calculated by the exit flow of the company (EBIT or EBITDA) and the amount of the debt thathas been paid over the time horizon. This kind of strategy is mostly used in leveraged finance with sponsors like Private Equity firms who want to acquire companies to sell them at a profit in the future.
#3 - Comparable Company Analysis Model
A comparable company analysis (CCA) is a process used to evaluate the value of a firm using the metrics of other businesses of similar size in the same industry. It operates under the assumption that similar companies will have similar valuation multiples, such as the EV/EBITDA. Subsequently, investors can compare a particular company to its competitors on a relative basis.
Broadly the selection criteria for comparable companies can be bifurcated as follows:
| Business Profile | Financial Profile |
|---|---|
| Sector | Size |
| Products & Services | Profitability |
| Customer and End Markets | Growth Profile |
| Distribution Channels | Return on Investment |
| Geography | Credit Rating |
The most integral multiples that are considered for comparative analysis are:
PE Multiple
- PE Valuation Multiple, also known as “Price Multiple” or “Earnings Multiple,” is calculated as :
- Price per share / Earnings Per Share OR Market Capitalization/Net Income
- This multiple indicates the price an investor is willing to pay for each $ of earnings.
EV/EBITDA Multiple
- Another common multiple is EV/EBITDA, which is calculated as follows: Enterprise Value / EBITDA.
- where EV represents all business (Common Equity + Net Debt + Preferred Stock + Minority Interest).
- This aids in neutralizing the effect of capital structure. EBITDA accrues to both debt and equity holders since it is before the interest component.
Price to Book Value Ratio
- PBV Ratio is the Price/Book ratio is an equity multiple calculated as the Market Price of a share/Book Value per share or Market Capitalization/Total Shareholder’s Equity
The steps to keep in mind for executing a comparative valuation are:
- Pick a group of competitors/similar companies with comparable industries and fundamental characteristics.
- Calculate the market capitalization = Share Price X No. of shares outstanding[.
- Calculate the Enterprise Value
- Use historical formulas from the company filings and projections from the management, equity analysts, etc.
- Calculate the various spread multiples, which will give a ballpark view of how the firm is performing, reflecting the truth behind the financial information.
- Value the target company by picking the appropriate benchmark valuation multiple for the peer group, and value the target company based on that multiple. Generally, an average or median is used.
#4 - Mergers and Acquisitions Model
The investment Banking fraternity widely uses this type of model from the different types of financial forecasting models. The fundamental objective of merger modeling is to display the impact of the acquisition on the acquirer’s EPS and how this EPS is comparable in the industry.
The basic steps for building an M&A model are as follows:
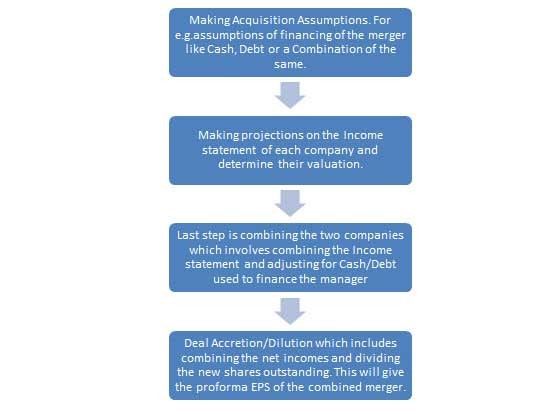
The focus of this model involves the construction of the balance sheet post the merger of the two entities.
The sources and users model section of this model contains information regarding the flow of funds in an M&A transaction, specifically where the money is coming from and where the money is getting utilized.
An investment banker determines the amount of money raised through various Equity and Debt instruments and cash in hand to fund the purchase of the target company, which represents sources of the funds.
The uses of the funds will show the cash that is going out to purchase the target as well as various fees required to complete the transaction. The most important factor is that the Sources have to be Equal to the Uses of the Funds.
Cash on Hand = Total Uses of Funds – Total sources of funds excluding cash on hand =
(Purchase of Equity + Transaction Fees + Financing Fees) – (Equity + Debt)
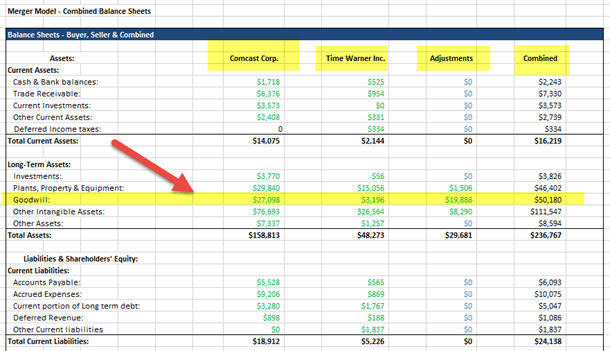
Goodwill: It is an asset that arises on an acquiring company’s Balance Sheet whenever it acquires a target for a price that exceeds the Book Value of Net Tangible assets (i.e., Total Tangible Assets – Total Liabilities) on the target’s Balance sheet. As a part of the transaction, some portion of the acquired assets of the target company will often be “written up” – the value of the assets will be increased upon transaction closure. This increase in asset valuation will appear as an increase in Other Intangible assets on the Buyer’s balance sheet. This will trigger a Deferred Tax liability, equal to the assumed tax rate times the write up to Other Intangible assets.
The formula used for computing the goodwill created in an M&A transaction:
New Goodwill = Purchase price of equity – (Total Tangible Assets – Total Liabilities) – Write up of assets * (1-Tax rate)
Goodwill is a long term asset but is never depreciated or amortized unless Impairment is found – if it is determined that the value of the acquired entity becomes lower than what the original buyer paid for it. In that case, a portion of the goodwill will be “written off” as a one-time expense i.e., the goodwill will be decreased by an equal amount of the impairment charge.
Examples
Let us understand the concept of types of financial forecasting models with the help of some suitable examples, as given below:
Example #1
Discounted Cash Flow Model
Let us consider an example for understanding the implications of the DCF Value Model:
| Year | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash Flow | (100,000) | 30,000 | 30,000 | 40,000 | 45,000 |
The initial cash flow is INR 100,000 for the initiation of the project post, which all are the cash inflows.
100,000 = 30,000/(1+r) 1 + 30,000/(1+r) 2 + 40,000/(1+r) 3 + 45,000/ (1+r) 4
On calculation, r = 15.37%. Thus, if the rate of return from the project is expected to be greater than 15.37%, then the project shall be accepted else to be rejected.
In Equity Research, DCF Analysis is used to find the fundamental value of the company (fair value of the firm)
Example #2
LBO Model
An illustrative example is stated below with the Parameters and Assumptions:
- XYZ Private Equity partners purchase ABC target company for five times forward EBITDA at the end of Year Zero (before the commencement of the operations)
- The Debt to Equity ratio = 60:40
- Assume the weighted average interest rate on debt is to be 10%
- ABC expects to reach $100 million in Sales Revenue with an EBITDA margin of 40% in Year 1.
- Revenue is expected to increase by 10% year on year.
- EBITDA margins are expected to remain flat during the term of the investment.
- Capital Expenditures are expected to be 15% of sales each year.
- Operating working capital is expected to increase by $5 million every year.
- Depreciation is expected to equal $20 million each year.
- Assuming a constant tax rate of 40%.
- XYZ exits the target investment after Year 5 at the same EBITDA multiple used at entry (5 times forward 12 months EBITDA) - see Terminal Value Multiples
Using the 5.0 entry model, the price paid for the purchase price of ABC Target Company is calculated by multiplying Year 1 EBITDA (which represents a 40% EBITDA margin on $100 million in revenue) multiplied by 5. Hence, the purchase price = 40*5 = $200 million.
The debt and equity funding is calculated taking into account the Debt: Equity ratio =
Debt portion = 60% * $200 million = $120 million
Equity portion = 40% * 200 million = $80 million
Based on the above assumptions we can construct the table as follows:
| ($ in mm) | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Revenue | 100 | 110 | 121 | 133 | 146 | 161 |
| EBITDA | 40 | 44 | 48 | 53 | 59 | 64 |
| Less: Depr & Amortization | (20) | (20) | (20) | (20) | (20) | (20) |
| EBIT | 20 | 24 | 28 | 33 | 39 | 44 |
| Less: Interest | (12) | (12) | (12) | (12) | (12) | (12) |
| EBT | 8 | 12 | 16 | 21 | 27 | 32 |
| Less: Taxes | (3) | (5) | (7) | (8) | (11) | (13) |
| PAT (Profits after Tax) | 5 | 7 | 9 | 13 | 16 | 19 |
Please note that since the exit value at the end of year five will be based on Forwarding EBITDA multiple, the sixth years’ worth of income statement and not the fifth year.
The Cumulative Leveraged Free cash flow can be calculated as follows:
| ($ in mm) | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBT (Tax-effected) | 5 | 7 | 10 | 13 | 16 | |
| Plus: D&A (Non-cash exp) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | |
| Less: Capital Expenditure | (15) | (17) | (18) | (20) | (22) | |
| Less: Increase in Net Working Capital | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | (5) | |
| Free Cash Flow (FCF) | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
We do not need to consider the information for the 6th year since the FCF from years 1 to 5 can be used to pay down the debt amount, assuming the entire FCF is utilized for debt payment. The exit returns can be calculated as follows:
Total Enterprise Value at Exit = taking forward EBITDA at an exit along with a 5.0 times exit multiple to calculate Exit TEV. $64 mm X 5.0 multiple = $320 million
Net Debt at Exit (also known as Ending Debt) is calculated as follows:
Ending Debt = Beginning debt – Debt Pay down
Ending Equity Value = Exit TEV – Ending Debt = $234mm
Multiple of Money (MoM) EV return is calculated as =
The following table is useful for estimating IRR based on five year MoM multiples:
| 2.0x MoM over 5 years ~ 15% IRR |
| 2.5x MoM over five years ~ 20% IRR |
| 3.0x MoM over 5 years ~ 25% IRR |
| 3.7x MoM over 5 years ~ 30% IRR |
Thus, we can assume that the implied IRR for the above case is approximately 25% or slightly below the same.
Example #3
Comparable Company Analysis Model
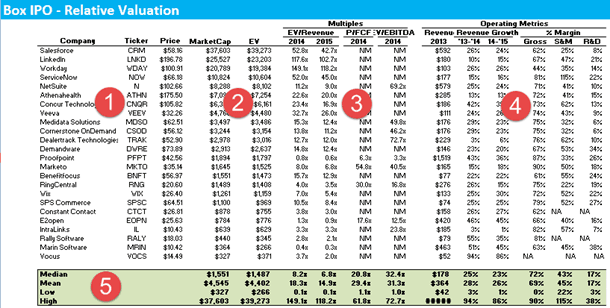
- The table above is the comparable comp for Box Inc. As you can see, there is a list of companies on the left-hand side along with its respective valuation multiples on the right-hand side.
- Valuable multiples include EV/sales, EV/EBITDA, Price to FCF, etc.
- You can take an average of these industry multiples to find the fair valuation of Box Inc.
- For more details, please refer to Box Valuation.
Example #4
Sample M&A Model - Combined Balance Sheet
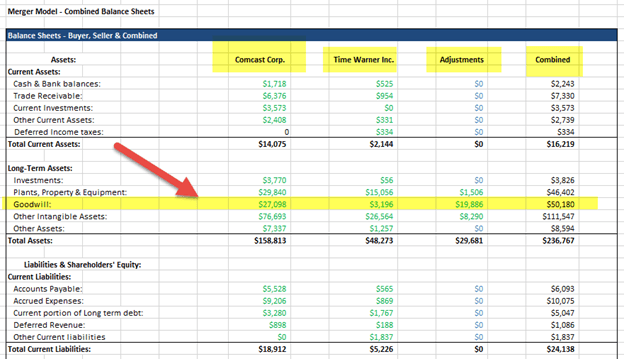
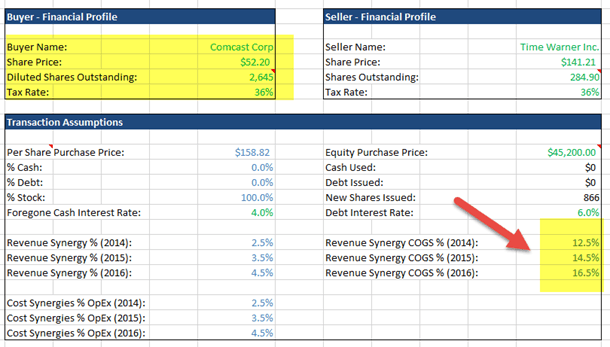
Sample Merger Model Scenarios
Thus, from the above examples, we clearly understand how the models are created using the historical and current data from the financial reports and used for making projections for the purpose of evaluation and decision-making in every business process.

